|
Northrop Grumman RQ-180
The Northrop Grumman RQ-180 is an American stealth unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) surveillance aircraft intended for contested airspace. , there had been no images or statements released, but growing evidence points to the existence of the RQ-180 and its use in regular front-line service. Development After the retirement of the SR-71 Blackbird in 1999, the US Air Force lacked an intelligence platform capable of penetrating airspace guarded by advanced air defense systems. The RQ-180 was designed to fulfill the mission previously accomplished by the high-speed SR-71. The RQ-180 appears to be a follow-on to the Joint Unmanned Combat Air Systems project which was cancelled in late 2005 when the United States Navy (USN) wanted a carrier-based aircraft (which led to the UCAS-D) while the United States Air Force (USAF) wanted a larger, long-range global strike platform. In December 2005, the program was split in two, with the USN starting the UCAS-D program which created the Northrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Air Force Plant 42
United States Air Force Plant 42 is a classified aircraft manufacturing plant owned by the United States Air Force in the Antelope Valley, about from downtown Los Angeles. It is also used by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Plant 42 shares a runway with Palmdale Regional Airport (PMD). Overview Plant 42 is owned by the United States Air Force and operated as a component of Edwards Air Force Base, which is northeast. Most of its facilities are operated by private contractors to build and maintain military aircraft and their components for the United States and its allies. Plant 42 has of industrial space and a replacement value of $1.1 billion. Some of its facilities build aircraft, including the Northrop Grumman RQ-4 Global Hawk and other unmanned aircraft. Others maintain and modify aircraft such as the Northrop Grumman B-2 Spirit bomber. Still others make spare parts. Aerospace contractors at Air Force Plant 42 share a runway complex, and either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edwards Air Force Base
Edwards Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation in California. Most of the base sits in Kern County, but its eastern end is in San Bernardino County and a southern arm is in Los Angeles County. The hub of the base is Edwards, California. The base was named after World War II USAAF veteran and test pilot Capt. Glen Edwards in 1950; prior to then the facility was named Muroc Air Force Base. It is the home of the Air Force Test Center, Air Force Test Pilot School, and NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center. It is the Air Force Materiel Command center for conducting and supporting research and development of flight, as well as testing and evaluating aerospace systems from concept to combat. It also hosts many test activities conducted by America's commercial aerospace industry. Notable occurrences at Edwards include Chuck Yeager's flight that broke the sound barrier in the Bell X-1, test flights of the North American X-15, the first landings of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypersonic Speed
In aerodynamics, a hypersonic speed is one that exceeds 5 times the speed of sound, often stated as starting at speeds of Mach 5 and above. The precise Mach number at which a craft can be said to be flying at hypersonic speed varies, since individual physical changes in the airflow (like molecular dissociation and ionization) occur at different speeds; these effects collectively become important around Mach 5-10. The hypersonic regime can also be alternatively defined as speeds where specific heat capacity changes with the temperature of the flow as kinetic energy of the moving object is converted into heat. Characteristics of flow While the definition of hypersonic flow can be quite vague and is generally debatable (especially due to the absence of discontinuity between supersonic and hypersonic flows), a hypersonic flow may be characterized by certain physical phenomena that can no longer be analytically discounted as in supersonic flow. The peculiarity in hypersonic flows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed Martin SR-72
The Lockheed Martin SR-72, colloquially referred to as "Son of Blackbird", is an American hypersonic UAV concept intended for intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) proposed privately in 2013 by Lockheed Martin as a successor to the retired Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird. The company expected an SR-72 test vehicle could fly by 2025. Design and development Background and early work The SR-71 Blackbird was retired by the USAF in 1998, leaving a potential coverage gap between surveillance satellites, crewed aircraft, and unmanned aerial vehicles for intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) and strike missions. With the growth of anti-satellite weapons, anti-access/area denial tactics, and counter-stealth technologies, it was thought that a high-speed aircraft could penetrate protected airspace and observe or strike a target before enemies could detect or intercept it. The proposed reliance on extremely high speed to penetrate defended airspace is considered a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Attack
An electronic countermeasure (ECM) is an electrical or electronic device designed to trick or deceive radar, sonar, or other detection systems, like infrared (IR) or lasers. It may be used both offensively and defensively to deny targeting information to an enemy. The system may make many separate targets appear to the enemy, or make the real target appear to disappear or move about randomly. It is used effectively to protect aircraft from guided missiles. Most air forces use ECM to protect their aircraft from attack. It has also been deployed by military ships and recently on some advanced tanks to fool laser/IR guided missiles. It is frequently coupled with stealth advances so that the ECM systems have an easier job. Offensive ECM often takes the form of jamming. Self-protecting (defensive) ECM includes using blip enhancement and jamming of missile terminal homers. History The first example of electronic countermeasures being applied in a combat situation took place durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prompt Global Strike
Prompt Global Strike (PGS) is a United States military effort to develop a system that can deliver a precision-guided conventional weapon airstrike anywhere in the world within one hour, in a similar manner to a nuclear ICBM. Such a weapon would allow the United States to respond far more swiftly to rapidly emerging threats than is possible with conventional forces. A PGS system could also be useful during a nuclear conflict, potentially replacing the use of nuclear weapons against up to 30% of targets. The PGS program encompasses numerous established and emerging technologies, including conventional surface-launched missiles and air- and submarine-launched hypersonic missiles, although no specific PGS system has yet been finalized as of 2018. System The PGS system is intended to complement existing American rapid-response forces, such as Forward Deployed Forces, Air Expeditionary Groups (which can deploy within 48 hours) and carrier battle groups (which can respond within 96 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Range Stand Off Weapon
The AGM-181 Long Range Stand Off Weapon (LRSO) is a nuclear-armed air-launched cruise missile under development by Raytheon Technologies that will replace the AGM-86 ALCM. Development As of August 24, 2017, Raytheon and Lockheed Martin received separate $900 million contracts from the Department of Defense and US Air Force and are developing their own versions. Contracts were intended to end in 2022, when the Department of Defense will select one design to continue further developments. To replace the ALCM, the USAF planned to award a contract for the development of the new Long-Range Stand-Off weapon in 2015. Unlike the AGM-86, the LRSO will be carried on multiple aircraft. The LRSO program is to develop a weapon that can penetrate and survive integrated air defense systems and prosecute strategic targets. The weapons are required to reach initial operational capability (IOC) before the retirement of their respective ALCM versions, around 2030. The technology development contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Range Strike Bomber
The Long Range Strike Bomber (LRS-B) is a development and acquisition program to develop a long-range strategic bomber for the United States Air Force, intended to be a heavy-payload stealth aircraft capable of delivering thermonuclear weapons. Initial capability is planned for the mid-2020s. A request for proposal to develop the aircraft was issued in July 2014. The Air Force plans to procure at least 100 of the LRS-B aircraft at a cost of an estimated $550 million each (2010 dollars), with potentially as many as 200 units being considered to enter service eventually. A development contract was awarded to Northrop Grumman for its B-21 Raider in October 2015. Due to the sensitive nature much about the project is highly classified and little information is available to the public. As of late 2019, it was known that construction of the aircraft had commenced. Origins Conception On 19 May 2009, Air Force Chief of Staff General Norton Schwartz said that the USAF's focus in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
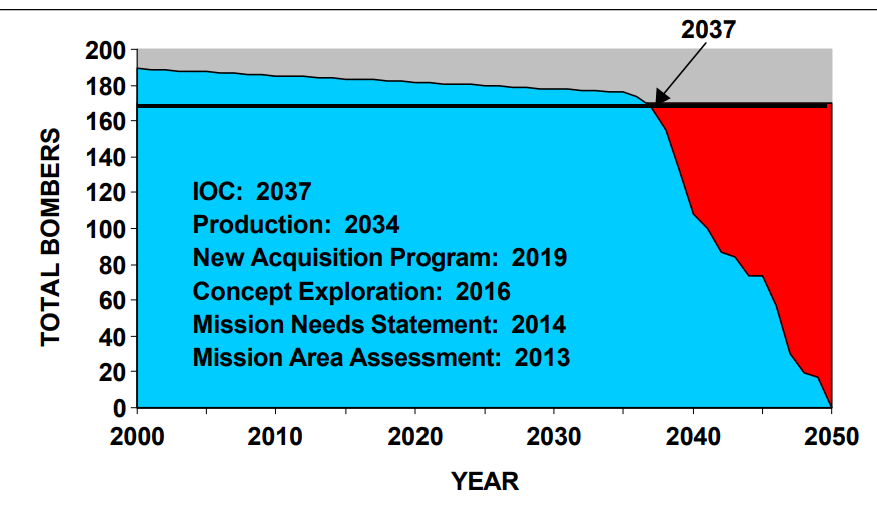
Next-Generation Bomber
The Next-Generation Bomber (NGB; unofficially called 2018 Bomber) was a program to develop a new medium bomber for the United States Air Force. The NGB was initially projected to enter service around 2018 as a stealthy, subsonic, medium-range, medium payload bomber to supplement and possibly—to a limited degree—replace the U.S. Air Force's aging bomber fleet (B-52 Stratofortress and B-1 Lancer). The NGB program was superseded by the Long Range Strike Bomber (LRS-B) heavy bomber program. Development 1999 Air Force White Paper on Long Range Bombers controversy In 1999, the Air Force released a white paper stating that it would need a new "capability" around 2037 to replace retiring bombers. The paper estimated that due to mishap attrition and other factors other than useful service life, the number of B-1 Lancer would not meet Air Force requirements of 89 aircraft by 2018. For the B-2, the number of aircraft would slip below the service's requirements of 19 aircraft by 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MQ-9 Reaper
The General Atomics MQ-9 Reaper (sometimes called Predator B) is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) capable of remotely controlled or autonomous flight operations developed by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems (GA-ASI) primarily for the United States Air Force (USAF). The MQ-9 and other UAVs are referred to as Remotely Piloted Vehicles/Aircraft (RPV/RPA) by the USAF to indicate their human ground controllers. The MQ-9 is the first hunter-killer UAV designed for long-endurance, high-altitude surveillance. In 2006, the then–Chief of Staff of the United States Air Force General T. Michael Moseley said: "We've moved from using UAVs primarily in intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance roles before Operation Iraqi Freedom, to a true hunter-killer role with the Reaper." The MQ-9 is a larger, heavier, and more capable aircraft than the earlier General Atomics MQ-1 Predator; it can be controlled by the same ground systems used to control MQ-1s. The Reaper has a 950- shaft- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MQ-1 Predator
The General Atomics MQ-1 Predator (often referred to as the predator drone) is an American remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) built by General Atomics that was used primarily by the United States Air Force (USAF) and Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). Conceived in the early 1990s for aerial reconnaissance and forward observation roles, the Predator carries cameras and other sensors. It was modified and upgraded to carry and fire two AGM-114 Hellfire missiles or other munitions. The aircraft entered service in 1995, and saw combat in the war in Afghanistan, Pakistan, the NATO intervention in Bosnia, 1999 NATO bombing of Yugoslavia, the Iraq War, Yemen, the 2011 Libyan civil war, the 2014 intervention in Syria, and Somalia. The USAF describes the Predator as a "Tier II" MALE UAS (medium-altitude, long-endurance unmanned aircraft system). The UAS consists of four aircraft or "air vehicles" with sensors, a ground control station (GCS), and a primary satellite link communication suite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Mach_7_computational_fluid_dynamic_(CFD).jpg)