|
Northern Muya Range
The Northern Muya Range (russian: Се́веро-Му́йский хребе́т, translit=Severo-Muyskiy khrebet) is a mountain range in Buryatia, Russia, part of the Stanovoy Highlands.Google Earth The Baikal Amur Mainline (BAM) railway traverses the southern end of the mountain range via the Severomuysky Tunnel. Geography The Northern Muya Range stretches from the valley of the Svetlaya river, a left tributary of the Upper Angara, in the southwest, to the valley of the Vitim in the northeast. The Upper Angara Depression lies to the northwest and the Muya-Kuanda Depression to the southeast. To the north it runs parallel with the Delyun-Uran Range just south of it, and to the south with the Muyakan Range. The highest summit of the range is a high mountain located in its extreme southwestern part. Peaks and ridges have sharp glacial shapes in the central sector of the range, while flat summits predominate on the periphery. In its southwestern part the Northern Muya Range is b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikal Amur Mainline
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, Irkutsk Oblasts of Russia, Oblast to the northwest and the Republic of Buryatia to the southeast. With of water, Lake Baikal is the world's List of lakes by volume, largest freshwater lake by volume, containing 22–23% of the world's fresh surface water, more than all of the North American Great Lakes combined. It is also the world's List of lakes by depth, deepest lake, with a maximum depth of , and the world's ancient lake, oldest lake, at 25–30 million years. At —slightly larger than Belgium—Lake Baikal is the world's List of lakes by area, seventh-largest lake by surface area. It is among the world's clearest lakes. Lake Baikal is home to thousands of species of Plant, plants and animals, many of them endemic to the region. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kotera (river)
*Kotera, song by Greek-American rapper MadClip Mad Clip (born Panagiotis Peter Anastasopoulos, ; May 25, 1987 – September 2, 2021) was an American-Greek rapper and songwriter. He released many songs such as "Dealer", "Kotera", "Sinthikes", which have grossed more than ten million pageviews ... *Kotera is a South-Indian surname of unknown orgin *Kotera (written: 小寺 lit. "small temple") is a Japanese surname. Notable people with the surname include: **, Japanese footballer **, Japanese footballer {{surname Japanese-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swamp
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in creating this environment. Swamps vary in size and are located all around the world. The water of a swamp may be fresh water, brackish water, or seawater. Freshwater swamps form along large rivers or lakes where they are critically dependent upon rainwater and seasonal flooding to maintain natural water level fluctuations.Hughes, F.M.R. (ed.). 2003. The Flooded Forest: Guidance for policy makers and river managers in Europe on the restoration of floodplain forests. FLOBAR2, Department of Geography, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK. 96 p. Saltwater swamps are found along tropical and subtropical coastlines. Some swamps have hammock (ecology), hammocks, or dry-land protrusions, covered by aquatic vegetation, or vegetation that tolerates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Tundra
Alpine tundra is a type of natural region or biome that does not contain trees because it is at high elevation, with an associated harsh climate. As the latitude of a location approaches the poles, the threshold elevation for alpine tundra gets lower until it reaches sea level, and alpine tundra merges with polar tundra. The high elevation causes an adverse climate, which is too cold and windy to support tree growth. Alpine tundra transitions to sub-alpine forests below the tree line; stunted forests occurring at the forest-tundra ecotone are known as ''Krummholz''. With increasing elevation it ends at the snow line where snow and ice persist through summer. Alpine tundra occurs in mountains worldwide. The flora of the alpine tundra is characterized by dwarf shrubs close to the ground. The cold climate of the alpine tundra is caused by adiabatic cooling of air, and is similar to polar climate. Geography Alpine tundra occurs at high enough altitude at any latitude. Portions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiga
Taiga (; rus, тайга́, p=tɐjˈɡa; relates to Mongolic and Turkic languages), generally referred to in North America as a boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches. The taiga or boreal forest has been called the world's largest land biome. In North America, it covers most of inland Canada, Alaska, and parts of the northern contiguous United States. In Eurasia, it covers most of Sweden, Finland, much of Russia from Karelia in the west to the Pacific Ocean (including much of Siberia), much of Norway and Estonia, some of the Scottish Highlands, some lowland/coastal areas of Iceland, and areas of northern Kazakhstan, northern Mongolia, and northern Japan (on the island of Hokkaidō). The main tree species, depending on the length of the growing season and summer temperatures, vary across the world. The taiga of North America is mostly spruce, Scandinavian and Finnish taiga consists of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larch
Larches are deciduous conifers in the genus ''Larix'', of the family Pinaceae (subfamily Laricoideae). Growing from tall, they are native to much of the cooler temperate northern hemisphere, on lowlands in the north and high on mountains further south. Larches are among the dominant plants in the boreal forests of Siberia and Canada. Although they are conifers, larches are deciduous trees that lose their needles in the autumn. Etymology The English name Larch ultimately derives from the Latin "larigna," named after the ancient settlement of Larignum. The story of its naming was preserved by Vitruvius: It is worth while to know how this wood was discovered. The divine Caesar, being with his army in the neighbourhood of the Alps, and having ordered the towns to furnish supplies, the inhabitants of a fortified stronghold there, called Larignum, trusting in the natural strength of their defences, refused to obey his command. So the general ordered his forces to the assault. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; ) is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Bolshaya rossiyskaya entsiklopediya'' (or '' Great Russian Encyclopedia'') in an updated and revised form. The GSE claimed to be "the first Marxist–Leninist general-purpose encyclopedia". Origins The idea of the ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' emerged in 1923 on the initiative of Otto Schmidt, a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences. In early 1924 Schmidt worked with a group which included Mikhail Pokrovsky, (rector of the Institute of Red Professors), Nikolai Meshcheryakov (Former head of the Glavit, the State Administration of Publishing Affairs), Valery Bryusov (poet), Veniamin Kagan (mathematician) and Konstantin Kuzminsky to draw up a proposal which was agreed to in April 1924. Also involved was Anatoly Lunacharsky, People's Commissar of Education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parama (river)
Parama is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Tomaszów Lubelski, within Tomaszów Lubelski County Tomaszów may refer to the following places in Poland: * Tomaszów Bolesławiecki, village in Lower Silesian Voivodeship * Tomaszów, Lublin Voivodeship, village in Puławy County * Tomaszów Lubelski County, county in Lublin Voivodeship ** Tomasz� ..., Lublin Voivodeship, in eastern Poland. References Parama {{TomaszówLubelski-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
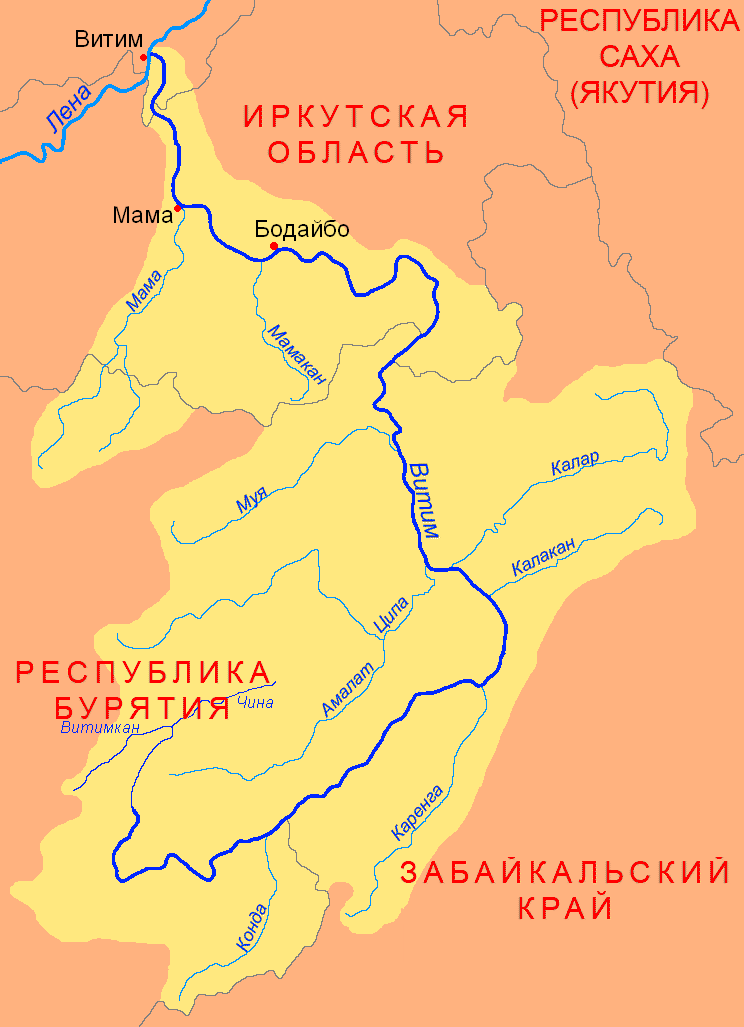
Mamakan (river)
The Mamakan (russian: Мамакан) is a river in Irkutsk Oblast, southern East Siberia, Russia. It is a tributary of the Vitim of the Lena basin. The river is long, and has a drainage basin of . There are no settlements by the river, only Mamakan near its mouth by the Vitim.Google Earth The Mamakan reservoir, the world's first hydroelectric power plant built on permafrost, is located in the lower course of the river, about from Bodaybo. Course The Mamakan is a left tributary of the Vitim. Its sources are in the Northern Muya Range, a subrange of the Stanovoy Highlands, at the northeastern limit of the Upper Angara Range. In its upper course it is known as the ''Sredny Mamakan'' (Middle Mamakan). The river flows roughly in a northwestward direction and is joined by the Left Mamakan and the Right Mamakan. It cuts across the Delyun-Uran Range (Делюн-Уранский хребет) and flows northwards. Finally near the Mamakan settlement it meets the Vitim from its mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angarakan
Mangala (Sanskrit: मङ्गल, IAST: ) is the personification, as well as the name for the planet Mars, in Hindu literature. Also known as Lohita (), he is the celibate deity of anger, aggression, as well as war. According to Vaishnavism, he is the son of Bhumi, the earth goddess, and Vishnu, born when the latter raised her from the depths of the primordial waters in his Varaha avatar. Nomenclature Mars (Mangala) is also called: * Raktavarna (रक्तवर्ण) - whose color is like blood. * Bhauma (भौम) - son of Bhumi. * Lohitānga (लोहिताङ्ग) - red bodied (Loha also means Iron, so could also mean Iron Bodied). * Kuja (कुज) - he who is born from Earth. * Bha (भ) - shining. Iconography He is painted red or flame colour, four-armed, carrying a trident (Sanskrit: '' trishūla''), mace (Sanskrit: ''gadā''), lotus (Sanskrit: '' Padma''), and a spear (Sanskrit: ''shūla).'' His mount (Sanskrit: ''vahana'') is a ram. He presides over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |