|
Northallerton Railway Station
Northallerton railway station is on the East Coast Main Line serving the town of Northallerton in North Yorkshire, England. It is north of between to the south and to the north. Its three-letter station code is NTR. The station is managed by TransPennine Express (TPE) and also served by Grand Central (GC) and London North Eastern Railway (LNER) trains. The station is on one of the fastest parts of the East Coast Main Line. LNER and CrossCountry express services pass through the station at speeds of up to . In 2014 the Wensleydale Railway opened a temporary station at . The heritage railway aims to run trains into the station from and eventually on the Settle–Carlisle line. History The station was opened by the Great North of England Railway on 30 March 1841. Eleven years later the Leeds Northern Railway's line from Leeds to Stockton passed through the town, but did not initially connect with the main line. Instead trains called at nearby ''Northallerton Town'' s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 802
The British Rail Class 802 is a type of high speed bi-mode multiple-unit passenger train designed and produced by the Japanese manufacturer Hitachi Rail. It has been operated by Great Western Railway, TransPennine Express, and Hull Trains; each of these train operating companies have given its own units a unique brand; Great Western Railway's units are branded ''Intercity Express Trains'' (IETs), TransPennine Express units are branded ''Nova 1s'' and Hull Trains' units are branded ''Paragons''. The Class 802 is based on the design of the Hitachi A-train, being a member of the Hitachi AT300 product family. It is broadly similar to the preceding Class 800, the primary difference between the two being the installation of more powerful engines and enlarged fuel tanks on the Class 802 to mitigate for their intended usage on lengthier unelectrified stretches of railway. Their introduction by the Great Western Railway facilitated not only the replacement of aging Intercity 125 high s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
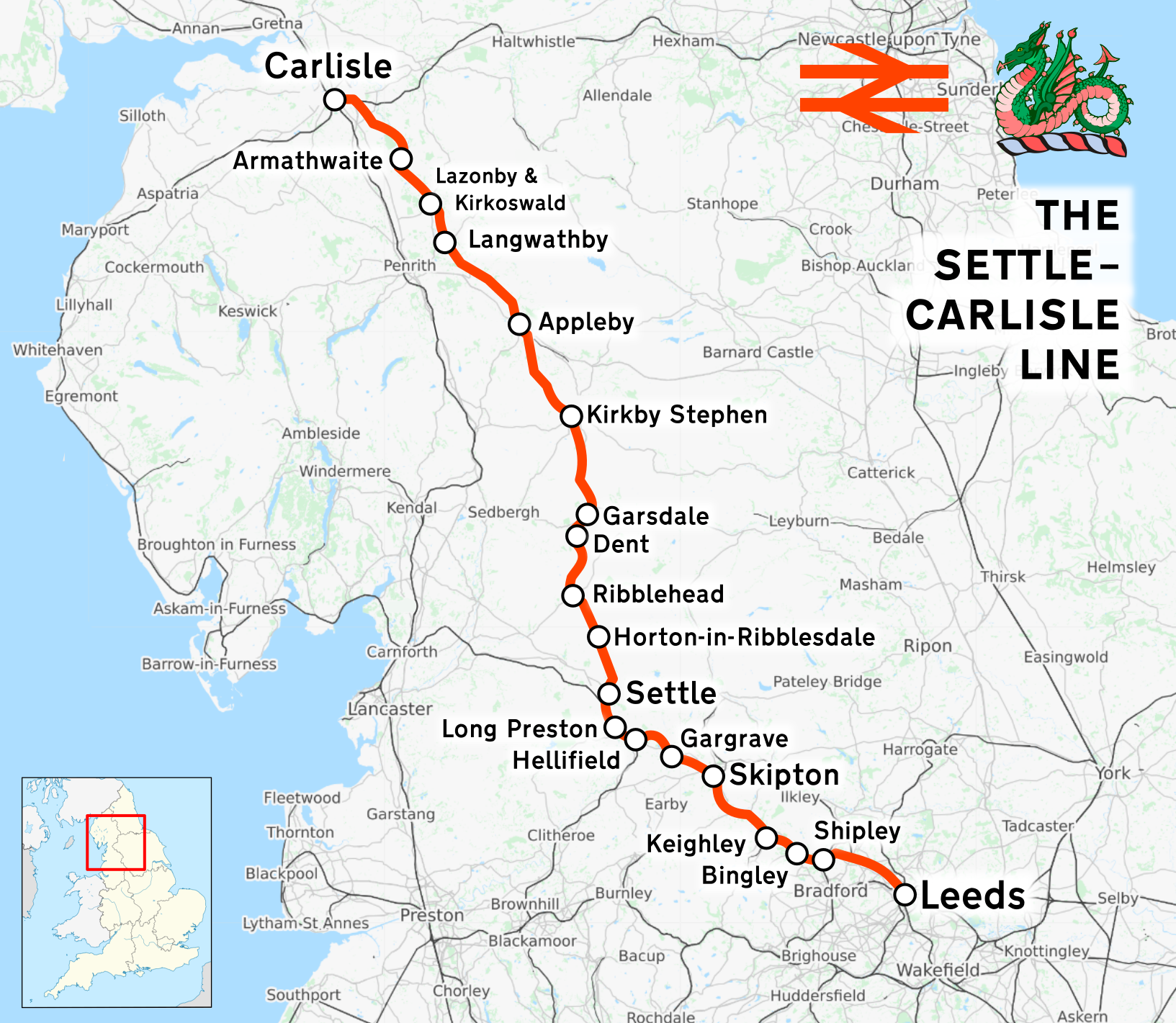
Settle–Carlisle Line
The Settle–Carlisle line (also known as the ''Settle and Carlisle'' (S&C)) is a main railway line in northern England. The route, which crosses the remote, scenic regions of the Yorkshire Dales and the North Pennines, runs between Settle Junction, on the Leeds–Morecambe line, and , near the English-Scottish borders. The historic line was constructed in the 1870s and has several notable tunnels and viaducts such as the imposing Ribblehead. The line is managed by Network Rail. All passenger services are operated by Northern apart from temporary diverted services (due to closures of the West Coast Main Line) and are part of the National Rail network. Stations serve towns such as Settle in North Yorkshire, Appleby-in-Westmorland in Cumbria and small rural communities along its route. In the 1980s, British Rail planned to close the Settle–Carlisle line. This prompted a campaign to save the line by rail groups, enthusiasts, local authorities and residents along the route. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four (British railway companies), Big Four British railway companies, and was privatisation of British Rail, privatised in stages between 1994 and 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. The period of nationalisation saw sweeping changes in the railway. A process of dieselisation and Railway electrification in Great Britain, electrification took place, and by 1968 steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction, except for the Vale of Rheidol Railway (a narrow-gauge railway, narrow-gauge tourist line). Passenger train, Passengers replaced freight train, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 801
The British Rail Class 801 ''Azuma'' is a type of electric multiple unit (EMU) built by Hitachi Rail for London North Eastern Railway. The units have been built since 2017 at Hitachi Newton Aycliffe, Hitachi's Newton Aycliffe Manufacturing Facility and have been used on services on the East Coast Main Line since 16 September 2019. As part of its production, the Class 801 units were ordered as part of the Intercity Express Programme and are in the Hitachi A-train, Hitachi AT300 product family, alongside the closely related British Rail Class 800, Class 800 units. LNER have branded the units as the ''Azuma'', just like on their Class 800 units. Background and design As part of the UK Government's Intercity Express Programme, the Class 801 units were to be built as replacements for the InterCity 125 and InterCity 225 sets which were the main trains used for services on the Great Western Main Line (GWML) and the East Coast Main Line (ECML) at the time. Differing from the Class 800 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beeching Cuts
The Beeching cuts (also Beeching Axe) was a plan to increase the efficiency of the nationalised railway system in Great Britain. The plan was outlined in two reports: ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' (1963) and ''The Development of the Major Railway Trunk Routes'' (1965), written by Richard Beeching and published by the British Railways Board. The first report identified 2,363 stations and of railway line for closure, amounting to 55% of stations, 30% of route miles, and 67,700 British Rail positions, with an objective of stemming the large losses being incurred during a period of increasing competition from road transport and reducing the rail subsidies necessary to keep the network running. The second report identified a small number of major routes for significant investment. The 1963 report also recommended some less well-publicised changes, including a switch to the now-standard practice of containerisation for rail freight, and the replacement of some services w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leeming Bar Railway Station
Leeming Bar railway station is a railway station in Leeming Bar, North Yorkshire, England. It is the eastern rail passenger terminus of the Wensleydale Railway, though the line continues towards . Trains are timed to link in with Dales and District service buses to Northallerton to connect with the National Rail network. History The station was opened by the York, Newcastle and Berwick Railway (a constituent company of the North Eastern Railway) in 1848 as the terminus of their branch from Northallerton. The station building was probably designed by George Townsend Andrews who may also have designed the Grade II listed locomotive shed. The line was then extended westwards to Leyburn by the ''Bedale and Leyburn Railway'' seven years later. A single-road locomotive shed was built at the west end of the station when the station opened up in 1848. The shed was still in use for the first and last trains of the day which terminated and started in . A shed had been proposed at Beda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reversing Siding
Reverse or reversing may refer to: Arts and media * ''Reverse'' (Eldritch album), 2001 * ''Reverse'' (2009 film), a Polish comedy-drama film * ''Reverse'' (2019 film), an Iranian crime-drama film * ''Reverse'' (Morandi album), 2005 * ''Reverse'' (TV series), a 2017–2018 South Korean television series *"Reverse", a 2014 song by SomeKindaWonderful * REVERSE art gallery, in Brooklyn, NY, US * Reverse tape effects including backmasking, the recording of sound in reverse * '' Reversing: Secrets of Reverse Engineering'', a book by Eldad Eilam *''Tegami Bachi: REVERSE'', the second season of the ''Tegami Bachi'' anime series, 2010 Driving * Reverse gear, in a motor or mechanical transmission * Reversing (vehicle maneuver), reversing the direction of a vehicle * Turning a vehicle through 180 degrees Sports and games * Reverse (American football), a trick play in American football *Reverse swing, a cricket delivery * Reverse (bridge), a type of bid in contract bridge Technology *Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Defence (United Kingdom)
The Ministry of Defence (MOD or MoD) is the department responsible for implementing the defence policy set by His Majesty's Government, and is the headquarters of the British Armed Forces. The MOD states that its principal objectives are to defend the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and its interests and to strengthen international peace and stability. The MOD also manages day-to-day running of the armed forces, contingency planning and defence procurement. The expenditure, administration and policy of the MOD are scrutinised by the Defence Select Committee, except for Defence Intelligence which instead falls under the Intelligence and Security Committee of Parliament. History During the 1920s and 1930s, British civil servants and politicians, looking back at the performance of the state during the First World War, concluded that there was a need for greater co-ordination between the three services that made up the armed forces of the United Kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leyburn Railway Station
Leyburn railway station is on the Wensleydale Railway, a seasonal, heritage service and serves the town of Leyburn in North Yorkshire, England. During the summer months it is served by at least three trains per day; at other times of the year the service is mainly at weekends and public holidays. The Leyburn branch of the Wensleydale Railway Association (which incorporates the Friends of Leyburn Station-FOLS) meets monthly at the station. The station postal address is Leyburn Station, Harmby Road, Leyburn, North Yorkshire, DL8 5ET. History The railway first reached Leyburn in November 1855, when the Bedale & Leyburn Railway opened its line from Leeming (where it made an end-on junction with the York, Newcastle and Berwick Railway branch from Northallerton). Passenger services commenced six months later, with a further extension westwards to Hawes being built by the North Eastern Railway in 1877/8 (the NER having also absorbed the B&L in 1857). At Hawes, another end-on j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
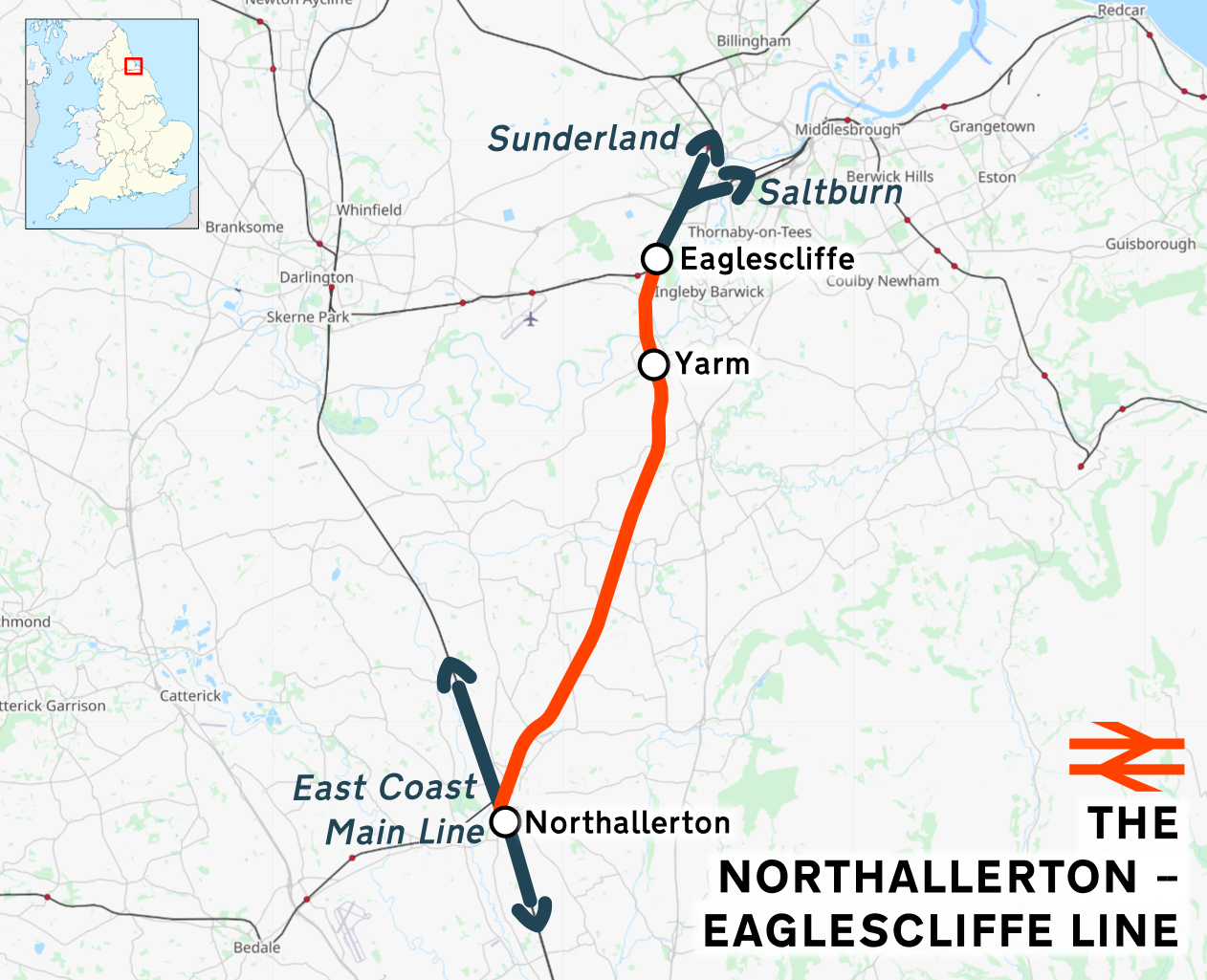
Northallerton–Eaglescliffe Line
The Northallerton–Eaglescliffe line runs between and stations. It connects the East Coast Main Line to the Tees Valley Line. It was built by the Leeds Northern Railway as part of their main line from to (via and ) which opened on 2 June 1852, although the connection to the ECML at the Northallerton end was not opened for a further four years. Stations Open The current stations on the line are: *Northallerton * Yarm * Eaglescliffe Closed A number of stations that used to serve towns and villages on the line were closed between 1954 and the end of local passenger services over the route on 6 September 1965, with those at Picton, Yarm and Brompton being the last to go. The station at Yarm was subsequently reopened by Regional Railways North East in February 1996. Services Most services are run by TransPennine Express between Manchester Airport and Middlesbrough. Services are roughly hourly and call at all stations as part of the North TransPennine route. A further fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirsk Railway Station
Thirsk railway station is on the East Coast Main Line and serves the town of Thirsk, North Yorkshire, England. It is down the line from and is situated between to the south and to the north. Its three-letter station code is THI. The station is about outside of Thirsk town centre and is actually on the edge of the village of Carlton Miniott. There are four tracks, but only the outer two have platforms; the platform faces serving the innermost pair of tracks were removed in the 1970s in preparation for higher-speed main line running using InterCity 125 trains. The station is operated by TransPennine Express. Other train services are provided by the open-access operator Grand Central (train operating company), Grand Central. History The railway line between York and was built by the Great North of England Railway, most of which was authorised in 1837; the line was formally opened on 30 March 1841. The station at Thirsk, which opened to the public on 31 March 1841, was origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



_(Tony_Radakin_cropped).jpg)
Jul2003.jpg)