|
North Auckland And Northland Grid Upgrade Project
The North Auckland and Northland (NAaN) grid upgrade project reinforced transmission into the Auckland Region and across the harbour to North Auckland and the Northland Region. It added new 220 kV transmission capacity to the National Grid by providing 37 km of underground cable between the Pakuranga, Penrose, and Albany substations. The project included new grid exit points at Hobson Street (Auckland CBD) and Wairau Road ( North Shore) and a cable across the Auckland Harbour Bridge. The estimated total cost of the cable aspects of the works was $415 million. The project was completed and the connection was commissioned in February 2014 at a final cost of NZ$473 million. Overview The NAan project established a 220 kV connection between the Pakuranga and Penrose substations, and a further 220 kV connection between the Penrose and Albany substations. The Penrose to Albany section included connections to the zone substations owned by Vector at Hobson Street i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakuranga
Pakuranga is an eastern suburb of Auckland, in northern New Zealand. Pakuranga covers a series of low ridges and previously swampy flats, now drained, that lie between the Pakuranga Creek and Tamaki River, two estuarial arms of the Hauraki Gulf. It is located to the north of Manukau and 15 kilometres southeast of the Auckland CBD. History The suburb's name comes from the Māori , meaning ''battle of the sunlight'' or ''battle of the sun's rays''. The name refers to a fierce battle at Ōhuiarangi / Pigeon Mountain over forbidden love raged between two - fairy people of the forest - until a priest caused the sun to rise and the earth to explode. Caught by the rays of the sun and volcanic eruptions, many patupaiarehe perished. Pakuranga is traditionally home to the Ngāi Tai Iwi also known as Ngāi Tai ki Tāmaki. The prominent pā were at Ohuiarangi / Pigeon Mountain and Mokoia Pā of Ngāti Paoa at Panmure on a cliff, at the intersection of the Te Wai Ō Taiki / Tamaki Riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Busway, Auckland
The Northern Busway is a segregated busway that runs along the eastern side of the Northern Motorway, part of State Highway 1, in the north of Auckland, New Zealand, linking the North Shore with the northern end of the Auckland Harbour Bridge. As of May 2022, the busway consists of two-way lanes running between Albany Station and Akoranga Station, and from Akoranga Station a southbound-only lane that joins the harbour bridge approaches just south of the Onewa Road on-ramp system. Between 2008 and 2022 the busway terminated at Constellation. Six stations provide access points for passengers to board; some stations have park and ride parking spaces; others have drop off and pick up zones only. City-bound Northern Express (NX1 and NX2) services commence from Hibiscus Coast Station or Albany Station; from Albany, the lanes reduced travel time to Britomart Transport Centre from around one hour by car during peak hours to about half an hour by bus. In the reverse direction, NX1 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electricity Commission (NZ)
The New Zealand Electricity Commission was a government authority set up in 2003 to regulate the electricity sector in New Zealand. It was succeeded by the Electricity Authority in November 2010. The Commission was established under the Electricity Act to regulate the operation of the electricity industry and markets (both wholesale and retail) in accordance with government energy policy. The Commission was established following extremely dry hydro years in 2001 and 2003, which led to government concerns that the electricity market did not provide adequate security of electricity supply. The first Electricity Commissioner was Roy Hemmingway, who was succeeded by David Caygill in 2007. See also * Electricity Authority (New Zealand) The New Zealand Electricity Authority ( mi, Te Mana Hiko) is an independent Crown entity responsible for the regulation of the New Zealand electricity market. The Authority was established in November 2010, following a government review of the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Roskill
Mount Roskill is a suburban area in the city of Auckland, New Zealand. It is named for the volcanic peak Puketāpapa (commonly called "Mount Roskill" in English). Description The suburb, named after the Mount, is located seven kilometres to the south of the city centre, and is surrounded by the neighbouring suburbs of Three Kings, New Zealand, Three Kings, Sandringham, New Zealand, Sandringham, Wesley, Hillsborough, Auckland, Hillsborough and Mount Albert, New Zealand, Mount Albert. The Mount Roskill shops are located at the intersection of Mount Albert and Dominion Roads. In the 1920s, a new subdivision off Dominion Road was established. It was named the Victory Estate after notable First World War personnel. One of the city's larger suburbs, it was largely farmland until after the Second World War. It was a separate borough from 1947 until local government reorganisation in 1989 amalgamated it with Auckland City. In the past, Mount Roskill was referred to as the Bible Bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glendene
Glendene is a suburb of West Auckland, in New Zealand. It is under the local governance of the Auckland Council. Glendene is a mainly residential suburb with the north-eastern portion devoted to light industry. History Glendene is named after a farm in the area owned by Percy Jones, which was later subdivided for housing. The Western shores of the Whau River were home to many clay and pottery yards in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, including the Malam, Laurie, Black & Scott and Hepburn yards. Most of the development of Glendene as a residential suburb occurred in the 1960s and 1970s. In April 2014, Glendene became a part of the new Kelston electorate. ThGlendene Community Hubwas opened in March 2015 in response to Council studies that showed a need for community development in the area. Demographics Glendene covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. Glendene had a population of 7,563 at the 2018 New Zealand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southdown Power Station
Southdown Power Station was a natural gas-fired combined cycle gas turbine cogeneration power station in Southdown, a suburb in southern Auckland, New Zealand. When operational, it was New Zealand's northernmost power station with a capacity exceeding 50 MW. History The plant was developed by the Southdown Cogeneration Joint Venture, a joint venture between TransAlta and Mercury Energy. The plant had two LM6000 gas turbines and one steam turbine, fueled on natural gas and producing 114MW. The plant was expected to emit about 410,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide annually. In 2000, Mighty River Power purchased 50% of the plant and purchased the remainder in 2002. A third LM6000 gas turbine was added in 2007. This was operated in open cycle mode. Operation Southdown was owned and operated by electricity generator Mighty River Power (now Mercury Energy), and complemented the company's renewable hydroelectric and geothermal stations. The station, strategically located in the south-ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maui Gas Field
The Maui natural gas field is the largest gas, natural gas condensate and oil field in New Zealand, producing nearly three-quarters of the country's hydrocarbons, as well as providing energy for electricity generation. It is located in the Tasman Sea, 35 km off the coast of Taranaki and to the southwest of New Plymouth. It covers an area of 157 square kilometres and is located in 110 metres of water. The gas field was discovered in 1969 by a joint venture of Royal Dutch/Shell, British Petroleum and Todd Petroleum. It was considered a "giant" field at the time of discovery. Government investment led to a government organisation later called Petrocorp taking a 50% interest. This was later bought out by Fletcher Challenge Energy. By the end of the Maui gas contract in 2009, the Maui Mining Companies were made up of Shell (83.75%), OMV New Zealand (10%), and Todd Energy (6.25%). OMV New Zealand owns and operates the Maui gas field having acquired the 83.75% share from Shell Explor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
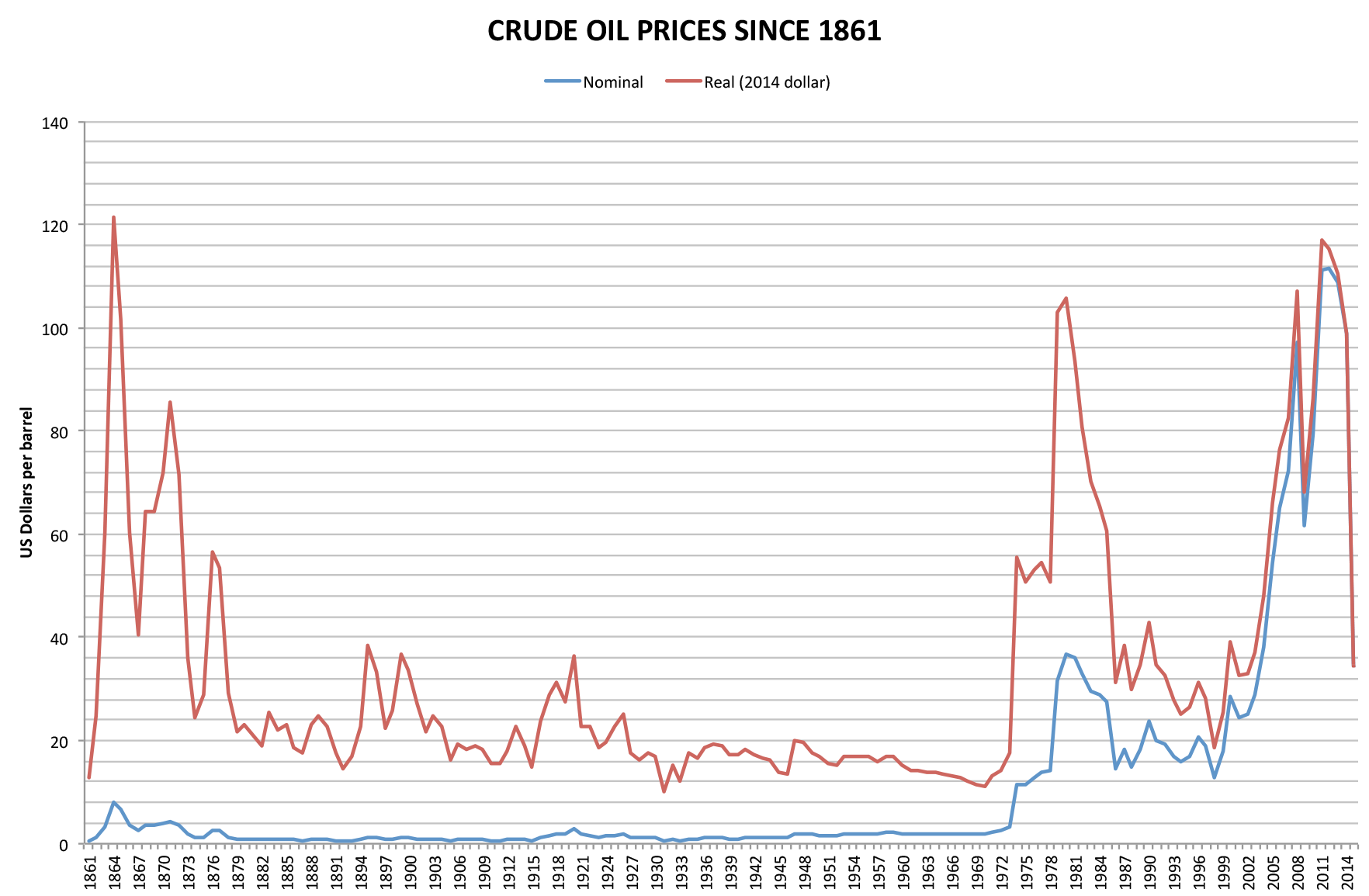
1979 Energy Crisis
The 1979 oil crisis, also known as the 1979 Oil Shock or Second Oil Crisis, was an energy crisis caused by a drop in oil production in the wake of the Iranian Revolution. Although the global oil supply only decreased by approximately four percent, the oil markets' reaction raised the price of crude oil drastically over the next 12 months, more than doubling it to . The sudden increase in price was connected with fuel shortages and long lines at gas stations similar to the 1973 oil crisis. In 1980, following the onset of the Iran–Iraq War, oil production in Iran fell drastically. Iraq's oil production also dropped significantly, triggering economic recessions worldwide. Oil prices did not return to pre-crisis levels until the mid-1980s. Oil prices after 1980 began a steady decline over the next 20 years, except for a brief uptick during the Gulf War, which then reached a 60% fall-off in the 1990s. Mexico, Nigeria, and Venezuela's major oil exporters expanded their produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1973 Oil Crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War. The initial nations targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the United States, though the embargo also later extended to Portugal, Rhodesia and South Africa. By the end of the embargo in March 1974, the price of oil had risen nearly 300%, from US to nearly globally; US prices were significantly higher. The embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long-term effects on global politics and the global economy. It was later called the "first oil shock", followed by the 1979 oil crisis, termed the "second oil shock". Background Arab-Israeli conflict Ever since the recreation of the State of Israel in 1948 there has been Arab–Israeli conflict in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |