|
Niwa Nagahide
, also known as Gorōzaemon (五郎左衛門), his other legal alias was Hashiba Echizen no Kami (羽柴越前守), was a Japanese samurai of the Sengoku through Azuchi-Momoyama periods of the 16th century. He served as senior retainer to the Oda clan, and was eventually a daimyō in his own right. Going on to fight in the Oda clan's major campaigns, including Mino Campaign 1567, Omi Campaign 1568, the Honganji Campaign from 1570 to 1580, and Iga Campaign 1581, he was named one of the administrators of Kyoto after Nobunaga entered that city in 1568. Early life Nagahide was born in what is now Nishi-ku, Nagoya, but then part of Aichi District, Owari Province. From his youth, Nagahide served Oda Nobunaga and became one of his senior retainers, He stayed by Nobunaga's side when his brother defied him during the Battle of Inō in 1555 and also Battle of Ukino 1558. Military life In 1560, Nagahide also had military service during the Battle of Okehazama, but he wasn't a part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niwa Clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan of northern Honshū that claimed descent from Emperor Kanmu via Prince Yoshimine no Yasuo (785-80) and Kodama Koreyuki (d.1069). Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d’histoire et de géographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003)"Niwa," ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 43 retrieved 2013-5-5. History The Kodama clan was one of several samurai clans originally located in Musashi Province. A branch of the clan settled in Owari Province, of which a branch resided in Niwa District. It is uncertain when they adopted the "Niwa" surname, but during the Muromachi period were in service of the Shiba clan, who were the '' DF 58 of 80/nowiki> retrieved 2013-05-03. History Th ..., who were the ''shugo'' of Owari Province. The clan rose to prominence in the Sengoku period">shugo">DF 58 of 80/nowiki> retrieved 2013-05-03. History Th ..., who were the ''shugo'' of Owari Province. The clan rose to prominence in the Sengoku period. Niwa Nagahide became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saimyō-ji (Kora)
, also known as or as is a Buddhist temple of the Tendai sect located in the town of Kōra, Shiga Prefecture, Japan. The ''honzon'' of the temple is Yakushi Nyōrai, the Buddha of healing. The temple was founded in the early Heian period and together with Kongōrin-ji in Aishō and Hyakusai-ji in Higashiōmi the temple forms a group of three temples known as . The complex includes several National Treasures and a garden designated as National Place of Scenic Beauty. History The foundations of Saimyō-ji are uncertain. According to the temple's legend, in the year 834, the monk Sanshū, while on a meditative walk along the western shore of Lake Biwa, saw purple clouds are a good omen in Mahayana Buddhist mythology in the eastern sky across the lake. A dazzling light suddenly appeared. The monk, interpreting this phenomenon as a sign of celestial power, crossed the lake and found a pond from which the light emitted. In response to his prayers, he had a vision of Nikkō ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Site Of Niwa Nagahide's Residence
Site most often refers to: * Archaeological site * Campsite, a place used for overnight stay in an outdoor area * Construction site * Location, a point or an area on the Earth's surface or elsewhere * Website, a set of related web pages, typically with a common domain name It may also refer to: * Site, a National Register of Historic Places property type * SITE (originally known as ''Sculpture in the Environment''), an American architecture and design firm * Site (mathematics), a category C together with a Grothendieck topology on C * ''The Site'', a 1990s TV series that aired on MSNBC * SITE Intelligence Group, a for-profit organization tracking jihadist and white supremacist organizations * SITE Institute, a terrorism-tracking organization, precursor to the SITE Intelligence Group * Sindh Industrial and Trading Estate, a company in Sindh, Pakistan * SITE Centers, American commercial real estate company * SITE Town, a densely populated town in Karachi, Pakistan * S.I.T.E Indust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iga Province
was a province of Japan located in what is today part of western Mie Prefecture. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Iga" in . Its abbreviated name was . Iga is classified as one of the provinces of the Tōkaidō. Under the '' Engishiki'' classification system, Iga was ranked as an "inferior country" ( ''gekoku'') and a "near country" ( ''kingoku''). Iga was bordered by Ise to the east and south, Ōmi to the north, Yamato to the west and south, and Yamashiro Province to the northwest. It roughly coincides with the modern municipalities of Iga and Nabari in Mie Prefecture. Surrounded by mountains, historically, Iga Province was rather inaccessible due to extremely poor road conditions. However, the area is now relatively easy to access from nearby Nara and Kyoto, as well as the larger cities of Osaka and Nagoya. History Asuka period Iga was separated from Ise Province during the Asuka period, around 680 AD. The provincial capital was located in what is now par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mino Province
was a province of Japan in the area of Japan that is today southern Gifu Prefecture. Mino was bordered by Ōmi to the west, Echizen and Hida to the north, and Shinano to the east, and Ise, Mikawa, and Owari to the south. Its abbreviated form name was . Under the ''Engishiki'' classification system, Mino was ranked as one of the 13 "great countries" (大国) in terms of importance, and one of the "near countries" (近国) in terms of distance from the capital. The provincial capital and '' ichinomiya'' were located in what is now the town of Tarui. Historical record "Mino" is an ancient place name, and appears in '' mokkan'' wooden tags from the ruins of Asuka-kyō, Fujiwara-kyō, and other ancient sites, but using the ''kanji'' "三野国". Per the '' Kujiki'', there were originally three separate countries in Mino, centered around what is now Ōgaki, Ōno, and Kakamigahara. Each had its own '' Kuni no miyatsuko'', and together with Motosu (in eastern Gifu) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
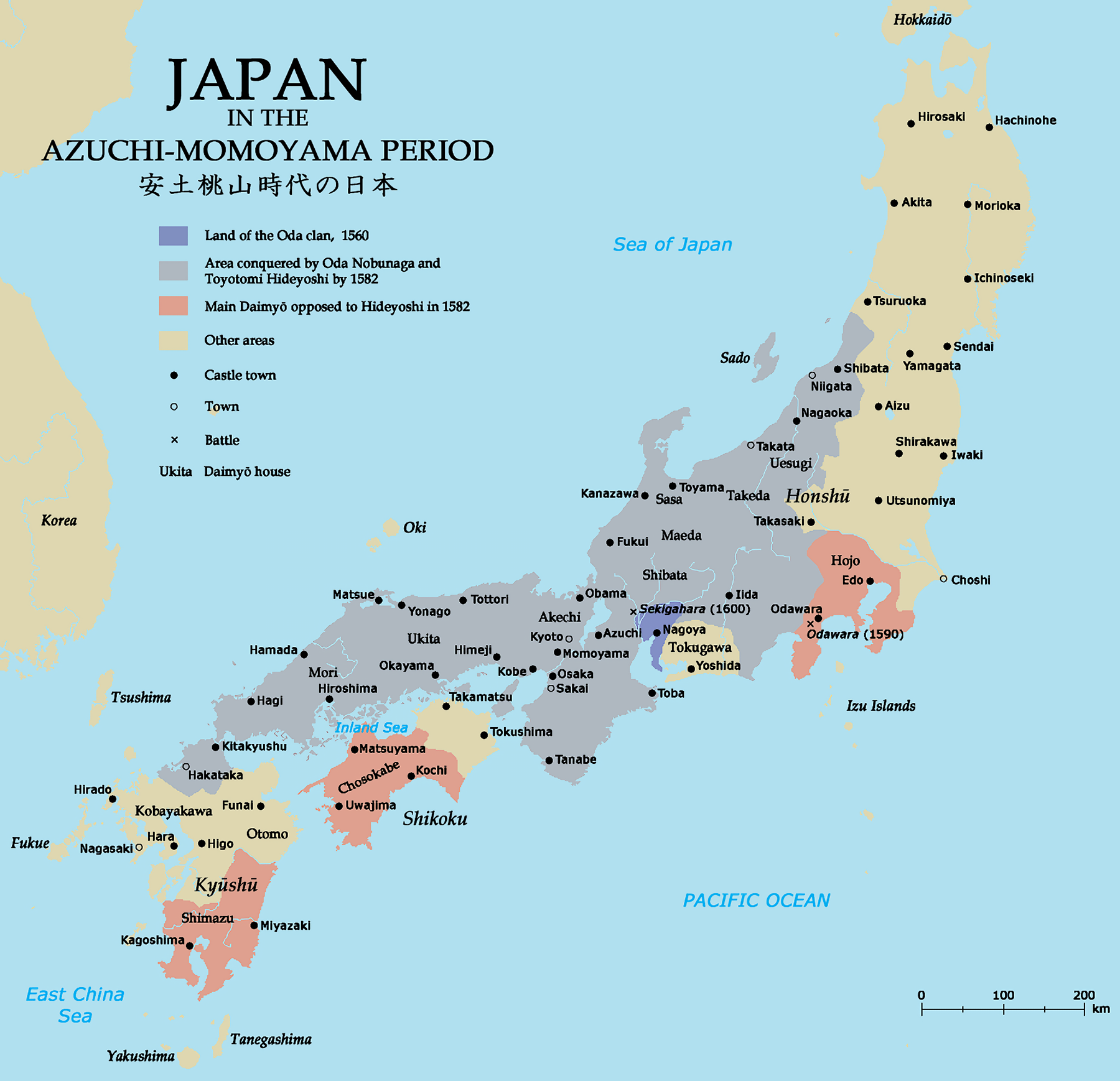
Daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominally to the emperor and the '' kuge''. In the term, means 'large', and stands for , meaning 'private land'. From the '' shugo'' of the Muromachi period through the Sengoku to the ''daimyo'' of the Edo period, the rank had a long and varied history. The backgrounds of ''daimyo'' also varied considerably; while some ''daimyo'' clans, notably the Mōri, Shimazu and Hosokawa, were cadet branches of the Imperial family or were descended from the ''kuge'', other ''daimyo'' were promoted from the ranks of the samurai, notably during the Edo period. ''Daimyo'' often hired samurai to guard their land, and they paid the samurai in land or food as relatively few could afford to pay samurai in money. The ''daimyo'' era ended soon after the Meiji R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sengoku Period
The was a period in Japanese history of near-constant civil war and social upheaval from 1467 to 1615. The Sengoku period was initiated by the Ōnin War in 1467 which collapsed the feudal system of Japan under the Ashikaga shogunate. Various samurai warlords and clans fought for control over Japan in the power vacuum, while the emerged to fight against samurai rule. The arrival of Europeans in 1543 introduced the arquebus into Japanese warfare, and Japan ended its status as a tributary state of China in 1549. Oda Nobunaga dissolved the Ashikaga shogunate in 1573 and launched a war of political unification by force, including the Ishiyama Hongan-ji War, until his death in the Honnō-ji Incident in 1582. Nobunaga's successor Toyotomi Hideyoshi completed his campaign to unify Japan and consolidated his rule with numerous influential reforms. Hideyoshi launched the Japanese invasions of Korea in 1592, but their eventual failure damaged his prestige before his death in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Shizugatake
The was a battle of the Sengoku period of Japan fought between Toyotomi Hideyoshi (then Hashiba Hideyoshi) and Shibata Katsuie in Shizugatake, Ōmi Province in May 1583. Katsuie supported Oda Nobutaka's claim as successor of Oda Nobunaga in a succession dispute within the Oda clan that benefitted Hideyoshi. Katsuie and Sakuma Morimasa attacked fortifications loyal to Hideyoshi at Shizugatake, defeating Nakagawa Kiyohide, but the other sieges by Toshiie and Kazumasu stalled. Katsuie ordered Sakuma to retreat but was ignored, and Hideyoshi launched a surprise counterattack that routed Sakuma and forced him to retreat. Hideyoshi pursued Sakuma and successfully besieged Kitanosho Castle which led to the suicide of Katsuie and Oichi. The Battle of Shizugatake allowed Hideyoshi to consolidate his position as Oda Nobunaga's successor, and was one of the last challenges to his rule along with the Battle of Komaki and Nagakute in 1584. George Sansom states the Battle of Shizu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Yamazaki
The was fought in 1582 in Yamazaki, Japan, located in current-day Kyoto Prefecture. This battle is sometimes referred to as the Battle of Mt. Tennō (天王山の戦い ''Tennō-zan no tatakai''). In the Honnō-ji Incident, Akechi Mitsuhide, a retainer of Oda Nobunaga, attacked Nobunaga as he rested in Honnō-ji, and forced him to commit ''seppuku''. Mitsuhide then took over Nobunaga's power and authority around the Kyoto area. Thirteen days later, Oda's forces under Toyotomi Hideyoshi met Mitsuhide at Yamazaki and defeated him, avenging his lord (Nobunaga) and taking Nobunaga's authority and power for himself. Background Honnō-ji Incident When Nobunaga died, Hideyoshi was busy fighting the Mōri clan in the Siege of Takamatsu. After betraying and defeating Nobunaga at Honnō-ji, Mitsuhide sent a letter to the Mōri. The letter contained a request for an alliance to crush Hideyoshi, but the letter's messenger was intercepted by Hideyoshi's forces and the plot was reveale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenshō Iga War
is the name of two invasions of Iga province by the Oda clan during the Sengoku period. The province was conquered by Oda Nobunaga in 1581 after an unsuccessful attempt in 1579 by his son Oda Nobukatsu. The names of the wars are derived from the Tenshō era name (1573–1592) in which they occurred. Other names for the campaign include or . Background Geographically, the Iga region was surrounded by mountains on all sides that could be passed through only via narrow pathways. This, plus the distance of the region from major transportation routes, meant that Iga was easily defendable by a relatively small number of men and was not a priority target for outside forces. The Niki clan had served as shugo of the province for the Ashikaga shogunate, but their control had never been strong and soon weakened further as the shōgun's authority diminished. No great warlord rose to take their place, although the Rokkaku to the north and the Kitabatake to the east extended their infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tedorigawa
The took place near the Tedori River in Japan's Kaga Province in 1577, between the forces of Oda Nobunaga against Uesugi Kenshin. Kenshin tricked Nobunaga into launching a frontal attack across the Tedorigawa and defeated him. Having suffered the loss of 1,000 men, the Oda withdrew south. This was destined to be Kenshin's last great battle. The battle site is in the modern-day Ishikawa Prefecture. Background After Oda Nobunaga's victory at Nagashino, Uesugi Kenshin broke off his alliance with Oda Nobunaga and Tokugawa Ieyasu, he then initiated an alliance in 1575 with the Ishiyama Honganji warrior monks (Ikko Ikki) and Takeda Katsuyori of the Takeda clan, with whom he had previously been at odds. The Tedorigawa Campaign was precipitated by an Uesugi intervention inside the domain of the Hatakeyama clan in Noto Province, an Oda client state. A coup d'état led by the pro-Oda General Chō Shigetsura, killed Hatakeyama Yoshinori, the lord of Noto, and replaced him with Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |