|
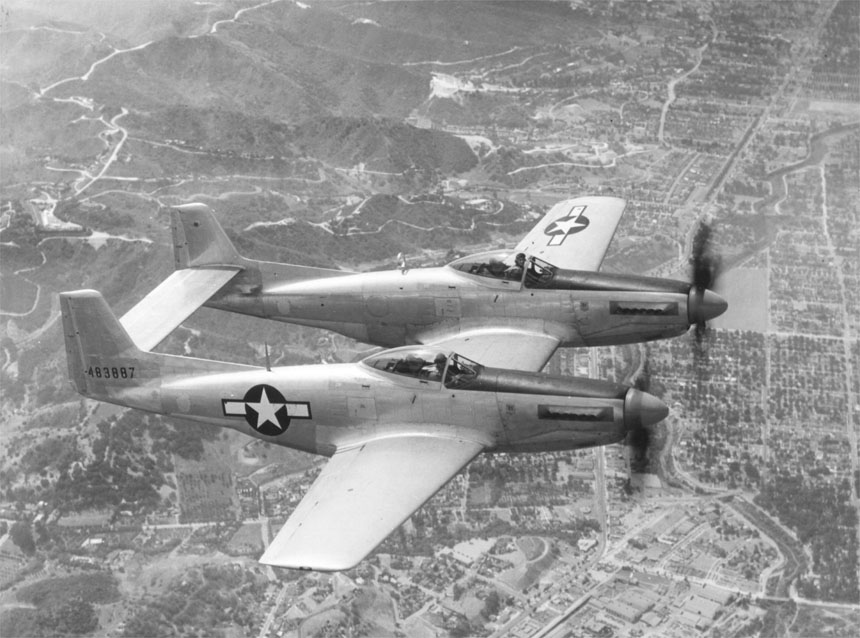
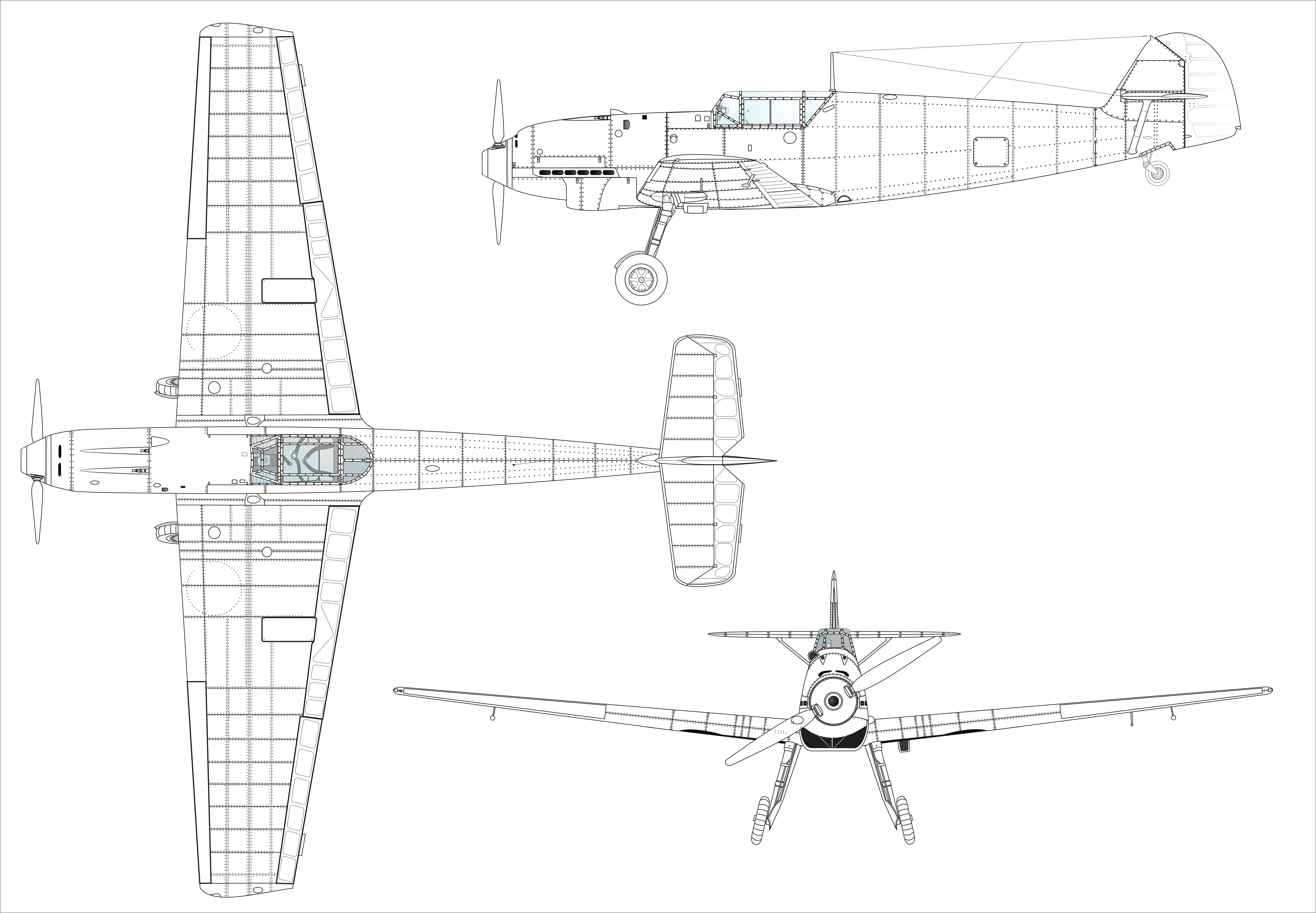
North American F-82F Twin Mustang
The North American F-82 Twin Mustang is the last American piston-engined fighter ordered into production by the United States Air Force. Based on the North American P-51 Mustang, the F-82 was originally designed as a long-range escort fighter for the Boeing B-29 Superfortress in World War II. The war ended well before the first production units were operational. In the postwar era, Strategic Air Command used the aircraft as a long-range escort fighter. Radar-equipped F-82s were used extensively by the Air Defense Command as replacements for the Northrop P-61 Black Widow as all-weather day/night interceptors. During the Korean War, Japan-based F-82s were among the first USAF aircraft to operate over Korea. The first three North Korean aircraft destroyed by U.S. forces were shot down by F-82s, the first being a North-Korean Yak-11 downed over Gimpo Airfield by the USAF 68th Fighter Squadron. Design and development Initially intended as a very long-range (VLR) escort fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escort Fighter
The escort fighter was a concept for a fighter aircraft designed to escort bombers to and from their targets. An escort fighter needed range long enough to reach the target, loiter over it for the duration of the raid to defend the bombers, and return. A number of twin-engined heavy fighters with high fuel capacity were designed for escort duties prior to the outbreak of World War II. Such heavy fighters largely failed in their intended escort role during the war, as they were commonly outmaneuvered by more agile single-engined fighters. As the war progressed, longer-range fighter designs and the use of drop tanks allowed single-engined fighters to perform escort duties. In the post-war era the introduction of jet engines and their inherent short range made escort fighters very difficult to build. The related concept of a penetration fighter emerged briefly in the 1950s and again in the 1960s, but did not result in any production aircraft. The escort role has been diminished as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrender Of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) had become incapable of conducting major operations and an Allied invasion of Japan was imminent. Together with the United Kingdom and China, the United States called for the unconditional surrender of the Japanese armed forces in the Potsdam Declaration on 26 July 1945—the alternative being "prompt and utter destruction". While publicly stating their intent to fight on to the bitter end, Japan's leaders (the Supreme Council for the Direction of the War, also known as the "Big Six") were privately making entreaties to the publicly neutral Soviet Union to mediate peace on terms more favorable to the Japanese. While maintaining a sufficient level of diplomatic engagement with the Japanese to give them the impression they might be wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolls-Royce Merlin
The Rolls-Royce Merlin is a British liquid-cooled V-12 piston aero engine of 27-litres (1,650 cu in) capacity. Rolls-Royce designed the engine and first ran it in 1933 as a private venture. Initially known as the PV-12, it was later called ''Merlin'' following the company convention of naming its four-stroke piston aero engines after birds of prey. After several modifications, the first production variants of the PV-12 were completed in 1936. The first operational aircraft to enter service using the Merlin were the Fairey Battle, Hawker Hurricane and Supermarine Spitfire. The Merlin remains most closely associated with the Spitfire and Hurricane, although the majority of the production run was for the four-engined Avro Lancaster heavy bomber. A series of rapidly-applied developments, brought about by wartime needs, markedly improved the engine's performance and durability. Starting at 1,000 hp for the first production models, most late war versions produced just ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-82-productionine-1948
The Vought F-8 Crusader (originally F8U) is a single-engine, supersonic, carrier-based air superiority jet aircraft built by Vought for the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps (replacing the Vought F7U Cutlass), and for the French Navy. The first F-8 prototype was ready for flight in February 1955. The F-8 served principally in the Vietnam War. The Crusader was the last American fighter with guns as the primary weapon, earning it the title "The Last of the Gunfighters".Tillman 1990 The RF-8 Crusader was a photo-reconnaissance development and operated longer in U.S. service than any of the fighter versions. RF-8s played a crucial role in the Cuban Missile Crisis, providing essential low-level photographs impossible to acquire by other means. United States Navy Reserve units continued to operate the RF-8 until 1987. Design and development In September 1952, the United States Navy announced a requirement for a new fighter. It was to have a top speed of Mach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission (mechanics)
Propulsion transmission is the mode of transmitting and controlling propulsion power of a machine. The term ''transmission'' properly refers to the whole drivetrain, including clutch, gearbox, prop shaft (for rear-wheel drive vehicles), differential, and final drive shafts. In the United States the term is sometimes used in casual speech to refer more specifically to the gearbox alone, and detailed usage differs. The transmission reduces the higher engine speed to the slower wheel speed, increasing torque in the process. Transmissions are also used on pedal bicycles, fixed machines, and where different rotational speeds and torques are adapted. Often, a transmission has multiple gear ratios (or simply "gears") with the ability to switch between them as the speed varies. This switching may be done manually (by the operator) or automatically (by a control unit). Directional (forward and reverse) control may also be provided. Single-ratio transmissions also exist, which simply cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packard V-1650 Merlin
The Packard V-1650 Merlin is a version of the Rolls-Royce Merlin aircraft engine, produced under license in the United States by the Packard Motor Car Company.Gunston 1995, p. 144. The engine was licensed to expand production of the Rolls-Royce Merlin for British use. The engine also filled a gap in the U.S. at a time when similarly powered American-made engines were not available. The first V-1650s, with a one-stage supercharger, equivalent to the Merlin XX, were used in the P-40F Kittyhawk fighter and in Canadian-built Hawker Hurricanes. Later versions based on the Merlin 60 series included a more advanced two-stage supercharger for improved performance at high altitudes. It found its most notable application in the North American P-51 Mustang fighter, improving the aircraft's performance so it could escort Allied heavy bombers from Britain to Germany and back. Design and development At the outbreak of World War Two, the British aviation industry expanded greatly. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conventional Landing Gear
Conventional landing gear, or tailwheel-type landing gear, is an aircraft undercarriage consisting of two main wheels forward of the center of gravity and a small wheel or skid to support the tail.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 133. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. From the Ground Up, 27th edition, page 11 The term taildragger is also used, although some argue it should apply only to those aircraft with a tailskid rather than a wheel. The term "conventional" persists for historical reasons, but all modern jet aircraft and most modern propeller aircraft use tricycle gear. History In early aircraft, a tailskid made of metal or wood was used to support the tail on the ground. In most modern aircraft with conventional landing gear, a small articulated wheel assembly is attached to the rearmost part of the airframe in place of the skid. This wheel may be steered by the pilot through a connection to the rudder pedals, allowing the rudd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M3 Browning
The M2 machine gun or Browning .50 caliber machine gun (informally, "Ma Deuce") is a heavy machine gun that was designed towards the end of World War I by John Browning. Its design is similar to Browning's earlier M1919 Browning machine gun, which was chambered for the .30-06 cartridge. The M2 uses Browning's larger and more powerful .50 BMG (12.7 mm) cartridge. The design has had many designations; the official U.S. military designation for the current infantry type is Browning Machine Gun, Cal. .50, M2, HB, Flexible. It is effective against infantry, unarmored or lightly armored vehicles and boats, light fortifications, and low-flying aircraft. The gun has been used extensively as a vehicle weapon and for aircraft armament by the United States since the 1930s. It was heavily used during World War II, the Korean War, the Vietnam War, the Falklands War, the Soviet–Afghan War, the Gulf War, the Iraq War, and the War in Afghanistan. It is the primary heavy machine gun of NATO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgar Schmued
Edgar O. "Ed" Schmued (Schmüd), German-American aircraft designer (1899–1985) was famed for his design of the iconic North American P-51 Mustang and, later, the F-86 Sabre while at North American Aviation. He later worked on other aircraft designs as an aviation consultant. Early life Edgar Schmued was born in Hornbach, Germany, 30 December 1899. At the age of eight, he first saw an airplane in flight and decided that aviation was to be his life's work. Edgar embarked early on a rigorous program of self-study to become an engineer, and later served an apprenticeship in a small engine factory. He also designed several innovative engine components for which he received patents. In his spare time, he continued the self-study of aviation. Schmued left his native Bavaria for Brazil in 1925, seven years after World War I had shattered the German economy. His experience in Germany led to employment with the General Aviation, the air branch of General Motors Corporation in São Paulo, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messerschmitt Bf 109 Variants
Due to the Messerschmitt Bf 109's versatility and time in service with the German and foreign air forces, numerous variants were produced in Germany to serve for over eight years with the Luftwaffe. Additional variants were produced abroad totalling in 34,852 Bf 109s built. Bf 109 A/B/C/D The Bf 109A was the first version of the Bf 109. Armament was initially planned to be just two cowl-mounted 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 17 machine guns. However, possibly due to the introduction of the Hurricane and Spitfire, each with eight 7.7 mm (.303 in) machine guns, experiments were carried out with a third machine gun firing through the propeller shaft. V4 and some A-0 were powered by a 640 PS (631 hp, 471 kW) Junkers Jumo 210B engine driving a two-blade fixed- pitch propeller, but production was changed to the 670 PS (661 hp, 493 kW) Jumo 210D as soon as it became available. The A-0 was not of a uniform type; there were several changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin-fuselage Aircraft
A twin-fuselage aircraft has two main fuselages. It is distinct from the twin-boom aircraft, twin-boom configuration which has a single main fuselage with two subsidiary boom structures. Twin fuselages have been adopted for various reasons, and a few types have entered production. Early seaplanes A twin-float arrangement offers stability on the water without the need for wing tip stabilising floats. Mounting the float immediately below, or integrally with, the fuselage provides a strong airframe with minimal additional weight. During and after World War I a number of such twin-fuselage floatplanes and twin-hulled flying boats were constructed, and a few entered production. As early as 1913, the Radley-England Waterplane racing flying boat demonstrated the concept at the hands of pilot Eric Gordon England, Gordon England. The Blackburn Twin Blackburn, Twin Blackburn of 1915 was a long-range floatplane for anti-Zeppelin patrol. A handful of production examples were delivered but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-82 And P-51 In Formation (060728-F-1234S-017)
The Vought F-8 Crusader (originally F8U) is a single-engine, supersonic, Carrier-based aircraft, carrier-based Air superiority fighter, air superiority jet aircraft built by Vought for the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps (replacing the Vought F7U Cutlass), and for the French Navy. The first F-8 prototype was ready for flight in February 1955. The F-8 served principally in the Vietnam War. The Crusader was the last American fighter with guns as the primary weapon, earning it the title "The Last of the Gunfighters".Barrett Tillman, Tillman 1990 The RF-8 Crusader was a photo-reconnaissance development and operated longer in U.S. service than any of the fighter versions. RF-8s played a crucial role in the Cuban Missile Crisis, providing essential low-level photographs impossible to acquire by other means. United States Navy Reserve units continued to operate the RF-8 until 1987. Design and development In September 1952, the United States Navy announced a requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |