|
North American A-5 Vigilante
The North American A-5 Vigilante was an American carrier-based supersonic bomber designed and built by North American Aviation (NAA) for the United States Navy. Prior to 1962 unification of Navy and Air Force designations, it was designated the A3J Vigilante.Wagner 1982, p. 361. Development of the A-5 had started in 1954 as a private venture by NAA, who sought to produce a capable supersonic long distance bomber as a successor to the abortive North American XA2J Super Savage. It was a large and complex aircraft that incorporated several innovative features, such as being the first bomber to feature a digital computer, while its ability to attain speeds of up to Mach 2 while carrying a nuclear strike payload was also relatively ambitious for the era. The US Navy saw the value of such a bomber, leading to a contract for its full development and production being issued to the firm on 29 August 1956. The type performed its first flight just over two years later, on 31 August 1958. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maiden Flight
The maiden flight, also known as first flight, of an aircraft is the first occasion on which it leaves the ground under its own power. The same term is also used for the first launch of rockets. The maiden flight of a new aircraft type is always a historic occasion for the type and can be quite emotional for those involved. In the early days of aviation it could be dangerous, because the exact handling characteristics of the aircraft were generally unknown. The maiden flight of a new type is almost invariably flown by a highly experienced test pilot. Maiden flights are usually accompanied by a chase plane, to verify items like altitude, airspeed, and general airworthiness. A maiden flight is only one stage in the development of an aircraft type. Unless the type is a pure research aircraft (such as the X-15), the aircraft must be tested extensively to ensure that it delivers the desired performance with an acceptable margin of safety. In the case of civilian aircraft, a new typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BAC TSR-2
The British Aircraft Corporation TSR-2 is a cancelled Cold War strike and reconnaissance aircraft developed by the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC), for the Royal Air Force (RAF) in the late 1950s and early 1960s. The TSR-2 was designed around both conventional and nuclear weapons delivery: it was to penetrate well-defended frontline areas at low altitudes and very high speeds, and then attack high-value targets in rear areas. Another intended combat role was to provide high-altitude, high-speed stand-off, side-looking radar and photographic imagery and signals intelligence, aerial reconnaissance. Only one airframe flew and test flights and weight-rise during design indicated that the aircraft would be unable to meet its original stringent design specifications. The design specifications were reduced as the result of flight testing.Burke 2010, p. 109. The TSR-2 was the victim of ever-rising costs and inter-service squabbling over Britain's future defence needs, which tog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dassault Mirage IV
The Dassault Mirage IV was a French supersonic strategic bomber and deep-reconnaissance aircraft. Developed by Dassault Aviation, the aircraft entered service with the French Air Force in October 1964. For many years it was a vital part of the nuclear triad of the ''Force de Frappe'', France's nuclear deterrent striking force. The Mirage IV was retired from the nuclear strike role in 1996, and the type was entirely retired from operational service in 2005. During the 1960s, there were plans to export the Mirage IV. In one proposal, Dassault would have entered a partnership with the British Aircraft Corporation to jointly produce a Mirage IV variant for the Royal Air Force and potentially for other export customers, but this project did not come to fruition. The Mirage IV was ultimately not adopted by any other operators. Development Origins During the 1950s, France embarked on an extensive military program to produce nuclear weapons; however, it was acknowledged that existin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Electric Canberra
The English Electric Canberra is a British first-generation, jet-powered medium bomber. It was developed by English Electric during the mid- to late 1940s in response to a 1944 Air Ministry requirement for a successor to the wartime de Havilland Mosquito fast bomber. Among the performance requirements for the type was an outstanding high-altitude bombing capability and high speed. These were partly accomplished by making use of newly developed jet-propulsion technology. When the Canberra was introduced to service with the Royal Air Force (RAF), the type's first operator, in May 1951, it became the service's first jet-powered bomber. In February 1951, a Canberra set another world record when it became the first jet aircraft to make a nonstop transatlantic flight. Throughout most of the 1950s, the Canberra could fly at a higher altitude than any other aircraft in the world, and in 1957, a Canberra established a world altitude record of . Due to its ability to evade the early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Australian Air Force
"Through Adversity to the Stars" , colours = , colours_label = , march = , mascot = , anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration – 31 March , equipment = , equipment_label = , battles = * Second World War * Berlin Airlift * Korean War * Malayan Emergency * Indonesia–Malaysia Confrontation * Vietnam War * Operation Astute, East Timor * War in Afghanistan (2001–present), War in Afghanistan * Iraq War * American-led intervention in Iraq (2014–present), Military intervention against ISIL , decorations = , battle_honours = , battle_honours_label = , flying_hours = , website = , commander1 = Governor-General of Australia, Governor-General David Hurley as representative of Charles III as Monarchy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
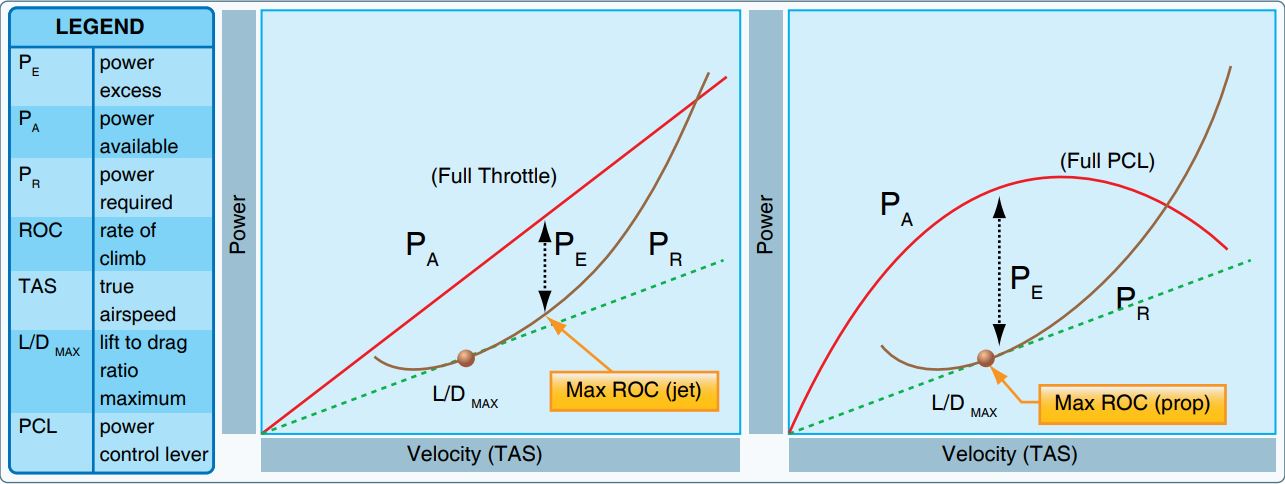
Climb Rate
In aeronautics, the rate of climb (RoC) is an aircraft's vertical speed, that is the positive or negative rate of altitude change with respect to time. In most ICAO member countries, even in otherwise metric countries, this is usually expressed in feet per minute (ft/min); elsewhere, it is commonly expressed in metres per second (m/s). The RoC in an aircraft is indicated with a vertical speed indicator (VSI) or instantaneous vertical speed indicator (IVSI). The temporal rate of decrease in altitude is referred to as the rate of descent (RoD) or sink rate. A negative rate of climb corresponds to a positive rate of descent: RoD = −RoC. Speed and rate of climb There are a number of V speeds, designated airspeeds relating to optimum rates of ascent, the two most important of these are ''VX'' and ''VY''. ''VX'' is the indicated forward airspeed for best angle of climb. This is the speed at which an aircraft gains the most altitude in a given horizontal , typically used to avoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication (electronic intelligence—abbreviated to ELINT). Signals intelligence is a subset of intelligence collection management. As classified and sensitive information is usually encrypted, signals intelligence in turn involves the use of cryptanalysis to decipher the messages. Traffic analysis—the study of who is signaling whom and in what quantity—is also used to integrate information again. History Origins Electronic interceptions appeared as early as 1900, during the Boer War of 1899–1902. The British Royal Navy had installed wireless sets produced by Marconi on board their ships in the late 1890s, and the British Army used some limited wireless signalling. The Boers captured some wireless sets and used them to make vital transmis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Linescan
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed radiant heat. In 1800 the astronomer Sir William Herschel discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Side Looking Airborne Radar
Side-looking airborne radar (SLAR) is an aircraft- or satellite-mounted imaging radar pointing perpendicular to the direction of flight (hence ''side-looking''). A squinted (nonperpendicular) mode is possible also. SLAR can be fitted with a standard antenna (real aperture radar) or an antenna using synthetic aperture. The platform of the radar moves in direction of the x-axis. The radar "looks" with the looking angle ''θ'' (or so called off-nadir angle). The angle ''α'' between x-axis and the line of sight (LOS) is called cone angle, the angle ''φ'' between the x-axis and the projection of the line of sight to the (x; y)-plane is called azimuth angle. Cone- and azimuth angle are related by cos''α'' = cos''φ'' ∙ cos''ε''. On the earth surface the wave comes in at the (nominal ellipsoidal) incident angle ''β'' with respect to the vertical axis at this point. (In some publications the incident angle is denominated to as ''θi''.) The antenna illuminate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drop Tank
In aviation, a drop tank (external tank, wing tank or belly tank) is used to describe auxiliary fuel tanks externally carried by aircraft. A drop tank is expendable and often capable of being jettisoned. External tanks are commonplace on modern military aircraft and occasionally found in civilian ones, although the latter are less likely to be discarded except in an emergency. Overview The primary disadvantage with drop tanks is that they impose a drag penalty on the aircraft. External fuel tanks will also increase the moment of inertia, thereby reducing roll rates for air maneuvers. Some of the drop tank's fuel is used to overcome the added drag and weight of the tank. Drag in this sense varies with the square of the aircraft's speed. The use of drop tanks also reduces the number of external hardpoints available for weapons, reduces the weapon-carrying capacity and increases the aircraft's radar signature. Usually the fuel in the drop tanks is consumed first, and only when a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RA-5C Vigilante Overhead Aerial View
The North American A-5 Vigilante was an American carrier-based supersonic bomber designed and built by North American Aviation (NAA) for the United States Navy. Prior to 1962 unification of Navy and Air Force designations, it was designated the A3J Vigilante.Wagner 1982, p. 361. Development of the A-5 had started in 1954 as a private venture by NAA, who sought to produce a capable supersonic long distance bomber as a successor to the abortive North American XA2J Super Savage. It was a large and complex aircraft that incorporated several innovative features, such as being the first bomber to feature a digital computer, while its ability to attain speeds of up to Mach 2 while carrying a nuclear strike payload was also relatively ambitious for the era. The US Navy saw the value of such a bomber, leading to a contract for its full development and production being issued to the firm on 29 August 1956. The type performed its first flight just over two years later, on 31 August 1958 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_in_July_1960.jpg)
.jpg)





.png)
