|
North Fork John Day Wilderness
The North Fork John Day Wilderness is a wilderness area within the Umatilla and Wallowa–Whitman National Forests in the Blue Mountains of northeastern Oregon. The wilderness consists of four separate units: the main unit of the North Fork John Day drainage; the Greenhorn Unit to the south; the Tower Mountain Unit to the north; and the Baldy Creek Unit to the east. Approximately of the Vinegar Hill-Indian Rock Scenic Area also lie within the wilderness.North Fork John Day Wilderness - Wilderness.net The North Fork John Day Wilderness is located within the larger Elkhorn Fire Management Area, and the area's fire plan allows for the use of Prescribed Natural Fire under certain circumstances. Topography [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grant County, Oregon
Grant County is one of the 36 counties in the U.S. state of Oregon. As of the 2020 census, the population was 7,233, making it Oregon's fourth-least populous county. The county seat is Canyon City. It is named for President Ulysses S. Grant, who served as an army officer in the Oregon Territory, and at the time of the county's creation was a Union general in the American Civil War. Grant County is included in the 8 county definition of Eastern Oregon. History Grant County was established on October 14, 1864, from parts of old Wasco and old Umatilla counties. Prior to its creation, cases brought to court were tried in The Dalles, county seat of the vast Wasco County. The great distance to The Dalles made law enforcement a difficult problem, and imposed a heavy burden on citizens who had a need to transact business at the courthouse. In 1889, more than half of the southern part of the original Grant County was taken to form Harney County. Also in 1899, a small part of north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands. Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archipelago, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the Lakshadweep Islands, the Galápagos Islands, the Japanese archipelago, the Philippine Archipelago, the Maldives, the Balearic Islands, The Bahamas, the Aegean Islands, the Hawaiian Islands, the Canary Islands, Malta, the Azores, the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, the British Isles, the islands of the Archipelago Sea, and Shetland. They are sometimes defined by political boundaries. For example, the Gulf archipelago off the northeastern Pacific coast forms part of a larger archipelago that geographically includes Washington state's San Juan Islands; while the Gulf archipelago and San Juan Islands are geographically related, they are not technically included in the same archipelago due to manmad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
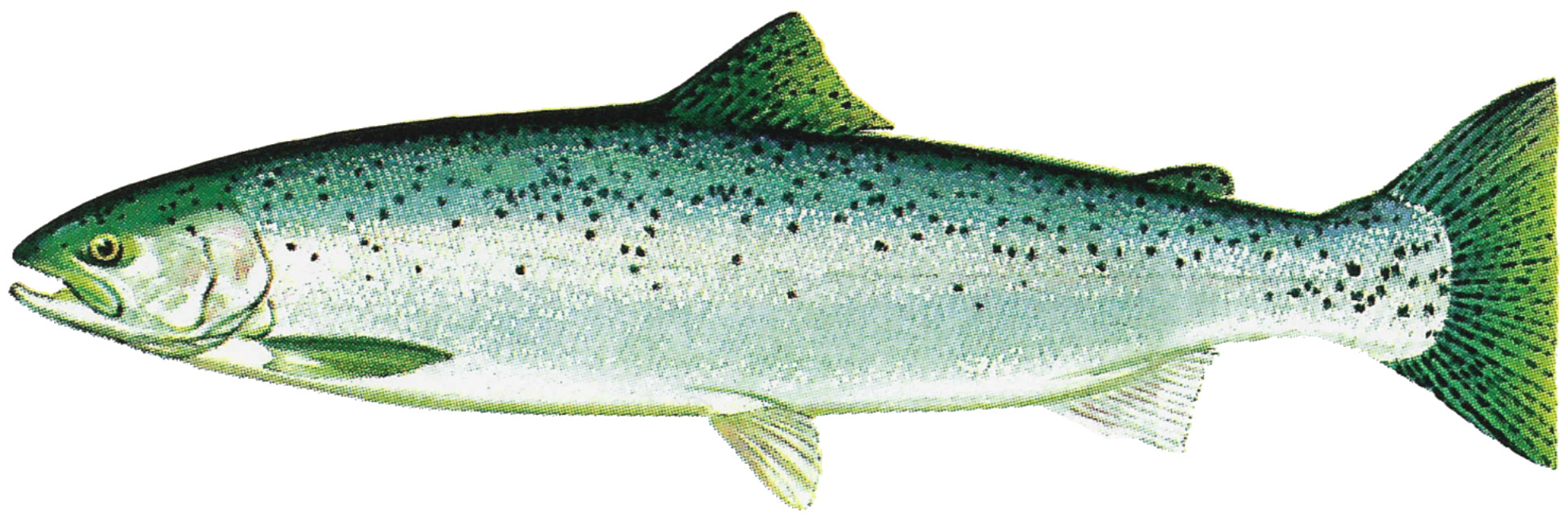
Rainbow Trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coastal rainbow trout or Columbia River redband trout that usually returns to freshwater to spawn after living two to three years in the ocean. Freshwater forms that have been introduced into the Great Lakes and migrate into tributaries to spawn are also called steelhead. Adult freshwater stream rainbow trout average between , while lake-dwelling and anadromous forms may reach . Coloration varies widely based on subspecies, forms, and habitat. Adult fish are distinguished by a broad reddish stripe along the lateral line, from gills to the tail, which is most vivid in breeding males. Wild-caught and hatchery-reared forms of the species have been transplanted and introduced for food or sport in at least 45 countries and every continent except ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinook Salmon
The Chinook salmon (''Oncorhynchus tshawytscha'') is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon in North America, as well as the largest in the genus ''Oncorhynchus''. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other vernacular names for the species include king salmon, Quinnat salmon, Tsumen, spring salmon, chrome hog, Blackmouth, and Tyee salmon. The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name ''chavycha'' (чавыча). Chinook are anadromous fish native to the North Pacific Ocean and the river systems of western North America, ranging from California to Alaska, as well as Asian rivers ranging from northern Japan to the Palyavaam River in the Arctic northeast Siberia. They have been introduced to other parts of the world, including New Zealand, thriving in Lake Michigan Great Lakes of North America and Michigan's western rivers, and Patagonia. A large Chinook is a prized and sought-after catch for a sporting angler. The flesh of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mule Deer
The mule deer (''Odocoileus hemionus'') is a deer indigenous to western North America; it is named for its ears, which are large like those of the mule. Two subspecies of mule deer are grouped into the black-tailed deer. Unlike the related white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), which is found throughout most of North America east of the Rocky Mountains and in the valleys of the Rocky Mountains from Idaho and Wyoming northward, mule deer are only found on the western Great Plains, in the Rocky Mountains, in the southwest United States, and on the west coast of North America. Mule deer have also been introduced to Argentina and Kauai, Kauai, Hawaii. Taxonomy Mule deer can be divided into two main groups: the mule deer (''sensu stricto'') and the black-tailed deer. The first group includes all subspecies, except ''O. h. columbianus'' and ''Sitka deer, O. h. sitkensis'', which are in the black-tailed deer group. The two main groups have been treated as separate species, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocky Mountain Elk
The Rocky Mountain elk (''Cervus canadensis nelsoni'') is a subspecies of elk found in the Rocky Mountains and adjacent ranges of Western North America. Habitat The winter ranges are most common in open forests and floodplain marshes in the lower elevations. In the summer it migrates to the subalpine forests and alpine basins. Elk have a diverse habitat range that they can reside in but are most often found in forest and forest edge habitat and in mountain regions they often stay in higher elevations during warmer months and migrate down lower in the winter. They may even come down the mountain and leave the forest into some grassland for part of the day but head back into the timber in the evening. Effects of climate change Climate change/warming can keep elk in their higher elevation habitats for longer into the winter than normal. Climate changes such as warming have in some cases even increased the seasonal range of elk in the winter. For example, in Yellowstone the climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumpter, Oregon
Sumpter is a city in Baker County, Oregon, United States. The population was 204 at the 2010 census. Sumpter is named after Fort Sumter by its founders. The name was inspired by a rock as smooth and round as a cannonball, which reminded a local resident of the American Civil War and Fort Sumter. Names Baker County was named for Edward Dickinson Baker, a U.S. Senator from Oregon who was killed in the Battle of Ball's Bluff during the American Civil War. Sumpter, first settled by Euro-Americans during this war, was named after Fort Sumter in the U.S. state of South Carolina. The fort was often mentioned in war dispatches read by the settlers.''Oregon Geographic Names'', pp. 922–23 An account in the Baker ''Democrat–Herald'' many decades later reported that a round rock found in the area in the early 1860s had looked to residents like a cannonball and, reinforced by the war news, had reminded them of Fort Sumter. In 1883, Joseph D. Young became the first postmaster of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumpter Valley Gold Dredge
The Sumpter Valley Gold Dredge is a historic gold dredge located in Sumpter, in the U.S. state of Oregon. Gold was discovered in Sumpter in 1862. Three gold dredges were put into service in the Sumpter Valley district between 1912 and 1934. Description A gold dredge works by having large buckets that pull the gold-bearing earth up into its machinery to be processed, keeping the gold and spewing the waste (known as "tailings") out the back by way of a stacker. Built on a shallow hull, these dredges did not need a lot of water to operate, as they moved their pond of water with them. The internal mechanics were not very sophisticated—they duplicated, on a larger scale, many of the devices used by placer mining throughout the gold rush, such as the gold pan and the sluice box. In essence, the dirt that was dug by the large electrically powered buckets was sifted and sorted, and the remainder was washed over a series of riffles allowing the gold to settle and be trapped. The pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilderness Act
The Wilderness Act of 1964 () was written by Howard Zahniser of The Wilderness Society. It created the legal definition of wilderness in the United States, and protected 9.1 million acres (37,000 km²) of federal land. The result of a long effort to protect federal wilderness and to create a formal mechanism for designating wilderness, the Wilderness Act was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson on September 3, 1964 after over sixty drafts and eight years of work. The Wilderness Act is well known for its succinct and poetic definition of wilderness: "A wilderness, in contrast with those areas where man and his own works dominate the landscape, is hereby recognized as an area where the earth and its community of life are untrammeled by man, where man himself is a visitor who does not remain." – Howard Zahniser When Congress passed and President Lyndon B. Johnson signed the Wilderness Act on September 3, 1964, it created the National Wilderness Preservation Sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. The metal is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental ( native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate anion. Gold is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is nearly alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |