|
North Thompson Indian Band
The Simpcw First Nation, formerly known as the North Thompson Indian Band, is a First Nations band government based in the Thompson Country of British Columbia, Canada. It is a member of the Shuswap Nation Tribal Council. It is a First Nations government of the Secwepemc (Shuswap) Nation, located in the Central Interior region of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The band's main community is at Chu Chua, British Columbia. Four of the five First Nation Reserves in Simpcw territory were designated on July 5, 1877 and the fifth was designated on February 24, 1916. The Shuswap language name for North Thompson Band's community and reserve is 'Simpcw'. Chief and Councillors The current chief and council were sworn in on June 1, 2015 at 1:00 pm, they will serve a 3-year term until the next election. Historical Leaders Chief Cinnitza was mentioned by Archibald McDonald from a trip in 1828. Chief André is mentioned in records from the time of settling First Nation Reserves i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Nations In Canada
First Nations (french: Premières Nations) is a term used to identify those Indigenous Canadian peoples who are neither Inuit nor Métis. Traditionally, First Nations in Canada were peoples who lived south of the tree line, and mainly south of the Arctic Circle. There are 634 recognized First Nations governments or bands across Canada. Roughly half are located in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia. Under Charter jurisprudence, First Nations are a "designated group," along with women, visible minorities, and people with physical or mental disabilities. First Nations are not defined as a visible minority by the criteria of Statistics Canada. North American indigenous peoples have cultures spanning thousands of years. Some of their oral traditions accurately describe historical events, such as the Cascadia earthquake of 1700 and the 18th-century Tseax Cone eruption. Written records began with the arrival of European explorers and colonists during the Age of Dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Mercer Dawson
George Mercer Dawson (August 1, 1849 – March 2, 1901) was a Canadian geologist and surveyor. Biography He was born in Pictou, Nova Scotia, the eldest son of Sir John William Dawson, Principal of McGill University and a noted geologist, and his wife, Lady Margaret Dawson. By age 11, he was afflicted with tuberculosis of the spine ( Pott's disease) that resulted in a deformed back and stunted growth. Physical limitations, however, did not deter Dawson from becoming one of Canada's greatest scientists. Tutors and his father provided his education during his slow recovery from the illness. Dawson later attended the High School of Montreal and McGill University (part-time) before moving to London to study geology and paleontology at the Royal School of Mines (now part of Imperial College London) in 1869. Dawson graduated after three years with the highest marks in his class. Dawson began his career in the 1870s as a professor of chemistry at Morrin College in Quebec City ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missionary Oblates Of Mary Immaculate
The Missionary Oblates of Mary Immaculate (OMI) is a missionary religious congregation in the Catholic Church. It was founded on January 25, 1816, by Eugène de Mazenod, a French priest born in Aix-en-Provence in the south of France on August 1, 1782, who was to be recognized later as a Catholic saint. The congregation was given recognition by Pope Leo XII on February 17, 1826. , the congregation was composed of 3,631 priests and lay brothers usually living in community. Oblate means a person dedicated to God or God's service. Their traditional salutation is ("Praised be Jesus Christ"), to which the response is ("And Mary Immaculate"). Members use the post-nominal letters, "OMI". As part of its mission to evangelize the "abandoned poor", OMI are known for their mission among the Indigenous peoples of Canada, and their historic administration of at least 57 schools within the Canadian Indian residential school system. Those oblate schools have been associated with many cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John McLeod (explorer)
John McLeod (1795 – after 1842) was a Scottish-born explorer of Canada, in his capacity as a fur trader with the North West Company and Hudson's Bay Company. He is remembered primarily for his explorations of several major rivers of the southwestern Northwest Territories, southern Yukon Territory, and northern British Columbia. Fur Trade McLeod arrived in Montreal, headquarters of the North West Company, in 1816. From there, he was assigned to the Churchill River area as a clerk. Following the merger of the two fur trading companies in 1821, McLeod served at various posts in the Athabasca and Mackenzie River Districts of the Hudson's Bay Company. In 1823, McLeod was assigned as manager of the Fort Simpson fur trading post, located at the junction of the Liard and Mackenzie Rivers, where he would remain nine years as deputy to the Chief Trader. In 1823-24, McLeod completed explorations of nine mountain ranges adjacent to the South Nahanni River, during which he opened tradi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tête Jaune Cache, British Columbia
Tête Jaune Cache () is an unincorporated rural area and the site of an important abandoned historic town in British Columbia, Canada. Its population is approximately 500. It is located on the Fraser River in the Robson Valley at the intersection of Yellowhead Highways 5 and 16. Tête Jaune Cache is located 18 km north of Valemount, B.C., 101 km west of Jasper, Alberta, 241 km east of Prince George, B.C., and 332 km north of Kamloops, B.C., by road. History Tête Jaune Cache was named after a Métis fur trader and trapper named Pierre Bostonais who guided for the Hudson's Bay Company in the 1800s. Bostonais was nicknamed Tête Jaune by the French-speaking voyageurs because of his blonde hair. ( is French for "yellow head".) The Secwepemc had an established village of tents and quiggly holes on the banks of the Fraser in this area rich in salmon and wild berries when encountered by Bostonais, but the townsite land of Tête Jaune Cache was officially loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Teit
James Alexander Teit (15 April 1864 — 30 October 1922) was an anthropologist, photographer and guide who worked with Franz Boas to study Interior Salish First Nations peoples in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. He led expeditions throughout British Columbia and made many contributions towards native ethnology. He also worked with Edward Sapir of the Geological Survey of Canada in 1911. In the later part of his life Teit worked tirelessly with the native people to preserve their human rights, as discussed by Wendy Wickwire in her work ''At the Bridge''. Teit was born in Lerwick, Shetland, Scotland but immigrated to Canada and married a Nlaka'pamux woman named Susanna Lucy Antko. It was through his wife that he became knowledgeable of the culture and language Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WWII
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
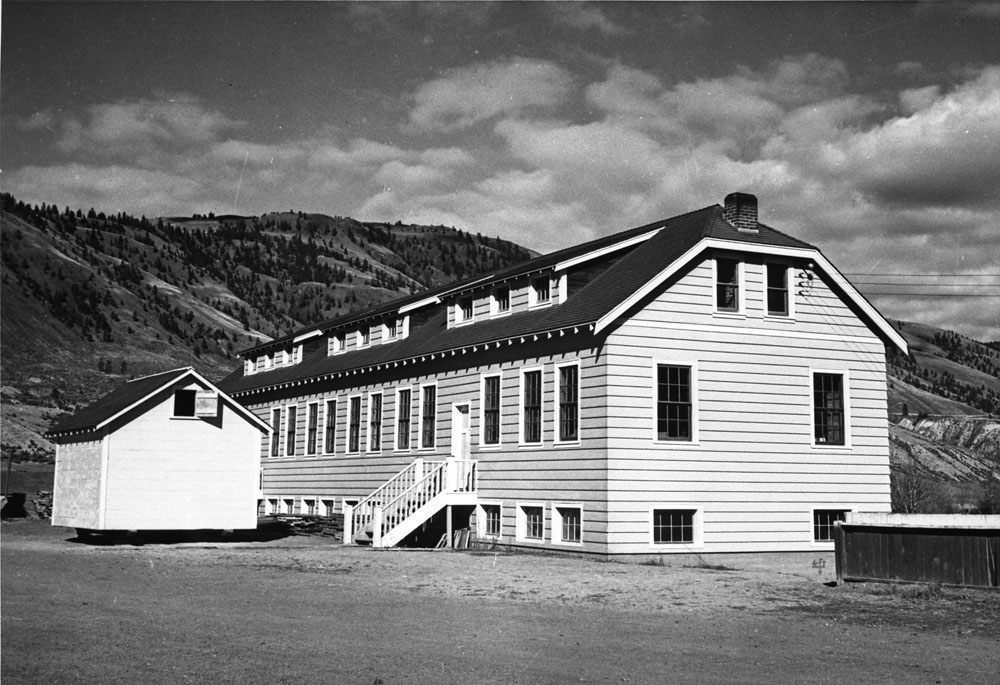
Kamloops Indian Residential School
The Kamloops Indian Residential School was part of the Canadian Indian residential school system. Located in Kamloops, British Columbia, it was once the largest residential school in Canada, with its enrolment peaking at 500 in the 1950s. The school was established in 1890 and remained in operation until 1969, when it was taken over by the federal government from the Catholic Church to be used as a day school residence. It closed in 1978. The school building still stands today, and is located on the Tk’emlúps te Secwépemc First Nation. In the early 2000s, a tourist discovered a juvenile rib in the area, and in the late 1990s a child's tooth was found. In 2021, Sarah Beaulieu—an anthropologist at the University of the Fraser Valley—surveyed the area with ground-penetrating radar and concluded the probable presence of about 200 unmarked graves, though "only forensic investigation with excavation" could confirm if these were actually human remains. As of May 2022, debates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: baie d'Hudson), sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba and southeast of Nunavut, but politically entirely part of Nunavut. Although not geographically apparent, it is for climatic reasons considered to be a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It Hudson Bay drainage basin, drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of southeastern Nunavut, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Ontario, Quebec, all of Manitoba, and parts of the U.S. states of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana. Hudson Bay's southern arm is called James Bay. The Cree language, Eastern Cree name for Hudson an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adams Lake
Adams Lake is a large, deep, coldwater lake in British Columbia, Canada; its average depth ranks 6th in the world. The southern end of the lake is approximately north of the town of Chase in the Shuswap Country region of British Columbia. The lake's upper reaches lie in the northern Monashee Mountains, while its lower end penetrates the Shuswap Highland. The lake supports Chinook, Sockeye and Coho salmon, Kokanee, mountain whitefish and rainbow trout. Geography The lake is long and between and wide. The surface elevation is above sea level. The lake is very deep; with a mean depth of and maximum depth of it is the second deepest lake in British Columbia (next to Quesnel Lake, which has a maximum depth of ) and 6th deepest lake in the world by mean depth. Water flows into the lake though many tributaries (most notably the Upper Adams River, , and Bush Creek). The water drains from the lake as the Lower Adams River which is home to a very large and famous sockeye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
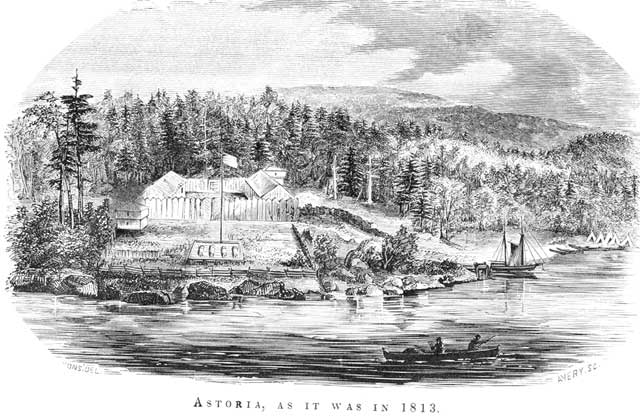
Fort Astoria
Fort Astoria (also named Fort George) was the primary fur trading post of John Jacob Astor's Pacific Fur Company (PFC). A maritime contingent of PFC staff was sent on board the '' Tonquin'', while another party traveled overland from St. Louis. This land based group later became known as the Astor Expedition. Built at the entrance of the Columbia River in 1811, Fort Astoria was the first American-owned settlement on the Pacific coast of North America. The inhabitants of the fort differed greatly in background and position, and were structured into a corporate hierarchy. The fur trading partners of the company were at the top, with clerks, craftsmen, hunters, and laborers in descending order. Nationalities included Americans, Scots, French Canadian voyageurs, Native Hawaiian Kanakas, and various indigenous North Americans, including Iroquois and others from Eastern Canada. They found life quite monotonous, with the fish and vegetable diet boring. Venereal diseases were problem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)