|
Non-bonding Orbital
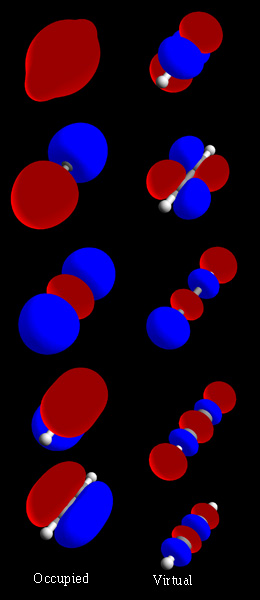
A non-bonding orbital, also known as ''non-bonding molecular orbital'' (NBMO), is a molecular orbital whose occupation by electrons neither increases nor decreases the bond order between the involved atoms. Non-bonding orbitals are often designated by the letter n in molecular orbital diagrams and Molecular electronic transition, electron transition notations. Non-bonding orbitals are the equivalent in molecular orbital theory of the lone pairs in Lewis structures. The energy level of a non-bonding orbital is typically in between the lower energy of a valence shell bonding orbital and the higher energy of a corresponding antibonding orbital. As such, a non-bonding orbital with electrons would commonly be a HOMO (highest occupied molecular orbital). According to molecular orbital theory, molecular orbitals are often modeled by the linear combination of atomic orbitals. In a simple diatomic molecule such as hydrogen fluoride (chemical formula: HF), one atom may have many more elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Orbital
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms ''atomic orbital'' and ''molecular orbital'' were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean ''one-electron orbital wave functions''. At an elementary level, they are used to describe the ''region'' of space in which a function has a significant amplitude. In an isolated atom, the orbital electrons' location is determined by functions called atomic orbitals. When multiple atoms combine chemically into a molecule, the electrons' locations are determined by the molecule as a whole, so the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The electrons from the constituent atoms occupy the molecular orbitals. Mathematically, molecular orbitals are an approximate solution to the Schrödin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |