|
Nodularin
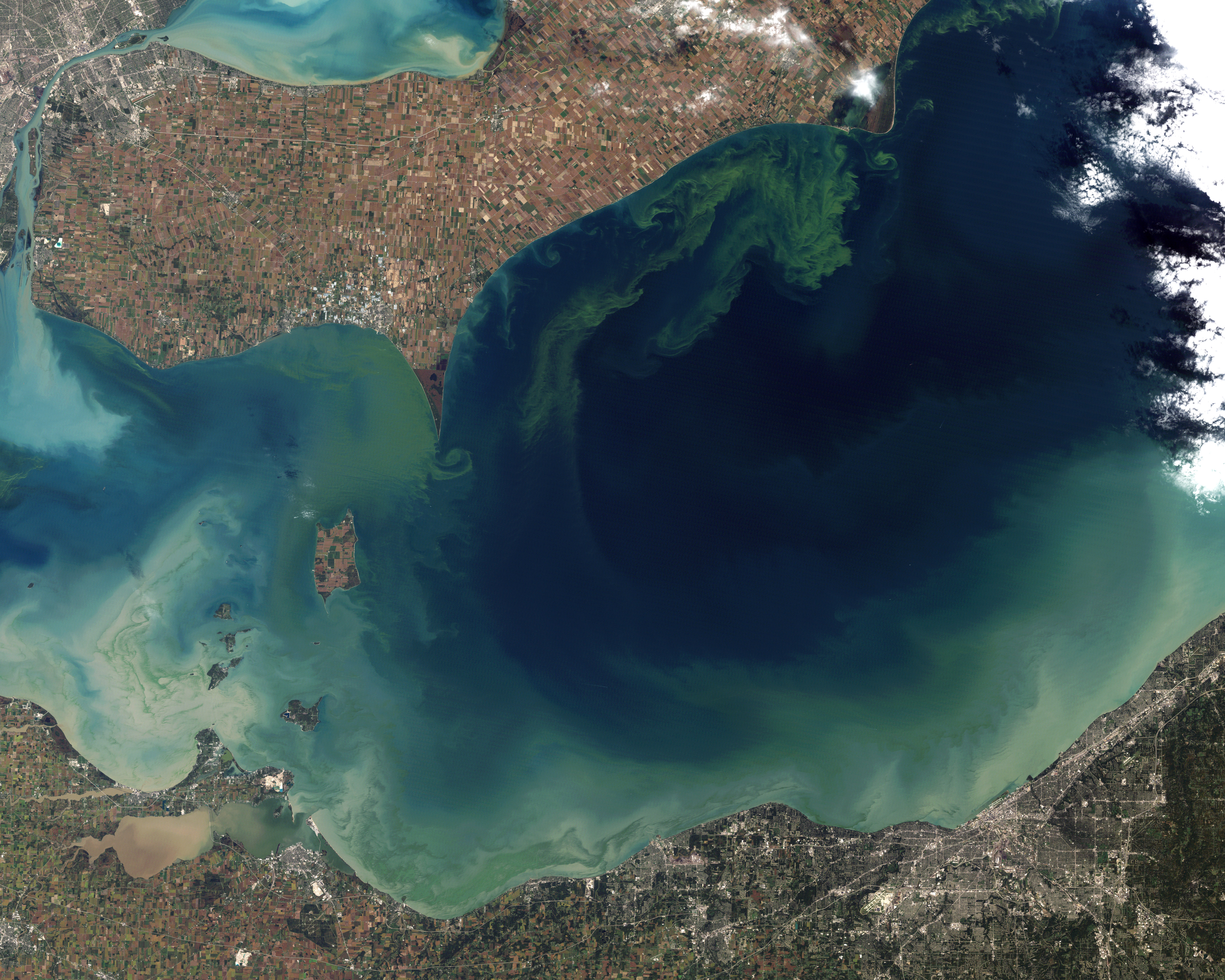
Nodularins are potent toxins produced by the cyanobacterium ''Nodularia spumigena'', among others. This aquatic, photosynthetic cyanobacterium forms visible colonies that present as algal blooms in brackish water bodies throughout the world. The late summer blooms of ''Nodularia spumigena'' are among the largest cyanobacterial mass occurrences in the world. Cyanobacteria are composed of many toxic substances, most notably of microcystins and nodularins: the two are not easily differentiated. A significant homology of structure and function exists between the two, and microcystins have been studied in greater detail. Because of this, facts from microcystins are often extended to nodularins. Nodularin-R is the predominant toxin variant, though 10 variants of nodularin have been discovered to date. Nodularins are cyclic nonribosomal pentapeptides and contain several unusual non-proteinogenic amino acids such as N-methyl-didehydroaminobutyric acid and the β-amino acid ADDA. These c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodularin Key Sites
Nodularins are potent toxins produced by the cyanobacterium ''Nodularia spumigena'', among others. This aquatic, photosynthetic cyanobacterium forms visible colonies that present as algal blooms in brackish water bodies throughout the world. The late summer blooms of ''Nodularia spumigena'' are among the largest cyanobacterial mass occurrences in the world. Cyanobacteria are composed of many toxic substances, most notably of microcystins and nodularins: the two are not easily differentiated. A significant homology of structure and function exists between the two, and microcystins have been studied in greater detail. Because of this, facts from microcystins are often extended to nodularins. Nodularin-R is the predominant toxin variant, though 10 variants of nodularin have been discovered to date. Nodularins are cyclic nonribosomal pentapeptides and contain several unusual non-proteinogenic amino acids such as N-methyl-didehydroaminobutyric acid and the β-amino acid ADDA (molecule), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanotoxins
Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae). Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they reproduce exponentially to form blooms. Blooming cyanobacteria can produce cyanotoxins in such concentrations that they poison and even kill animals and humans. Cyanotoxins can also accumulate in other animals such as fish and shellfish, and cause poisonings such as shellfish poisoning. Some of the most powerful natural poisons known are cyanotoxins. They include potent neurotoxins, hepatotoxins, cytotoxins, and endotoxins. Despite the similarity in name, they are unrelated to cyanides. Exposure to cyanobacteria can result in gastro-intestinal and hayfever symptoms or pruritic skin rashes. Exposure to the cyanobacteria neurotoxin BMAA may be an environmental cause of neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson's d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcystins
Microcystins—or cyanoginosins—are a class of toxins produced by certain freshwater cyanobacteria, commonly known as blue-green algae. Over 250 different microcystins have been discovered so far, of which microcystin-LR is the most common. Chemically they are cyclic heptapeptides produced through nonribosomal peptide synthases. Cyanobacteria can produce microcystins in large quantities during algal blooms which then pose a major threat to drinking and irrigation water supplies, and the environment at large. Characteristics Microcystins—or cyanoginosins—are a class of toxins produced by certain freshwater cyanobacteria; primarily ''Microcystis aeruginosa'' but also other ''Microcystis'', as well as members of the ''Planktothrix'', ''Anabaena'', ''Oscillatoria'' and ''Nostoc'' genera. Over 250 different microcystins have been discovered so far, of which microcystin-LR is the most common. Chemically they are cyclic heptapeptides produced through nonribosomal peptide synthas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcystin
Microcystins—or cyanoginosins—are a class of toxins produced by certain freshwater cyanobacteria, commonly known as blue-green algae. Over 250 different microcystins have been discovered so far, of which microcystin-LR is the most common. Chemically they are cyclic heptapeptides produced through nonribosomal peptide synthases. Cyanobacteria can produce microcystins in large quantities during algal blooms which then pose a major threat to drinking and irrigation water supplies, and the environment at large. Characteristics Microcystins—or cyanoginosins—are a class of toxins produced by certain freshwater cyanobacteria; primarily ''Microcystis aeruginosa'' but also other ''Microcystis'', as well as members of the ''Planktothrix'', ''Anabaena'', ''Oscillatoria'' and ''Nostoc'' genera. Over 250 different microcystins have been discovered so far, of which microcystin-LR is the most common. Chemically they are cyclic heptapeptides produced through nonribosomal peptide synthase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacterium
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blue-green algae, although they are not usually scientifically classified as algae. They appear to have originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Sericytochromatia, the proposed name of the paraphyletic and most basal group, is the ancestor of both the non-photosynthetic group Melainabacteria and the photosynthetic cyanobacteria, also called Oxyphotobacteria. Cyanobacteria use photosynthetic pigments, such as carotenoids, phycobilins, and various forms of chlorophyll, which absorb energy from light. Unlike heterotrophic prokaryotes, cyanobacteria have internal membranes. These are flattened sacs called thylakoids where photosynthesis is performed. Phototrophic eukaryotes such as green plants perform photosynthesis in plastids t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodularia Spumigena
''Nodularia'' is a genus of filamentous nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria, or blue-green algae. They occur mainly in brackish or salinic waters, such as the hypersaline Makgadikgadi Pans, the Peel-Harvey Estuary in Western Australia or the Baltic Sea. ''Nodularia'' cells occasionally form heavy algal blooms. Some strains produce a cyanotoxin called nodularin R, which is harmful to humans. The type species for the genus is '' Nodularia spumigena'' Mertens ex Bornet & Flahault, 1886. Morphology ''Nodularia'' may form solitary filaments or groups of filaments. They reproduce by the formation of hormogonia Hormogonia are motile filaments of cells formed by some cyanobacteria in the order Nostocales and Stigonematales. They are formed during vegetative reproduction in unicellular, filamentous cyanobacteria, and some may contain heterocysts and ..., filament breakage, and by akinetes .Martin Dworkin and Stanley Falkow, 2006 See also Kruger, T., Oelmuller, R., and Luckas, B. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADDA (molecule)
ADDA ((all-''S'',all-''E'')-3-amino-9-methoxy-2,6,8-trimethyl-10-phenyldeca-4,6-dienoic acid) is a non-proteinogenic amino acid found in toxins made by cyanobacteria. Toxins which include this amino acid include microcystins and nodularin Nodularins are potent toxins produced by the cyanobacterium ''Nodularia spumigena'', among others. This aquatic, photosynthetic cyanobacterium forms visible colonies that present as algal blooms in brackish water bodies throughout the world. The l ...s. References Non-proteinogenic amino acids {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma (Rb) is a rare form of cancer that rapidly develops from the immature cells of a retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. It is the most common primary malignant intraocular cancer in children, and it is almost exclusively found in young children. Though most children survive this cancer, they may lose their vision in the affected eye(s) or need to have the eye removed. Almost half of children with retinoblastoma have a hereditary genetic defect associated with retinoblastoma. In other cases, it is caused by a congenital mutation in the chromosome 13 gene 13q14 (retinoblastoma protein). Signs and symptoms Retinoblastoma is universally known as the most intrusive intraocular cancer among children. The chance of survival and preservation of the eye depends fully on the severity. Retinoblastoma is extremely rare as there are only about 200 to 300 cases every year in the United States. Looking at retinoblastoma globally, only 1 in about 15,000 children have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homologous TNF domain. As an adipokine, TNF promotes insulin resistance, and is associated with obesity-induced type 2 diabetes. As a cytokine, TNF is used by the immune system for cell signaling. If macrophages (certain white blood cells) detect an infection, they release TNF to alert other immune system cells as part of an inflammatory response. TNF signaling occurs through two receptors: TNFR1 and TNFR2. TNFR1 is constituitively expressed on most cell types, whereas TNFR2 is restricted primarily to endothelial, epithelial, and subsets of immune cells. TNFR1 signaling tends to be pro-inflammatory and apoptotic, whereas TNFR2 signaling is anti-inflammatory and promotes cell proliferation. Suppression of TNFR1 signaling has been important fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-jun
Transcription factor Jun is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''JUN'' gene. c-Jun, in combination with protein c-Fos, forms the AP-1 early response transcription factor. It was first identified as the Fos-binding protein p39 and only later rediscovered as the product of the JUN gene. c-jun was the first oncogenic transcription factor discovered. The proto-oncogene c-Jun is the cellular homolog of the viral oncoprotein v-jun (). The viral homolog v-jun was discovered in avian sarcoma virus 17 and was named for ''ju-nana'', the Japanese word for 17. The human JUN encodes a protein that is highly similar to the viral protein, which interacts directly with specific target DNA sequences to regulate gene expression. This gene is intronless and is mapped to 1p32-p31, a chromosomal region involved in both translocations and deletions in human malignancies. Function Regulation Both Jun and its dimerization partners in AP-1 formation are subject to regulation by diverse extr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nostoc
''Nostoc'', also known as star jelly, troll’s butter, spit of moon, fallen star, witch's butter (not to be confused with the fungi commonly known as witches' butter), and witch’s jelly, is the most common genus of cyanobacteria found in various environments that may form colonies composed of filaments of moniliform cells in a gelatinous sheath of polysaccharides. ''Nostoc'' is a genus of photosynthetic, Gram-negative cyanobacteria that can be found in both terrestrial and aquatic environments. It may also grow symbiotically within the tissues of plants, providing nitrogen to its host through the action of terminally differentiated cells known as heterocysts. ''Nostoc'' is a genus that includes many species that are diverse in morphology, habitat distribution, and ecological function. ''Nostoc'' can be found in soil, on moist rocks, at the bottom of lakes and springs, and rarely in marine habitats. It may also be found in terrestrial temperate, desert, tropical, or polar env ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-fos
Protein c-Fos is a proto-oncogene that is the human homolog of the retroviral oncogene v-fos. It is encoded in humans by the ''FOS'' gene. It was first discovered in rat fibroblasts as the transforming gene of the FBJ MSV (Finkel–Biskis–Jinkins murine osteogenic sarcoma virus) (Curran and Tech, 1982). It is a part of a bigger Fos family of transcription factors which includes c-Fos, FosB, Fra-1 and Fra-2. It has been mapped to chromosome region 14q21→q31. c-Fos encodes a 62 kDa protein, which forms heterodimer with c-jun (part of Jun family of transcription factors), resulting in the formation of AP-1 (Activator Protein-1) complex which binds DNA at AP-1 specific sites at the promoter and enhancer regions of target genes and converts extracellular signals into changes of gene expression. It plays an important role in many cellular functions and has been found to be overexpressed in a variety of cancers. Structure and function c-Fos is a 380 amino acid protein with a basic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Figure_2.jpg)
