|
Non-metallic Inclusions
Non-metallic inclusions are chemical compounds and nonmetals that are present in steel and other alloys. They are the product of chemical reactions, physical effects, and contamination that occurs during the melting and pouring process. These inclusions are categorized by origin as either endogenous or exogenous. Endogenous inclusions, also known as indigenous, occur within the metal and are the result of chemical reactions. These products precipitate during cooling and are typically very small. Exogenous inclusions are caused by the entrapment of nonmetals. Their size varies greatly and their source can include slag, dross, Flux (metallurgy), flux residues, and pieces of the Casting (metalworking), mold. Sources of inclusions formation Non-metallic inclusions arise because of many physical-chemical effects that occur in molten and consolidated metal during production. Non-metallic inclusions that arise because of different Chemical reaction, reactions during metal production ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonmetal
In chemistry, a nonmetal is a chemical element that generally lacks a predominance of metallic properties; they range from colorless gases (like hydrogen) to shiny solids (like carbon, as graphite). The electrons in nonmetals behave differently from those in metals. With some exceptions, those in nonmetals are fixed in place, resulting in nonmetals usually being poor conductors of heat and electricity and brittle or crumbly when solid. The electrons in metals are generally free moving and this is why metals are good conductors and most are easily flattened into sheets and drawn into wires. Nonmetal atoms tend to attract electrons in chemical reactions and to form acidic compounds. Two nonmetals, hydrogen and helium, make up about 99% of ordinary matter in the observable universe by mass. Five nonmetallic elements, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and silicon, largely make up the Earth's crust, atmosphere, oceans and biosphere. Most nonmetals have biological, technological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
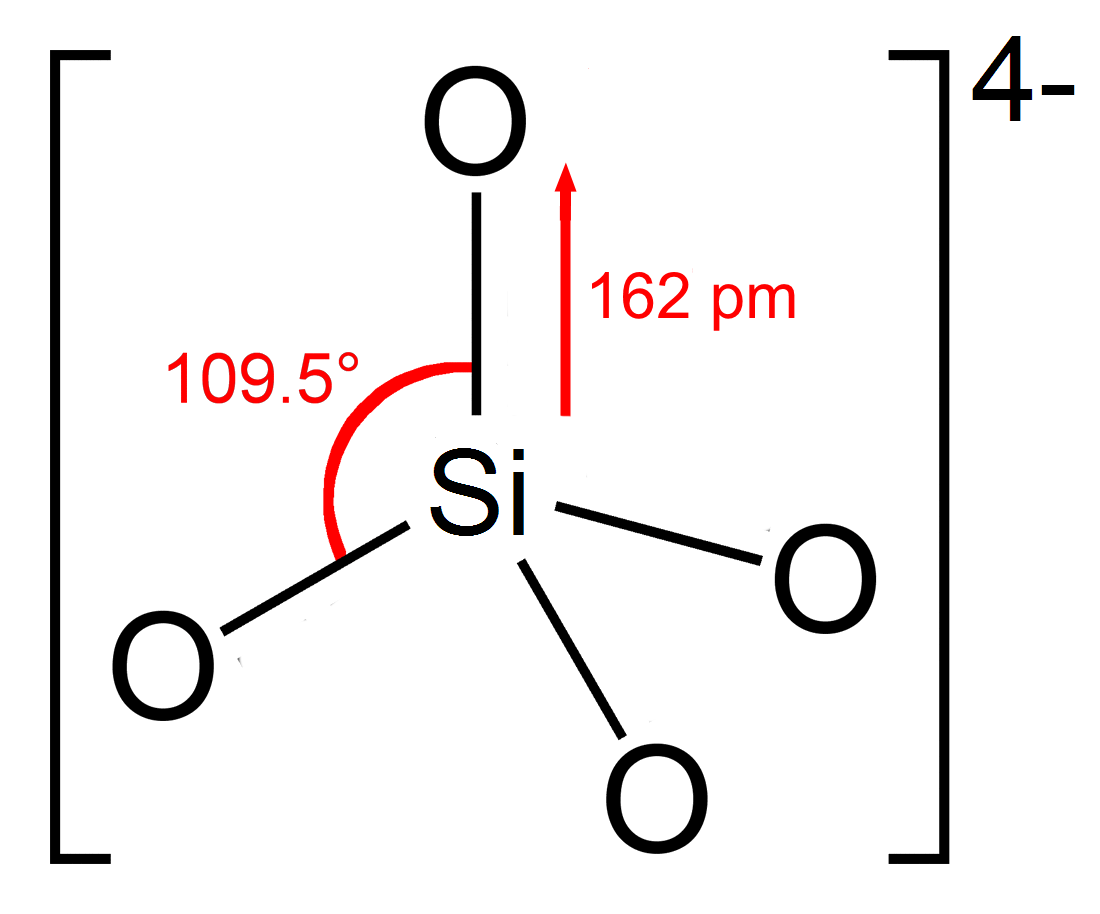
Silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate .Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In all silicates, silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedron whose corner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Alloy Inclusions
An inclusion is a solid particle in liquid aluminium alloy. It is usually non-metallic and can be of different nature depending on its source. Problems related to inclusions Inclusions can create problems in the casting when they are large and in too high concentration. Here are examples of problems related to inclusions: * Pinholes in light gauge foil * Flange cracks in beverage containers * Surface streaks in bright automotive trim and lithographic material * Breakage in wire drawing operation * Increased tool wear and tear * Increased porosity * Loss of pressure tightness of engine blocks * Poor machinability * Cosmetic defect in apparent surfaces * Diminished mechanical properties (e.g. Ultimate Tensile Strength, Yield Strength, Elongation) Inclusion types Oxide films In contact with ambient air, liquid aluminium reacts with the oxygen and form an oxide film layer (gamma-Al2O3). This layer becomes thicker with time. When molten aluminium is disturbed, this oxide film gets m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
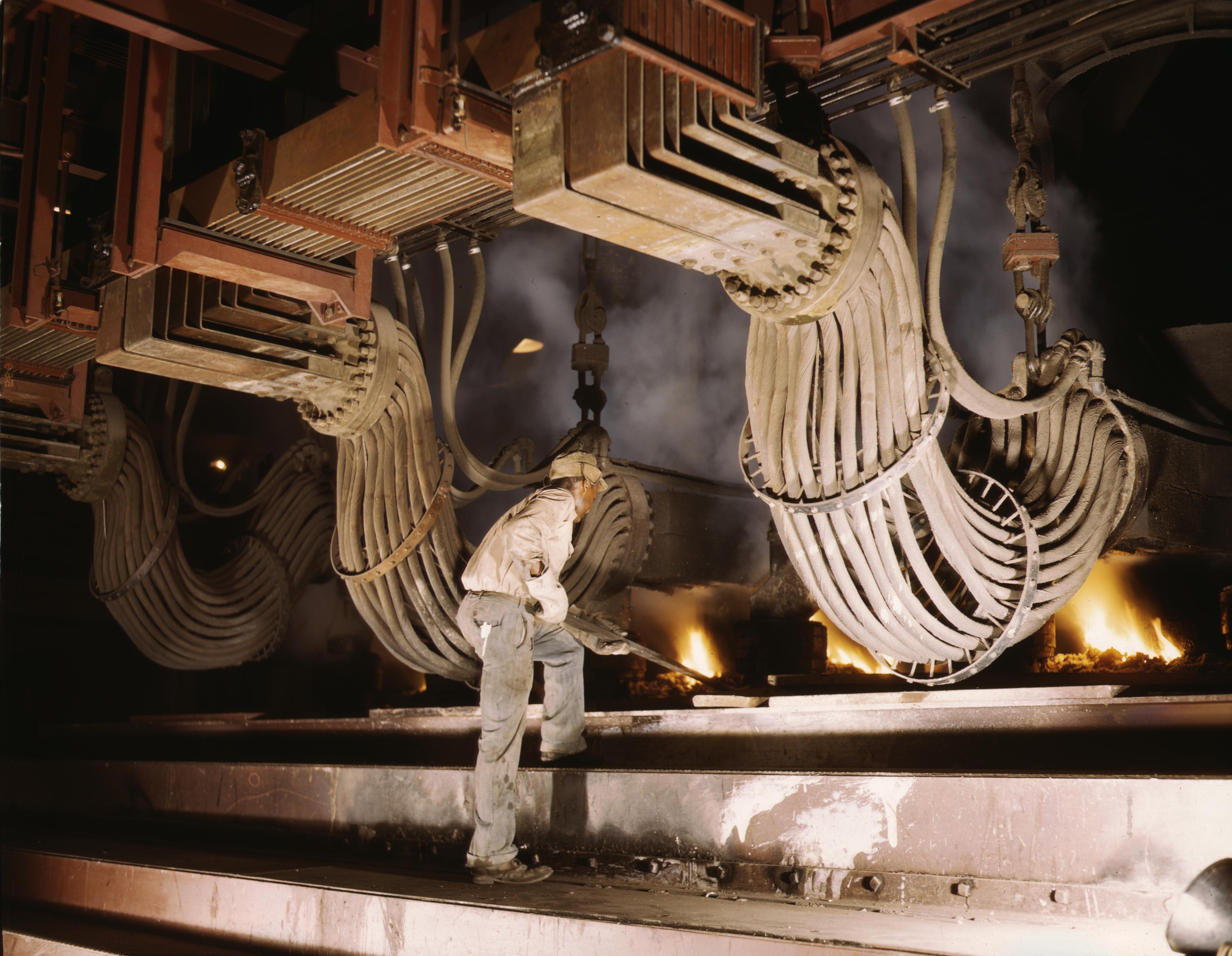
Smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore, to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals. Smelting uses heat and a chemical reducing agent to decompose the ore, driving off other elements as gases or slag and leaving the metal base behind. The reducing agent is commonly a fossil fuel source of carbon, such as coke—or, in earlier times, charcoal. The oxygen in the ore binds to carbon at high temperatures due to the lower potential energy of the bonds in carbon dioxide (). Smelting most prominently takes place in a blast furnace to produce pig iron, which is converted into steel. The carbon source acts as a chemical reactant to remove oxygen from the ore, yielding the purified metal element as a product. The carbon source is oxidized in two stages. First, the carbon (C) combusts with oxygen (O2) in the air to produce carbon monoxide (CO). Second, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue (material)
In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface. The crack will continue to grow until it reaches a critical size, which occurs when the stress intensity factor of the crack exceeds the fracture toughness of the material, producing rapid propagation and typically complete fracture of the structure. Fatigue has traditionally been associated with the failure of metal components which led to the term metal fatigue. In the nineteenth century, the sudden failing of metal railway axles was thought to be caused by the metal ''crystallising'' because of the brittle appearance of the fracture surface, but this has since been disproved. Most materials, such as composites, plastics and ceramics, seem to experience some sort of fatigue-related failure. To aid in predicting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamping (metalworking)
Stamping (also known as pressing) is the process of placing flat sheet metal in either blank or coil form into a stamping press where a tool and die surface forms the metal into a net shape. Stamping includes a variety of sheet-metal forming manufacturing processes, such as punching using a machine press or stamping press, blanking, embossing, bending, flanging, and coining. This could be a single stage operation where every stroke of the press produces the desired form on the sheet metal part, or could occur through a series of stages. The process is usually carried out on sheet metal, but can also be used on other materials, such as polystyrene. Progressive dies are commonly fed from a coil of steel, coil reel for unwinding of coil to a straightener to level the coil and then into a feeder which advances the material into the press and die at a predetermined feed length. Depending on part complexity, the number of stations in the die can be determined. Stamping is usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forge
A forge is a type of hearth used for heating metals, or the workplace (smithy) where such a hearth is located. The forge is used by the smith to heat a piece of metal to a temperature at which it becomes easier to shape by forging, or to the point at which work hardening no longer occurs. The metal (known as the "workpiece") is transported to and from the forge using tongs, which are also used to hold the workpiece on the smithy's anvil while the smith works it with a hammer. Sometimes, such as when hardening steel or cooling the work so that it may be handled with bare hands, the workpiece is transported to the slack tub, which rapidly cools the workpiece in a large body of water. However, depending on the metal type, it may require an oil quench or a salt brine instead; many metals require more than plain water hardening. The slack tub also provides water to control the fire in the forge. Types Coal/coke/charcoal forge A forge typically uses bituminous coal, indu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a ''transaction''. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction. In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ''ACID'', building on earlier work by Jim Gray who named atomicity, consistency, and durability, but not isolation, when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties are the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, the IBM Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of the molten form; some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring. The most familiar, and historically the oldest, types of manufactured glass are "silicate glasses" based on the chemical compound silica (silicon dioxide, or quartz), the primary constituent of sand. Soda–lime glass, containing around 70% silica, accounts for around 90% of manufactured glass. The term ''glass'', in popular usage, is often used to refer only to this type of material, although silica-free glasses often have desirable properties for applications in modern communications technology. Some objects, such as drinking glasses and eyeglasses, are so commonly made of silicate-based glass that they are simply called by the name of the material. Despite bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinel
Spinel () is the magnesium/aluminium member of the larger spinel group of minerals. It has the formula in the cubic crystal system. Its name comes from the Latin word , which means ''spine'' in reference to its pointed crystals. Properties Spinel crystallizes in the isometric system; common crystal forms are octahedra, usually twinned. It has no true cleavage, but shows an octahedral parting and a conchoidal fracture. Its hardness is 8, its specific gravity is 3.5–4.1, and it is transparent to opaque with a vitreous to dull luster. It may be colorless, but is usually various shades of red, lavender, blue, green, brown, black, or yellow. Some spinels are among the most famous gemstones; among them are the Black Prince's Ruby and the "Timur ruby" in the British Crown Jewels, and the "Côte de Bretagne", formerly from the French Crown jewels. The Samarian Spinel is the largest known spinel in the world, weighing . The transparent red spinels were called spinel-rubies or b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide () typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium and chromium. It is a rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the presence of transition metal impurities in its crystalline structure. Corundum has two primary gem varieties: ruby and sapphire. Rubies are red due to the presence of chromium, and sapphires exhibit a range of colors depending on what transition metal is present. A rare type of sapphire, padparadscha sapphire, is pink-orange. The name "corundum" is derived from the Tamil- Dravidian word ''kurundam'' (ruby-sapphire) (appearing in Sanskrit as ''kuruvinda''). Because of corundum's hardness (pure corundum is defined to have 9.0 on the Mohs scale), it can scratch almost all other minerals. It is commonly used as an abrasive on sandpaper and on large tools used in machining metals, plastics, and wood. Emery, a variety of corundum with no value a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of jewelry and hardstone carvings, especially in Eurasia. Quartz is the mineral defining the val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |