|
No. 52 Wing RAF
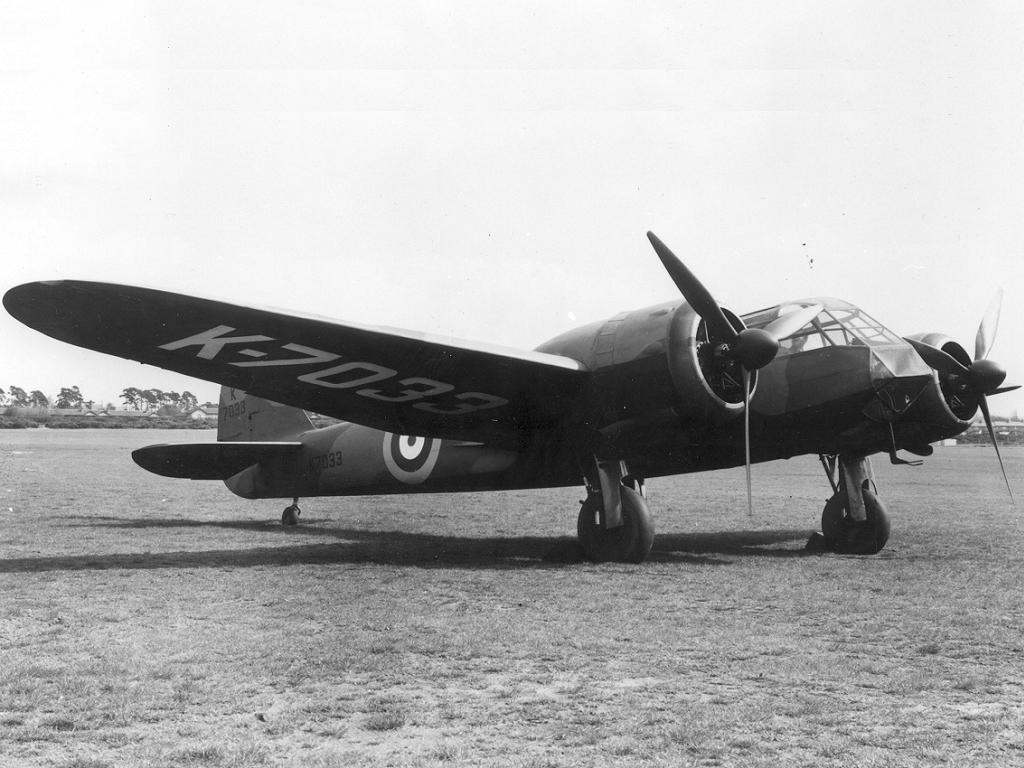
No. 52 Wing RAF was a wing of the Royal Air Force during the Second World War. 52 Wing composed No. 59 and 53 Squadrons in France from October 1939 until May 1940. They were stationed in Poix until returning to the UK. Both units flew the Bristol Blenheim Mk. IV bomber on reconnaissance sorties in the Air Component of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and later under BAFF (British Air Forces in France British Air Forces in France (BAFF) was a Royal Air Force (RAF) Command set up on 15 January 1940 under the command of Air Marshal Arthur Barratt, to provide unified command of the RAF in France. The Royal Air Force Component of the British E ...). See also * List of Wings of the Royal Air Force References No. 52 Military units and formations disestablished in the 1940s {{World-War-II-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensign Of The Royal Air Force
An ensign is the national flag flown on a vessel to indicate nationality. The ensign is the largest flag, generally flown at the stern (rear) of the ship while in port. The naval ensign (also known as war ensign), used on warships, may be different from the civil ensign (merchant ships) or the yacht ensign (recreational boats). Large versions of naval ensigns called battle ensigns are used when a warship goes into battle. The ensign differs from the jack (flag), jack, which is flown from a jackstaff at the bow of a vessel. In its widest sense, an ensign is just a flag or other standard. The European military rank of Ensign (rank), ensign, once responsible for bearing a unit's standard (whether national or regimental), derives from it (in the cavalry, the equivalent rank was Cornet (rank), cornet, named after a type of flag). Ensigns, such as the ancient Roman ensigns in the Arch of Constantine, are not always flags. National ensigns In nautical use, the ensign is flown on a shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS). Following the Allied victory over the Central Powers in 1918, the RAF emerged as the largest air force in the world at the time. Since its formation, the RAF has taken a significant role in British military history. In particular, it played a large part in the Second World War where it fought its most famous campaign, the Battle of Britain. The RAF's mission is to support the objectives of the British Ministry of Defence (MOD), which are to "provide the capabilities needed to ensure the security and defence of the United Kingdom and overseas territories, including against terrorism; to support the Government's foreign policy objectives particularly in promoting international peace and security". The R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
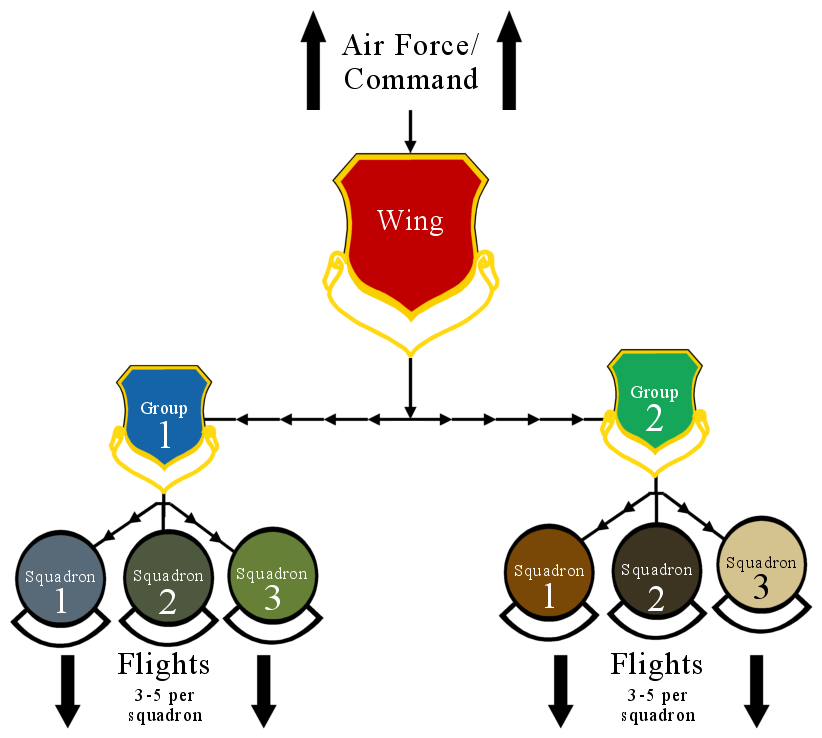
Wing (military Aviation Unit)
In military aviation, a wing is a unit of command. In most military aviation services, a wing is a relatively large formation of planes. In Commonwealth countries a wing usually comprises three squadrons, with several wings forming a group (around 10 squadrons). Each squadron will contain around 20 planes. Commonwealth usage Origins On its establishment in 1912, the British Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was intended to be an inter-service, combined force of the British Army and Royal Navy. Given the rivalry that existed between the army and navy, new terminology was used, in order to avoid marking the corps out as having an army or navy ethos. While the term "wing" had been used in the cavalry, its more general use predominated. Accordingly, the word "wing", with its allusion of flight, was chosen as the term of subdivision and the corps was split into a "Military Wing" (i.e. an army wing) and a "Naval Wing". Each wing consisted of a number of squadrons (the term "squadro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poix-de-Picardie
Poix-de-Picardie (, literally ''Poix of Picardy''; pcd, Poé-d’Picardie) is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. Geography The commune is situated at the junction of the N1 and N29 roads, some southwest of Amiens, at the bottom of a rather steep-sided valley, confined by Normandy to the south and Picardy to the north. The commune has rail access at the Poix-de-Picardie station, on the Rouen to Amiens line. Population Places of interest * The sixteenth century church of Saint-Denis’ priory. In flamboyant Gothic style, the base of the tower dates from the twelfth century. Before becoming the parish church, it was the chapel of the château. * Military cemetery. Containing the graves of 149 Second World War Commonwealth aircrew. Tyrrel family The Tyrrel, or Tirel, family were Lords of Poix from the twelfth to the fifteenth century. The most famous member of this family was Walter Tirel, who killed King William Rufus of England, son of Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Blenheim
The Bristol Blenheim is a British light bomber aircraft designed and built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company (Bristol) which was used extensively in the first two years of the Second World War, with examples still being used as trainers until the end of the war. Development began with the ''Type 142'', a civil airliner, in response to a challenge from Lord Rothermere to produce the fastest commercial aircraft in Europe. The ''Type 142'' first flew in April 1935, and the Air Ministry, impressed by its performance, ordered a modified design as the ''Type 142M'' for the Royal Air Force (RAF) as a bomber. Deliveries of the newly named Blenheim to RAF squadrons commenced on 10 March 1937. In service the Type 142M became the Blenheim Mk.I which would be developed into the longer Type 149, designated the Blenheim Mk.IV, except in Canada where Fairchild Canada built the Type 149 under licence as the Bolingbroke. The Type 160 Bisley was also developed from the Blenheim, but was already o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Expeditionary Force (World War II)
The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) was the name of the contingent of the British Army sent to France in 1939 after Britain and France declared war on Nazi Germany on 3 September, beginning the Second World War. The BEF existed from 2 September 1939 when the BEF GHQ was formed until 31 May 1940, when GHQ closed down and its troops reverted to the command of Home Forces. During the 1930s, the British government had planned to deter war by abolishing the Ten Year Rule and rearming from the very low level of readiness of the early 1930s. The bulk of the extra money went to the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force but plans were made to re-equip a small number of Army and Territorial Army divisions for service overseas. General Lord Gort was appointed to the command of the BEF on 3 September 1939 and the BEF began moving to France on 4 September 1939. The BEF assembled along the Belgian–French border. The BEF took their post to the left of the French First Army under the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Air Forces In France
British Air Forces in France (BAFF) was a Royal Air Force (RAF) Command set up on 15 January 1940 under the command of Air Marshal Arthur Barratt, to provide unified command of the RAF in France. The Royal Air Force Component of the British Expeditionary Force (Air Component, Air Vice-Marshal Charles Blount) for air support of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and the Advanced Air Striking Force (AASF, Air Vice-Marshal Patrick Playfair) for independent Bomber Command operations from French airfields. Barratt was charged with giving "full assurance" to the BEF of air support and to provide the BEF with Since the British held only a small part of the Western Front, Barratt must also operate in the context of the immediate needs of the Allies. In France the new arrangement worked well but the War Office and the Air Ministry never agreed on what support should be given to the Field Force of the BEF. The AASF consisted of RAF light bomber squadrons, based around Rheims i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wings Of The Royal Air Force In The Second World War
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is expressed as its lift-to-drag ratio. The lift a wing generates at a given speed and angle of attack can be one to two orders of magnitude greater than the total drag on the wing. A high lift-to-drag ratio requires a significantly smaller thrust to propel the wings through the air at sufficient lift. Lifting structures used in water include various foils, such as hydrofoils. Hydrodynamics is the governing science, rather than aerodynamics. Applications of underwater foils occur in hydroplanes, sailboats and submarines. Etymology and usage For many centuries, the word "wing", from the Old Norse ''vængr'', referred mainly to the foremost limb (anatomy), limbs of birds (in addition to the architectural aisle). But in recent centuries the word's m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |