|
Noel Wild
Colonel Harry Noel Havelock Wild OBE (born 10 November 1903;''Daily Telegraph'' obituary, page 23, 14 June 1995 usually referred to as Noel Wild) was a British Army officer during the Second World War. He is notable for being second in command of the deception organisation 'A' Force and well as head of Ops. B (the department responsible for part of the Operation Bodyguard planning). He was educated at Eton College.''Daily Telegraph'' obituary as above Wild joined the Territorial Army in 1924 and obtained a transfer, via the influence of his uncle at the War Office, to the 11th Hussars the following year. He served with the 11th in England and Egypt (from 1933) before being posted home - first for training and then to teach at Bovington camp. Wild spent some time trying to return to his regiment, but was unsuccessful. Upon his eventual return to Egypt (where the 11th Hussars were still based) he was posted as a staff officer at GHQ Middle East Command. Whilst in Cairo, dishearte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkhas, and 28,330 volunteer reserve personnel. The modern British Army traces back to 1707, with antecedents in the English Army and Scots Army that were created during the Restoration in 1660. The term ''British Army'' was adopted in 1707 after the Acts of Union between England and Scotland. Members of the British Army swear allegiance to the monarch as their commander-in-chief, but the Bill of Rights of 1689 and Claim of Right Act 1689 require parliamentary consent for the Crown to maintain a peacetime standing army. Therefore, Parliament approves the army by passing an Armed Forces Act at least once every five years. The army is administered by the Ministry of Defence and commanded by the Chief of the General Staff. The Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffs (Royal East Kent Regiment)
The Buffs (Royal East Kent Regiment), formerly the 3rd Regiment of Foot, was a line infantry regiment of the British Army traditionally raised in the English county of Kent and garrisoned at Canterbury. It had a history dating back to 1572 and was one of the oldest regiments in the British Army, being third in order of precedence (ranked as the 3rd Regiment of the line). The regiment provided distinguished service over a period of almost four hundred years accumulating one hundred and sixteen battle honours. In 1881, under the Childers Reforms, it was known as the Buffs (East Kent Regiment) and later, on 3 June 1935, was renamed the Buffs (Royal East Kent Regiment). In 1961, it was amalgamated with the Queen's Own Royal West Kent Regiment to form the Queen's Own Buffs, The Royal Kent Regiment, which was later merged, on 31 December 1966, with the Queen's Royal Surrey Regiment, the Royal Sussex Regiment and the Middlesex Regiment (Duke of Cambridge's Own) to form the Queen's Reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twenty Committee
The Double-Cross System or XX System was a World War II counter-espionage and deception operation of the British Security Service (a civilian organisation usually referred to by its cover title MI5). Nazi agents in Britain – real and false – were captured, turned themselves in or simply announced themselves, and were then used by the British to broadcast mainly disinformation to their Nazi controllers. Its operations were overseen by the Twenty Committee under the chairmanship of John Cecil Masterman; the name of the committee comes from the number 20 in Roman numerals: "XX" (i.e. a double cross). The policy of MI5 during the war was initially to use the system for counter-espionage. It was only later that its potential for deception purposes was realised. Of the agents from the German intelligence services, ''Abwehr'' and ''Sicherheitsdienst'' (SD), some were apprehended, while many of the agents who reached British shores turned themselves in to the authorities; others were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Controlling Section
The London Controlling Section (LCS) was a British secret department established in September 1941, under Oliver Stanley, with a mandate to coordinate Allied strategic military deception during World War II. The LCS was formed within the Joint Planning Staff at the offices of the War Cabinet, which was presided over by Winston Churchill as Prime Minister. At first the department struggled to have any impact, and Stanley spent time away from the office due to his wife's terminal illness. In June his post of Controlling Officer was handed over to Colonel John Bevan, who managed the LCS until the end of the war. The organisation was publicly revealed by Sir Ronald Wingate in 1969. Early deception Following the onset of the Second World War, the Allied nations began to recognise deception as a useful strategy. In early 1941 Lieutenant-Colonel Dudley Clarke's 'A' Force department, based in Cairo, undertook deception operations for the North African campaign. As their work came to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bevan (British Army Officer)
Colonel (United Kingdom), Colonel John Henry "Johnny" Bevan (5 April 1894 – 3 December 1978) was a British Army officer who, during the Second World War, made an important contribution to military deception, culminating in Operation Bodyguard, the plan to conceal the D-Day landings in Normandy. In civilian life he was a respected stockbroker in his father's firm. Bevan had an upper-class upbringing, including an education at Eton College, Eton and University of Oxford, Oxford. During the First World War he fought with the Hertfordshire Regiment in France and later became involved with intelligence analysis. His latter work came to the attention of wartime leaders, including Winston Churchill. Bevan stayed in the army for a while following the end of the war, and then took up a career in stock brokerage. He joined his father's firm, got married, and built up his profile as an honest businessman. At the outbreak of the Second World War, Bevan was recalled to his Territorial Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force
Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force (SHAEF; ) was the headquarters of the Commander of Allied forces in north west Europe, from late 1943 until the end of World War II. U.S. General Dwight D. Eisenhower was the commander in SHAEF throughout its existence. The position itself shares a common lineage with Supreme Allied Commander Europe and Atlantic, but they are different titles. History during the Second World War Eisenhower transferred from command of the Mediterranean Theater of Operations to command SHAEF, which was formed in Camp Griffiss, Bushy Park, Teddington, London, from December 1943; an adjacent street named Shaef Way, and a gate into the park called Shaef Gate, remain to this day. Southwick House was used as an alternative headquarters near Portsmouth. Its staff took the outline plan for Operation Overlord created by Lieutenant General Sir Frederick E. Morgan, Chief of Staff to the Supreme Allied Commander (Designate) (COSSAC), and Major General Ray Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of El Alamein
The Second Battle of El Alamein (23 October – 11 November 1942) was a battle of the Second World War that took place near the Egyptian Railway station, railway halt of El Alamein. The First Battle of El Alamein and the Battle of Alam el Halfa had prevented the Axis powers, Axis from advancing further into Egypt. In August 1942, General (United Kingdom), General Claude Auchinleck had been relieved as Commander-in-Chief Middle East Command and his successor, Lieutenant-General William Gott was killed on his way to replace him as commander of the Eighth Army (United Kingdom), Eighth Army. Lieutenant-general (United Kingdom), Lieutenant-General Bernard Montgomery was appointed and led the Eighth Army offensive. The British victory was the beginning of the end of the Western Desert Campaign, eliminating the Axis threat to Egypt, the Suez Canal and the Middle Eastern and Persian oil fields. The battle revived the morale of the Allies, being the first big success against the Axis sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Treatment
Operation or Operations may refer to: Arts, entertainment and media * ''Operation'' (game), a battery-operated board game that challenges dexterity * Operation (music), a term used in musical set theory * ''Operations'' (magazine), Multi-Man Publishing's house organ for articles and discussion about its wargaming products * ''The Operation'' (film), a 1973 British television film * ''The Operation'' (1990), a crime, drama, TV movie starring Joe Penny, Lisa Hartman, and Jason Beghe * ''The Operation'' (1992–1998), a reality television series from TLC * The Operation M.D., formerly The Operation, a Canadian garage rock band * "Operation", a song by Relient K from ''The Creepy EP'', 2001 Business * Business operations, the harvesting of value from assets owned by a business * Manufacturing operations, operation of a facility * Operations management, an area of management concerned with designing and controlling the process of production Military and law enforcement * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
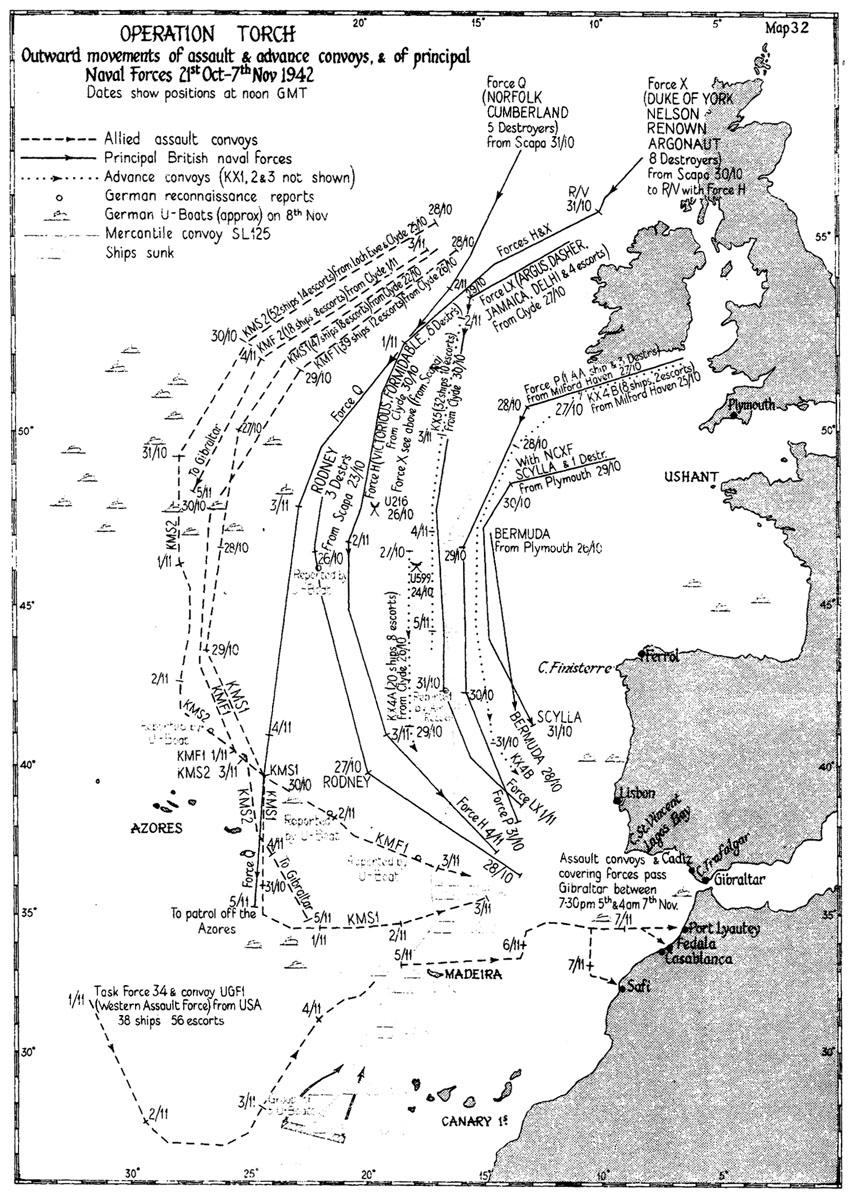
Operation Torch
Operation Torch (8 November 1942 – Run for Tunis, 16 November 1942) was an Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of securing victory in North Africa while allowing American armed forces the opportunity to engage in the fight against Nazi Germany on a limited scale. It was the first mass involvement of US troops in the Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II, European–North African Theatre, and saw the first major airborne assault carried out by the United States. While the French colonies were formally aligned with Germany via Vichy France, the loyalties of the population were mixed. Reports indicated that they might support the Allies. American General Dwight D. Eisenhower, supreme commander of the Allied forces in Mediterranean Theater of Operations, planned a three-pronged attack on Casablanca (Western), Oran (Center) and Algiers (Easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East Command
Middle East Command, later Middle East Land Forces, was a British Army Command established prior to the Second World War in Egypt. Its primary role was to command British land forces and co-ordinate with the relevant naval and air commands to defend British interests in the Middle East and eastern Mediterranean region. During the Second World War, Middle East Command supervised military operations in and around the Mediterranean basin and the Middle East. Following the defeat of the Axis forces in the Western Desert at the Battle of El Alamein and the landing of additional Anglo-American forces during Operation Torch, it transferred control of land forces to the newly created Allied Forces Headquarters. Role of Middle East Command Middle East Command was established in Cairo,Playfair, p. 459 during June 1939, due to the rising tensions in Europe.Playfair, p. 32 Its purpose was to provide a centralised command structure in times of war for the three separate army commands bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staff College, Camberley
Staff College, Camberley, Surrey, was a staff college for the British Army and the presidency armies of British India (later merged to form the Indian Army). It had its origins in the Royal Military College, High Wycombe, founded in 1799, which in 1802 became the Senior Department of the new Royal Military College. In 1858 the name of the Senior Department was changed to "Staff College", and in 1870 this was separated from the Royal Military College. Apart from periods of closure during major wars, the Staff College continued to operate until 1997, when it was merged into the new Joint Services Command and Staff College. The equivalent in the Royal Navy was the Royal Naval Staff College, Greenwich, and the equivalent in the Royal Air Force was the RAF Staff College, Bracknell. Origins In 1799, Colonel John Le Marchant submitted a proposal to the Duke of York, the Commander-in-Chief of the Forces, for a Royal Military College. A private officer training school, based on the id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovington Camp
Bovington Camp () is a British Army military base in Dorset, England. Together with Lulworth Camp it forms part of Bovington Garrison. The garrison is home to The Armour Centre and contains two barracks complexes and two forest and heathland training areas that support Phase Two training for soldiers of the Royal Armoured Corps and trade training for the Household Cavalry Regiment as well as other armoured units. It also houses The Tank Museum on its property. It is run by the resident RSM W01 Joshua Wisdom History The camps at Bovington and Lulworth were originally established in 1899 as an infantry training area and ranges. In 1916, they became training camps for the Heavy Branch of the Machine Gun Corps which relocated from Norfolk. The Heavy Branch was responsible for the operation of the tank in the British Army. In 1917 the Heavy Branch split from the Machine Gun Corps to become the Tank Corps, with the Depot and Central Schools being based at Bovington. In 1937 the Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)