|
North Abbey, Youghal
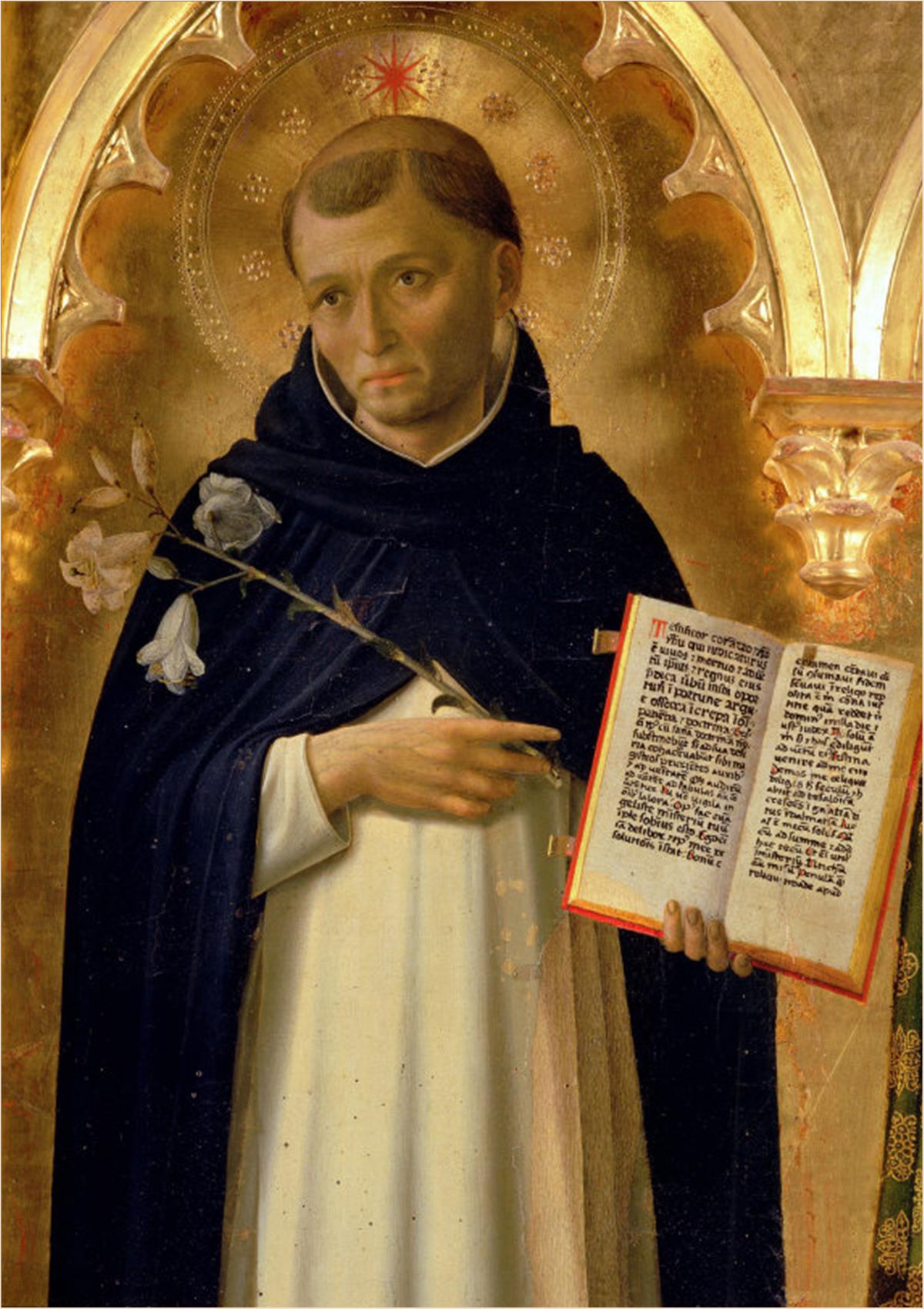
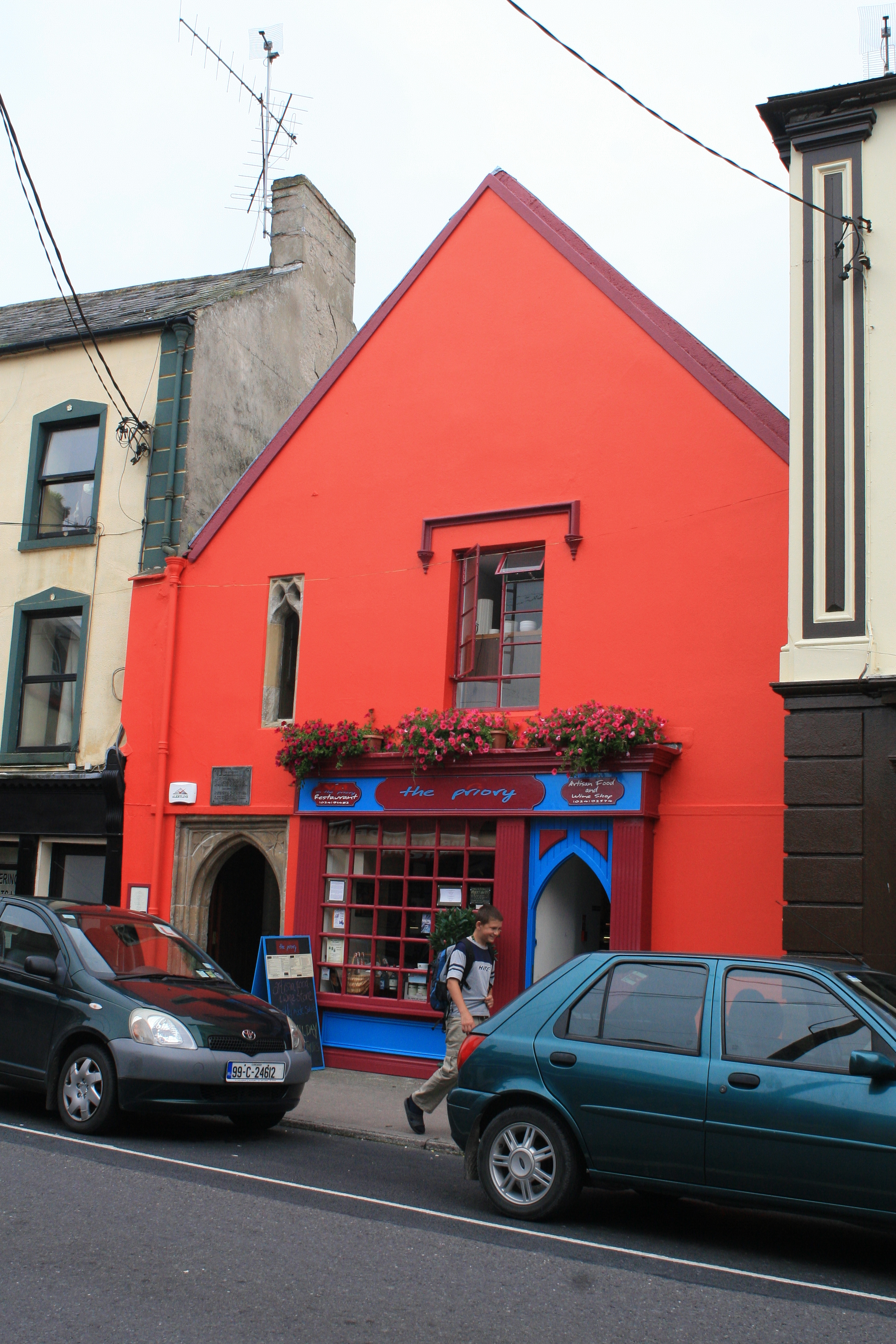
The Priory of Our Lady of Graces, known locally as the North Abbey, was a 13th-century Irish Dominican Order, Dominican monastery situated north of Youghal, County Cork. History The priory was founded in 1268 by Thomas FitzGerald, 2nd Baron Desmond, Thomas FitzMaurice FitzGerald, the second baron of Earl of Desmond, Desmond, whose maternal grandfather, Maurice FitzGerald, 2nd Lord of Offaly, had founded the Franciscan Friary of South Abbey, Youghal. The Dominican priory was initially dedicated to the Christian cross, Holy Cross, but was changed to 'Our Lady of Graces' in the late 15th century following the re-discovery of a small, ivory statue of the Madonna and Child. Samuel Lewis (publisher), Samuel Lewis in his ''Samuel Lewis (publisher)#A Topographical Dictionary of Ireland, Topographical Dictionary of Ireland'', written in 1837, said of it: "Thomas, whose son, in 1263 or 1271, founded a Dominican monastery, called the Priory of St. Mary of Graces." This statue had ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers ( la, Ordo Praedicatorum) abbreviated OP, also known as the Dominicans, is a Catholic mendicant order of Pontifical Right for men founded in Toulouse, France, by the Spanish priest, saint and mystic Dominic of Caleruega. It was approved by Pope Honorius III via the papal bull ''Religiosam vitam'' on 22 December 1216. Members of the order, who are referred to as ''Dominicans'', generally carry the letters ''OP'' after their names, standing for ''Ordinis Praedicatorum'', meaning ''of the Order of Preachers''. Membership in the order includes friars, nuns, active sisters, and lay or secular Dominicans (formerly known as tertiaries). More recently there has been a growing number of associates of the religious sisters who are unrelated to the tertiaries. Founded to preach the Gospel and to oppose heresy, the teaching activity of the order and its scholastic organisation placed the Preachers in the forefront of the intellectual life of the Middle Ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Lewis (publisher)
Samuel Lewis (c. 1782 – 1865) was the editor and publisher of topographical dictionaries and maps of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The aim of the texts was to give in 'a condensed form', a faithful and impartial description of each place. The firm of Samuel Lewis and Co. was based in London. Samuel Lewis the elder died in 1865. His son of the same name predeceased him in 1862. ''A Topographical Dictionary of England'' This work contains every fact of importance tending to illustrate the local history of England. Arranged alphabetically by place (village, parish, town, etc.), it provides a faithful description of all English localities as they existed at the time of first publication (1831), showing exactly where a particular civil parish was located in relation to the nearest town or towns, the barony, county, and province in which it was situated, its principal landowners, the diocese in which it was situated, and—of novel importance—the Roman Catholic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
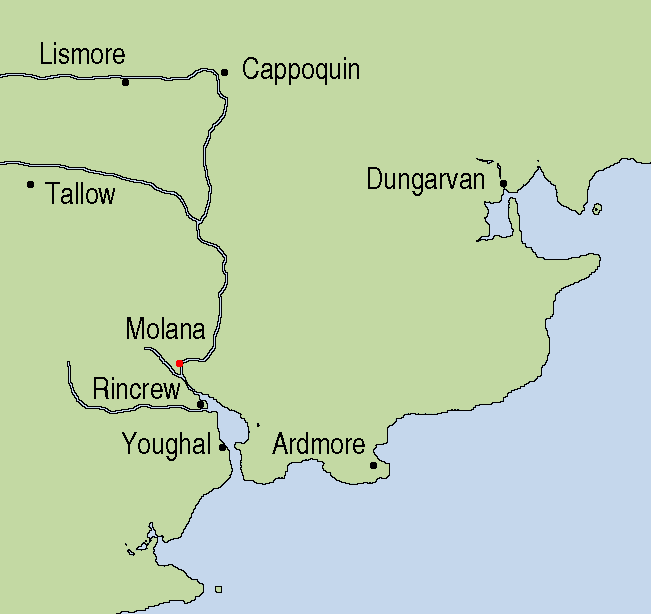
Molana Abbey
Molana Abbey ( ga, Mainistir Mhaolanfaidh) is a 6th-century Abbey located on the south coast of Ireland in the Diocese of Waterford and Lismore, near Youghal. The abbey lies on an island in the River Blackwater. The monks of the monastery helped co-edit Collectio canonum Hibernensis in the 8th century. It came under the control of the Augustinian canons in the 12th century before being seized by the English Crown during the Reformation and gradually falling into ruin. Name of the monastery The Irish name for the island is Dairinis, which can be translated as "Oak Island". Early Middle Ages text sources also use this name for the abbey. However, since there was another monastery island of that name in Wexford, the name of the founder, Máel Anfaid, was added to differentiate between the two. In later centuries, the old Irish name was dropped and only the founder's name was used. This name was later anglicised to Molana. Geographic location The monastery is located on a form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Youghal Priory
St John's House is a former 12th-century Irish Benedictine monastery situated in the centre of Youghal, County Cork. It was one of several religious houses in that city known by the name of Youghal Priory. History The monastery was founded on the Main Street in 1185. It was a dependency of St. John Priory in Waterford, a double monastery that also provided hospital care and which was itself a dependency of Bath Abbey in England. It served as a hospital for the sick until the Dissolution of the Monasteries. Oliver Cromwell made his headquarters here during the winter of 1649, and he inspected his troops every morning from the monastery. Features Small portions of the building still survive, which include a Gothic moulded door, ornamental spandrels and original ambry. The archway beyond the door leads to a passage of the original structure. See also * List of abbeys and priories in Ireland (County Cork) * North Abbey, Youghal The Priory of Our Lady of Graces, known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Abbeys And Priories In Ireland
This is a list of the abbeys, priories, friaries and other monastic religious houses in Ireland. This article provides a gazetteer for the whole of Ireland. Links to individual county lists ''To navigate the listings on this page, use the map or the table of contents. Alternatively, for listings which include the geographical coordinates and online references specific to the listed establishments, or if the entire listing is difficult to navigate, follow the links here (these links are also provided in the headings to each county in the main listing on this page):'' Overview Article layout The list is presented alphabetically by County. Foundations are listed alphabetically within each county. Communities/provenance: shows the status and communities existing at each establishment, together with such dates as have been established as well as the fate of the establishment after dissolution, and the current status of the site. Formal Name or Dedication: shows the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James FitzGerald, 8th Earl Of Desmond
James FitzGerald, 8th Earl of Desmond (1459– 1487) was the son of Thomas FitzGerald, 7th Earl of Desmond and his wife, Ellice de Barry, daughter of William Barry, 8th Baron Barry, and Ellen de la Roche. Life The execution of the 7th Earl of Desmond provoked an immediate and violent reaction. The dead earl’s elder sons ‘raised their standards and drew their swords, resolved to avenge their father’s murder’. James's younger brother, Gerald, laid waste a great deal in Leith and Munster in revenge for his father. According to a later account, Edward IV admonished the new Earl of Desmond by letters, and promised them his pardon if they would lay down their arms, which they did. "Now James FitzThomas, having made terms with King Edward, and received immunity for any act which he had committed to avenge his father's death, became Earl of Desmond," in 1471. Webb, Alfred. A Compendium of Irish Biography'. Dublin: 1878. The king felt the need to make amends to the dead ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James FitzGerald, 6th Earl Of Desmond
James FitzGerald, 6th Earl of Desmond (d. 1462), called 'the Usurper', was a younger son of Gerald FitzGerald, 3rd Earl of Desmond, and Lady Eleanor, daughter of James Butler, 2nd Earl of Ormond. Life The younger brother of John FitzGerald, 4th Earl of Desmond, James was uncle to the 4th Earl's only son Thomas FitzGerald, 5th Earl of Desmond, whom he was able to deprive of his earldom and dispossess in 1418 for marrying far below his station. The marriage between a man of Norman ancestry and a woman of Gaelic blood was in violation of the Statutes of Kilkenny. James FitzGerald took a leading role in forcing his nephew into exile in France where he died at Rouen two years later. Although not acknowledged until 1422, he was in 1420 made Seneschal of Imokilly, Inchiquin, and the town of Youghal, by James Butler, 4th Earl of Ormond. Also in 1420, he founded the Franciscan friary at Askeaton Abbey. In 1423 he was made Constable of Limerick for life. In 1445 he was excused attend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John FitzGerald, 4th Earl Of Desmond
John FitzGerald, 4th Earl of Desmond (died 1399) was the son of Gerald FitzGerald, 3rd Earl of Desmond. Burke, Bernard, A Genealogical History of the Dormant, Abeyant, Forfeited, and Extinct Peerages of the British Empire'. London: Harrison. 1866. p. 204Cokayne, George Edward, Complete Peerage of England, Scotland, Ireland, Great Britain and the United Kingdom, Extant, Extinct, or Dormant. Volume III'. London: George Bell & Sons. 1890. p. 83 He married and had one son, Thomas, who succeeded him as Earl of Desmond. According to Burke, John FitzGerald married Joan Roche, the daughter of Lord Fermoy. On 4 March 1399, FitzGerald drowned at Ardfinnan on the River Suir, returning from an incursion into the territory of the Earl of Ormond.. He was buried at Youghal, and succeeded by his son Thomas FitzJohn FitzGerald, 5th Earl of Desmond. References John John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Abbey, Youghal Pillar
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography. Etymology The word ''north'' is related to the Old High German ''nord'', both descending from the Proto-Indo-European unit *''ner-'', meaning "left; below" as north is to left when facing the rising sun. Similarly, the other cardinal directions are also related to the sun's position. The Latin word ''borealis'' comes from the Greek '' boreas'' "north wind, north", which, according to Ovid, was personified as the wind-god Boreas, the father of Calais and Zetes. ''Septentrionalis'' is from ''septentriones'', "the seven plow oxen", a name of '' Ursa Major''. The Greek ἀρκτικός (''arktikós'') is named for the same constellation, and is the source of the English word '' Arctic''. Other languages have other derivations. For example, in Lezgian, ''kefe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Abbey, Youghal Wall
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography. Etymology The word ''north'' is related to the Old High German ''nord'', both descending from the Proto-Indo-European unit *''ner-'', meaning "left; below" as north is to left when facing the rising sun. Similarly, the other cardinal directions are also related to the sun's position. The Latin word ''borealis'' comes from the Greek '' boreas'' "north wind, north", which, according to Ovid, was personified as the wind-god Boreas, the father of Calais and Zetes. ''Septentrionalis'' is from ''septentriones'', "the seven plow oxen", a name of '' Ursa Major''. The Greek ἀρκτικός (''arktikós'') is named for the same constellation, and is the source of the English word '' Arctic''. Other languages have other derivations. For example, in Lezgian, ''kefe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of First Fruits
The Board of First Fruits () was an institution of the Church of Ireland that was established in 1711 by Anne, Queen of Great Britain to build and improve churches and glebe houses in Ireland. This was funded from taxes collected on clerical incomes which were in turn funded by tithes. The board was replaced in 1833 by the Board of Ecclesiastical Commissioners. History From the English Reformation in the 16th century, most Irish people chose to remain Roman Catholic and had by now to pay tithes valued at about 10% of an area's agricultural produce, to maintain and fund the established state church, the Anglican Church of Ireland, to which only a small minority of the population converted. Protests against this situation led to the Tithe war in the early 19th century. In 1711, Queen Anne agreed that the tax on clerical incomes be given to the Church of Ireland for the building of new churches and Glebe Houses. To that effect, with Jonathan Swift's influence, the Board of First ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |