|
Normal Vision
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of visual perception, vision, but technically rates an examinee's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity is dependent on optical and neural factors, i.e. (1) the sharpness of the retinal image within the Human eye, eye, (2) the health and functioning of the retina, and (3) the sensitivity of the interpretative faculty of the brain. The most commonly referred visual acuity is the far acuity (e.g. 6/6 or 20/20 acuity), which describes the examinee's ability to recognize small details at a far distance, and is relevant to people with myopia; however, for people with hyperopia, the near acuity is used instead to describe the examinee's ability to recognize small details at a near distance. A common cause of low visual acuity is refractive error (ametropia), errors in how the light is refracted in the eyeball, and errors in how the retinal image is interpreted by the brain. The latter is the primary cause for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snellen Chart
A Snellen chart is an eye chart that can be used to measure visual acuity. Snellen charts are named after the Dutch ophthalmologist Herman Snellen, who developed the chart in 1862. Many ophthalmologists and vision scientists now use an improved chart known as the LogMAR chart. History Snellen developed charts using symbols based in a 5×5 unit grid. The experimental charts developed in 1861 used abstract symbols. Snellen's charts published in 1862 used alphanumeric capitals in the 5×5 grid. The original chart shows A, C, E, G, L, N, P, R, T, 5, V, Z, B, D, 4, F, H, K, O, S, 3, U, Y, A, C, E, G, L, 2. Description The normal Snellen chart is printed with eleven lines of block letters. The first line consists of one very large letter, which may be one of several letters, for example E, H, or N. Subsequent rows have increasing numbers of letters that decrease in size. A person taking the test covers one eye from 6 metres or 20 feet away, and reads aloud the letters of each row, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Surgery
Refractive eye surgery is optional eye surgery used to improve the refractive state of the eye and decrease or eliminate dependency on glasses or contact lenses. This can include various methods of surgical remodeling of the cornea (keratomileusis), lens implantation or lens replacement. The most common methods today use excimer lasers to reshape the curvature of the cornea. Refractive eye surgeries are used to treat common vision disorders such as myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia and astigmatism. History The first theoretical work on the potential of refractive surgery was published in 1885 by Hjalmar August Schiøtz, an ophthalmologist from Norway. In 1930, the Japanese ophthalmologist Tsutomu Sato made the first attempts at performing this kind of surgery, hoping to correct the vision of military pilots. His approach was to make radial cuts in the cornea, correcting effects by up to 6 diopters. The procedure unfortunately produced a high rate of corneal degeneration, howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E Chart
An E chart, also known as a tumbling E chart, is an ophthalmological chart used to measure a patient's visual acuity. Uses This chart is useful for patients who are unable to read the Latin alphabet – for example, very young children. It is also used in countries where people do not use the alphabet in their native language – for example, in China. It contains rows of the letter "E" in various kinds of rotation. The patient is asked to state (usually by pointing) where the limbs of the E are pointing, "up, down, left or right." Depending on how far the patient can "read", his or her visual acuity is quantified. It works on the same principle as Snellen's distant vision chart. See also * Visual acuity * Landolt C The Landolt C, also known as a Landolt ring, Landolt broken ring, or Japanese vision test, is an optotype: a standardized symbol used for testing vision. It was developed by the Swiss-born ophthalmologist Edmund Landolt. The Landolt C consists ... Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lea Test
The LEA Vision Test System is a series of pediatric vision tests designed specifically for children who do not know how to read the letters of the alphabet that are typically used in eye charts. There are numerous variants of the LEA test which can be used to assess the visual capabilities of near vision and distance vision, as well as several other aspects of occupational health, such as contrast sensitivity, visual field, color vision, visual adaptation, motion perception, and ocular function and accommodation (eye). History The first version of the LEA test was developed in 1976 by Finnish pediatric ophthalmologist Lea Hyvärinen, MD, PhD. Dr. Hyvärinen completed her thesis on fluorescein angiography and helped start the first clinical laboratory in that area while serving as a fellow at the Wilmer Eye Institute of Johns Hopkins Hospital in 1967. During her time with the Wilmer Institute, she became interested in vision rehabilitation and assessment and has been working in that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landolt C
The Landolt C, also known as a Landolt ring, Landolt broken ring, or Japanese vision test, is an optotype: a standardized symbol used for testing vision. It was developed by the Swiss-born ophthalmologist Edmund Landolt. The Landolt C consists of a ring that has a gap, thus looking similar to the letter C. The gap can be at various positions (usually left, right, bottom, top and the 45° positions in between) and the task of the tested person is to decide on which side the gap is. The size of the C and its gap are reduced until the subject makes a specified rate of errors. The minimum perceivable angle of the gap is taken as measure of the visual acuity. It is generally practised in the laboratory. The stroke width is of the diameter, and the gap width is the same. This is identical to the letter C from a Snellen chart. The Landolt C is the standard optotype for acuity measurement in most European countries. It was standardized, together with measurement procedures, by the Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acuity
Acuity may refer to: *Visual acuity, the behavioral ability to resolve fine image details *Tactile acuity, the ability to resolve fine spatial details of an object with the sense of touch *Acuity Brands, a lighting and building management firm headquartered in Atlanta, GA., with operations throughout North America and in Europe and Asia. *Acuity Advisors Limited, a technology corporate finance company with headquarters in London, UK *Acuity Insurance, an insurance company with headquarters in Sheboygan, Wisconsin *Acuity Solutions, a manufacturing consulting company with headquarters in Tigard, Oregon *Acuity (Health Care) Acuity may refer to: Biology and medicine *Visual acuity, the behavioral ability to resolve fine image detail *Tactile acuity, resolving fine spatial details with the sense of touch * Acute Catheterization and Urgent Intervention Triage Strategy ( ..., Level of Care (Full-Time / Quarter Time care per patient). To prioritize patient care based on the acuity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Examination Visual Acuity
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and convert it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). In higher organisms, the eye is a complex optical system which collects light from the surrounding environment, regulates its intensity through a diaphragm, focuses it through an adjustable assembly of lenses to form an image, converts this image into a set of electrical signals, and transmits these signals to the brain through complex neural pathways that connect the eye via the optic nerve to the visual cortex and other areas of the brain. Eyes with resolving power have come in ten fundamentally different forms, and 96% of animal species possess a complex optical system. Image-resolving eyes are present in molluscs, chordates and arthropods. The most simple eyes, pit eyes, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
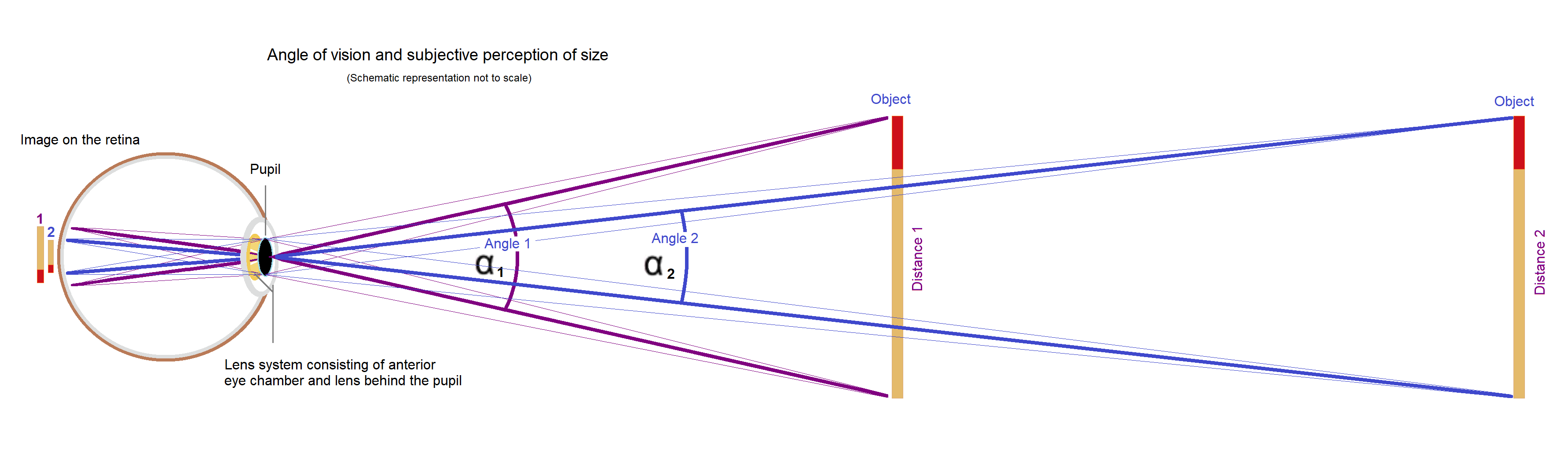
Visual Angle
Visual angle is the angle a viewed object subtends at the eye, usually stated in degrees of arc. It also is called the object's angular size. The diagram on the right shows an observer's eye looking at a frontal extent (the vertical arrow) that has a linear size S, located in the distance D from point O. For present purposes, point O can represent the eye's nodal points at about the center of the lens, and also represent the center of the eye's entrance pupil that is only a few millimeters in front of the lens. The three lines from object endpoint A heading toward the eye indicate the bundle of light rays that pass through the cornea, pupil and lens to form an optical image of endpoint A on the retina at point a. The central line of the bundle represents the chief ray. The same holds for object point B and its retinal image at b. The visual angle V is the angle between the chief rays of A and B. Measuring and computing The visual angle V can be measured directly using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Function
In mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle. Just as the points form a circle with a unit radius, the points form the right half of the unit hyperbola. Also, similarly to how the derivatives of and are and respectively, the derivatives of and are and respectively. Hyperbolic functions occur in the calculations of angles and distances in hyperbolic geometry. They also occur in the solutions of many linear differential equations (such as the equation defining a catenary), cubic equations, and Laplace's equation in Cartesian coordinates. Laplace's equations are important in many areas of physics, including electromagnetic theory, heat transfer, fluid dynamics, and special relativity. The basic hyperbolic functions are: * hyperbolic sine "" (), * hyperbolic cosine "" (),''Collins Concise Dictionary'', p. 328 from which are derived: * hyperbolic tangent "" (), * hyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Vision
Peripheral vision, or ''indirect vision'', is vision as it occurs outside the point of fixation, i.e. away from the center of gaze or, when viewed at large angles, in (or out of) the "corner of one's eye". The vast majority of the area in the visual field is included in the notion of peripheral vision. "Far peripheral" vision refers to the area at the edges of the visual field, "mid-peripheral" vision refers to medium eccentricities, and "near-peripheral", sometimes referred to as "para-central" vision, exists adjacent to the center of gaze. Boundaries Inner boundaries The inner boundaries of peripheral vision can be defined in any of several ways depending on the context. In everyday language the term "peripheral vision" is often used to refer to what in technical usage would be called "far peripheral vision." This is vision outside of the range of stereoscopic vision. It can be conceived as bounded at the center by a circle 60° in radius or 120° in diameter, centered arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fovea Centralis
The fovea centralis is a small, central pit composed of closely packed cones in the eye. It is located in the center of the macula lutea of the retina. The fovea is responsible for sharp central vision (also called foveal vision), which is necessary in humans for activities for which visual detail is of primary importance, such as reading and driving. The fovea is surrounded by the ''parafovea'' belt and the ''perifovea'' outer region. The parafovea is the intermediate belt, where the ganglion cell layer is composed of more than five layers of cells, as well as the highest density of cones; the perifovea is the outermost region where the ganglion cell layer contains two to four layers of cells, and is where visual acuity is below the optimum. The perifovea contains an even more diminished density of cones, having 12 per 100 micrometres versus 50 per 100 micrometres in the most central fovea. That, in turn, is surrounded by a larger peripheral area, which delivers highly compres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traumatic Brain Injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity (ranging from mild traumatic brain injury TBI/concussionto severe traumatic brain injury), mechanism ( closed or penetrating head injury), or other features (e.g., occurring in a specific location or over a widespread area). Head injury is a broader category that may involve damage to other structures such as the scalp and skull. TBI can result in physical, cognitive, social, emotional and behavioral symptoms, and outcomes can range from complete recovery to permanent disability or death. Causes include falls, vehicle collisions and violence. Brain trauma occurs as a consequence of a sudden acceleration or deceleration within the cranium or by a complex combination of both movement and sudden impact. In addition to the damage caused at the moment of injury, a variety of events following the injury may result in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |