|
Nokia 8
The Nokia 8 is a flagship Nokia-branded smartphone running the Android operating system. Announced on 16 August 2017 in London, England by HMD Global, the phone began sales in Europe in September 2017. Nokia 8 is the first high-end Nokia-branded device since the Nokia Lumia 930 in 2014. An improved version, the Nokia 8 Sirocco, was announced on 25 February 2018 at the Mobile World Congress in Barcelona. Specifications Design The Nokia 8 has a 5.3-inch display and averages 7.3 mm thick and 4.3 mm thick at the edges. It is available in four colors: Polished Blue, Polished Copper, Tempered Blue, and Steel. The device features a full-length graphite-shielded copper cooling pipe for efficient cooling. The phone is not water-resistant, but is IP54 splash-resistant. Hardware The Nokia 8 comes with the Qualcomm Snapdragon 835 CPU, backed by either 4 or 6 GB of RAM and 64 GB of internal storage (Tempered Blue, Steel, and Polished Copper-coloured models), or 6 GB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nokia
Nokia Corporation (natively Nokia Oyj, referred to as Nokia) is a Finnish multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications industry, telecommunications, technology company, information technology, and consumer electronics corporation, established in 1865. Nokia's main headquarters are in Espoo, Finland, in the greater Helsinki Greater Helsinki, metropolitan area, but the company's actual roots are in the Tampere region of Pirkanmaa.HS: Nokian juuret ovat Tammerkosken rannalla (in Finnish) In 2020, Nokia employed approximately 92,000 people across over 100 countries, did business in more than 130 countries, and reported annual revenues of around €23 billion. Nokia is a public limited company listed on the Helsinki Stock Exchange and New York Stock Exchange. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qualcomm Snapdragon
Snapdragon is a suite of system on a chip (SoC) semiconductor products for mobile devices designed and marketed by Qualcomm Technologies Inc. The Snapdragon's central processing unit (CPU) uses the ARM architecture. A single SoC may include multiple CPU cores, an Adreno graphics processing unit (GPU), a Snapdragon wireless modem, a Hexagon digital signal processor (DSP), a Qualcomm Spectra image signal processor (ISP) and other software and hardware to support a smartphone's global positioning system (GPS), camera, video, audio, gesture recognition and AI acceleration. As such, Qualcomm often refers to the Snapdragon as a "mobile platform" (e.g. Snapdragon 865 5G Mobile Platform). Snapdragon semiconductors are embedded in devices of various systems, including Android, Windows Phone and netbooks. They are also used in cars, wearable devices and other devices. In addition to the processors, the Snapdragon line includes modems, Wi-Fi chips and mobile charging products. The Sna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megapixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device. In most digital display devices, pixels are the smallest element that can be manipulated through software. Each pixel is a sample of an original image; more samples typically provide more accurate representations of the original. The intensity of each pixel is variable. In color imaging systems, a color is typically represented by three or four component intensities such as red, green, and blue, or cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. In some contexts (such as descriptions of camera sensors), ''pixel'' refers to a single scalar element of a multi-component representation (called a ''photosite'' in the camera sensor context, although ''sensel'' is sometimes used), while in yet other contexts (like MRI) it may refer to a set of component intensities for a spatial position. Etymology The w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorilla Glass 5
Gorilla Glass is a brand of chemically strengthened glass developed and manufactured by Corning, now in its seventh generation. Designed to be thin, light and damage-resistant, the glass gains its surface strength, ability to contain flaws, and crack-resistance by being immersed in a hot, potassium-salt, ion-exchange bath. As a brand, Gorilla Glass is specific to Corning, but close equivalents exist, including AGC Inc.'s Dragontrail and Schott AG's Xensation. The alkali-aluminosilicate sheet glass is used primarily as cover glass for portable electronic devices, including mobile phones, smartwatches, portable media players, portable computer displays, and television screens. It is manufactured in Harrodsburg, Kentucky; in Asan, South Korea; and in Taiwan. In October 2017, some five billion devices globally contained Gorilla Glass. While dominating its market, Gorilla Glass faces varying competition from rivals such as Dragontrail and synthetic sapphire. Background and develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1440p
1440p is a family of video display resolutions that have a vertical resolution of 1440 pixels. The ''p'' stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The 1440 pixel vertical resolution is double the vertical resolution of 720p, and one-third (about 33.3%) more than 1080p. QHD (Quad HD) or WQHD (Wide Quad HD) is the designation for a commonly used display resolution of pixels in a 16:9 aspect ratio. As a graphics display resolution between 1080p and 4K, Quad HD is regularly used in smartphone displays, and for computer and console gaming. Support 1440p video mastered from 4:3 ratio content can be displayed with 1920×1440 or higher resolution such as QXGA or 2304×1440 with scaling, windowboxing, or pillarboxing. Widescreen 16:9 aspect ratio 1440p requires 2560×1440 ( WQHD) resolution, possible with WQXGA, 2560×1920, or higher resolution with letterboxing, scaling, or windowboxing. The HDMI 1.3 specification supports WQXGA, and hence widescreen 1440p. Usage Early u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barometer
A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Many measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis to help find surface troughs, pressure systems and frontal boundaries. Barometers and pressure altimeters (the most basic and common type of altimeter) are essentially the same instrument, but used for different purposes. An altimeter is intended to be used at different levels matching the corresponding atmospheric pressure to the altitude, while a barometer is kept at the same level and measures subtle pressure changes caused by weather and elements of weather. The average atmospheric pressure on the earth's surface varies between 940 and 1040 hPa (mbar). The average atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1013 hPa (mbar). Etymology The word ''barometer'' is derived from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "weight", and (), meaning "measure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hall Sensor
In architecture, a hall is a relatively large space enclosed by a roof and walls. In the Iron Age and early Middle Ages in northern Europe, a mead hall was where a lord and his retainers ate and also slept. Later in the Middle Ages, the great hall was the largest room in castles and large houses, and where the servants usually slept. As more complex house plans developed, the hall remained a large room for dancing and large feasts, often still with servants sleeping there. It was usually immediately inside the main door. In modern British houses, an entrance hall next to the front door remains an indispensable feature, even if it is essentially merely a corridor. Today, the (entrance) hall of a house is the space next to the front door or vestibule leading to the rooms directly and/or indirectly. Where the hall inside the front door of a house is elongated, it may be called a passage, corridor (from Spanish ''corredor'' used in El Escorial and 100 years later in Castle How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, one that measures the direction of an ambient magnetic field, in this case, the Earth's magnetic field. Other magnetometers measure the magnetic dipole moment of a magnetic material such as a ferromagnet, for example by recording the effect of this magnetic dipole on the induced current in a coil. The first magnetometer capable of measuring the absolute magnetic intensity at a point in space was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall effect, which is still widely used. Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field, in geophysical surveys, to detect magnetic anomalies of various types, and to determine the dipole moment of magnetic materials. In an air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proximity Sensor
A proximity sensor is a sensor able to detect the presence of nearby objects without any physical contact. A proximity sensor often emits an electromagnetic field or a beam of electromagnetic radiation (infrared, for instance), and looks for changes in the field or return signal. The object being sensed is often referred to as the proximity sensor's target. Different proximity sensor targets demand different sensors. For example, a capacitive proximity sensor or photoelectric sensor might be suitable for a plastic target; an inductive proximity sensor always requires a metal target. Proximity sensors can have a high reliability and long functional life because of the absence of mechanical parts and lack of physical contact between the sensor and the sensed object. Proximity sensors are also used in machine vibration monitoring to measure the variation in distance between a shaft and its support bearing. This is common in large steam turbines, compressors, and motors that u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rotation (spin axis) is free to assume any orientation by itself. When rotating, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotation of the mounting, according to the conservation of angular momentum. Gyroscopes based on other operating principles also exist, such as the microchip-packaged MEMS gyroscopes found in electronic devices (sometimes called gyrometers), solid-state ring lasers, fibre optic gyroscopes, and the extremely sensitive quantum gyroscope. Applications of gyroscopes include inertial navigation systems, such as in the Hubble Space Telescope, or inside the steel hull of a submerged submarine. Due to their precision, gyroscopes are also used in gyrotheodolites to maintain direction in tunnel mining. Gyroscopes ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
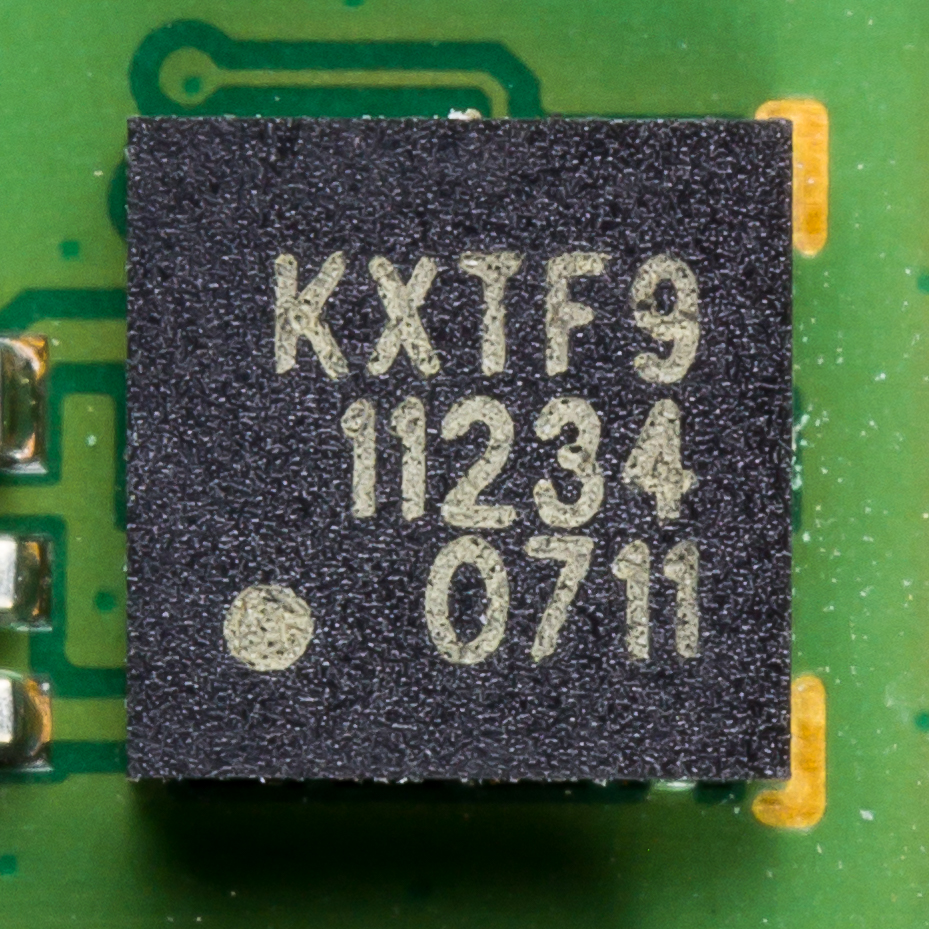
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise flight. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fingerprint Recognition
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfaces such as glass or metal. Deliberate impressions of entire fingerprints can be obtained by ink or other substances transferred from the peaks of friction ridges on the skin to a smooth surface such as paper. Fingerprint records normally contain impressions from the pad on the last joint of fingers and thumbs, though fingerprint cards also typically record portions of lower joint areas of the fingers. Human fingerprints are detailed, nearly unique, difficult to alter, and durable over the life of an individual, making them suitable as long-term markers of human identity. They may be employed by police or other authorities to identify individuals who wish to conceal their identity, or to identify people who are incapacitated or deceased and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)