|
Nivarox
Nivarox, also known as Nivarox - FAR SA is a Swiss company formed by a merger in 1984 between Nivarox SA and Fabriques d' Assortiments Réunis (FAR). It is currently owned by the Swatch Group. Nivarox is also the trade name of the metallic alloy from which its products are fabricated. Its notable property is that its coefficient of elasticity is remarkably constant with temperature. Nivarox is most famous for producing hairsprings that are attached to the balance wheel inside a mechanical watch movement, as well as mainsprings which provide the motive power for the watch. Nivarox was developed for use in watch hairsprings in 1933 by Reinhard Straumann in his Waldenbourg laboratory. FAR was the corporate name chosen in 1932 for the entity comprising several companies and subsidiaries located in Le Locle Switzerland, which at the time manufactured various watch components. Nivarox alloy As a trade name, Nivarox is an acronym from the German german: Nicht variabel oxydfest, label= ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hairspring
A balance spring, or hairspring, is a spring attached to the balance wheel in mechanical timepieces. It causes the balance wheel to oscillate with a resonant frequency when the timepiece is running, which controls the speed at which the wheels of the timepiece turn, thus the rate of movement of the hands. A regulator lever is often fitted, which can be used to alter the free length of the spring and thereby adjust the rate of the timepiece. The balance spring is a fine spiral or helical torsion spring used in mechanical watches, alarm clocks, kitchen timers, marine chronometers, and other timekeeping mechanisms to control the rate of oscillation of the balance wheel. The balance spring is an essential adjunct to the balance wheel, causing it to oscillate back and forth. The balance spring and balance wheel together form a harmonic oscillator, which oscillates with a precise period or "beat" resisting external disturbances, and is responsible for timekeeping accuracy. The addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ébauche
(loanword from French, meaning blank, outline or sketch) is a term used in art to denote the first preliminary underpainting or quick sketch in oils for an oil painting. Horology, clockmaking and watchmaking appropriated the term ébauche to refer to an incomplete or unassembled watch movement and its associated components. The French term is regularly used by English-speaking artists and art historians, as well as horologists and hobbyists. Art One early criticism of Impressionist painting was that its practitioners sought to elevate the status of the ébauche to the level of finished painting. Horology Until about 1850, the watchmaker’s ébauche consisted of two plates with pillars and bars, the barrel, fusée, index, pawl and ratchet-wheel, along with a few assembling screws. These parts were all roughly filed and milled. The steel and brass were manufactured in a special workshop. The ébauche was finished by watchmakers in a finishing shop. The (literally "assortment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elinvar
Elinvar is a nickel–iron–chromium alloy notable for having a modulus of elasticity which does not change much with temperature changes. The name is a contraction of the French ('invariable elasticity'). It was invented by Charles Édouard Guillaume, a Swiss physicist who also invented Invar, another alloy of nickel and iron with very low thermal expansion. Guillaume won the 1920 Nobel Prize in Physics for these discoveries, which shows how important these alloys were for scientific instruments. Elinvar originally consisted of 52% iron, 36% nickel, and 12% chromium. It is almost non-magnetic, and corrosion resistant. Other variations of the Elinvar alloy are * Iron- and cobalt-based ferromagnetic Elinvar alloy * Manganese- and chromium-based anti-ferromagnetic Elinvar alloy * Palladium-based non-magnetic Elinvar alloy The largest use of Elinvar was in balance springs for mechanical watches and chronometers. A major cause of inaccuracy in watches and clocks was that ordinar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel Alloys
This is a list of named alloys grouped alphabetically by base metal. Within these headings, the alloys are also grouped alphabetically. Some of the main alloying elements are optionally listed after the alloy names. Alloys by base metal Aluminium * AA-8000: used for electrical building wire in the U.S. per the National Electrical Code, replacing AA-1350. * Al–Li (2.45% lithium): aerospace applications, including the Space Shuttle * Alnico (nickel, cobalt): used for permanent magnets * Aluminium–Scandium (scandium) * Birmabright (magnesium, manganese): used in car bodies, mainly used by Land Rover cars. * Duralumin (copper) * Hiduminium or R.R. alloys (2% copper, iron, nickel): used in aircraft pistons * Hydronalium (up to 12% magnesium, 1% manganese): used in shipbuilding, resists seawater corrosion * Italma (3.5% magnesium, 0.3% manganese): formerly used to make coinage of the Italian lira * Magnalium (5-50% magnesium): used in airplane bodies, ladders, pyrotechnics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Science+Business Media
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watchmakers
A watchmaker is an artisan who makes and repairs watches. Since a majority of watches are now factory-made, most modern watchmakers only repair watches. However, originally they were master craftsmen who built watches, including all their parts, by hand. Modern watchmakers, when required to repair older watches, for which replacement parts may not be available, must have fabrication skills, and can typically manufacture replacements for many of the parts found in a watch. The term clockmaker refers to an equivalent occupation specializing in clocks. Most practising professional watchmakers service current or recent production watches. They seldom fabricate replacement parts. Instead they obtain and fit factory spare parts applicable to the watch brand being serviced. The majority of modern watchmakers, particularly in Switzerland and other countries in Europe, work directly for the watchmaking industry and may have completed a formal watchmaking degree at a technical schoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
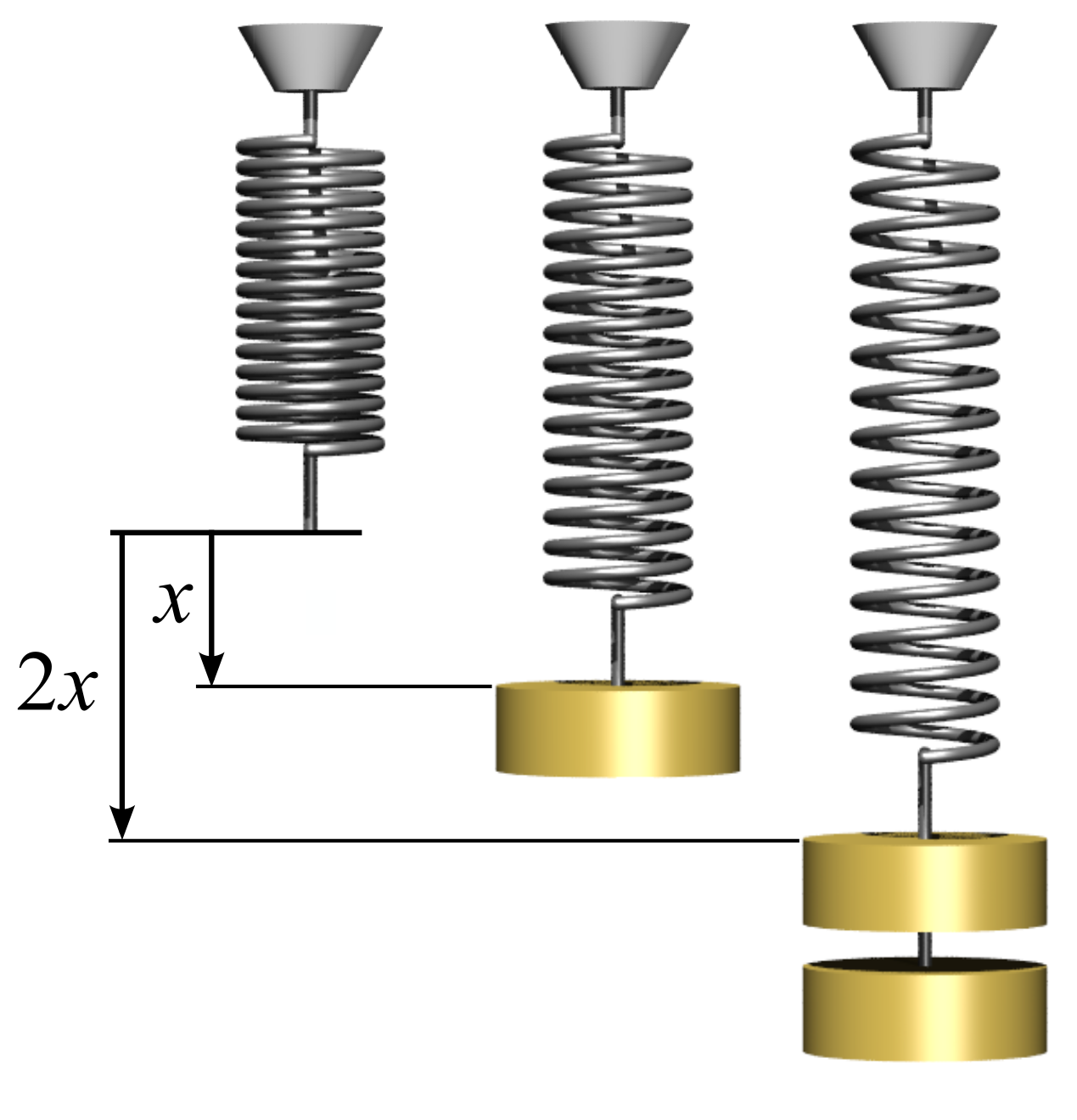
Spring Constant
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring (device), spring by some distance () Proportionality (mathematics)#Direct_proportionality, scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of the spring (i.e., its stiffness), and is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. The law is named after 17th-century British physicist Robert Hooke. He first stated the law in 1676 as a Latin anagram. He published the solution of his anagram in 1678 as: ("as the extension, so the force" or "the extension is proportional to the force"). Hooke states in the 1678 work that he was aware of the law since 1660. Hooke's equation holds (to some extent) in many other situations where an elasticity (physics), elastic body is Deformation (physics), deformed, such as wind blowing on a tall building, and a musician plucking a string (music), string of a guitar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasticity (physics)
In physics and materials science, elasticity is the ability of a body to resist a distorting influence and to return to its original size and shape when that influence or force is removed. Solid objects will deform when adequate loads are applied to them; if the material is elastic, the object will return to its initial shape and size after removal. This is in contrast to ''plasticity'', in which the object fails to do so and instead remains in its deformed state. The physical reasons for elastic behavior can be quite different for different materials. In metals, the atomic lattice changes size and shape when forces are applied (energy is added to the system). When forces are removed, the lattice goes back to the original lower energy state. For rubbers and other polymers, elasticity is caused by the stretching of polymer chains when forces are applied. Hooke's law states that the force required to deform elastic objects should be directly proportional to the distance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nivaflex
Nivaflex is an octavariant alloy important in watchmaking, used primarily for the mainspring. The name was registered as a trademark in 1957 by Reinhard Straumann, a Swiss metallurgist. Nivaflex is "wholly non-magnetic" and displays a very low coefficient of thermal expansion Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions. Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kineti .... Its composition is of 45% cobalt, 21% nickel, 18% chromium, 5% iron, 4% tungsten, 4% molybdenum, 1% titanium and 0.2% beryllium; carbon content is less than 0.1 percent of the alloy's weight. References {{reflist Horology Timekeeping components Springs (mechanical) Cobalt alloys Nickel alloys Ferroalloys Chromium alloys Tungsten alloys Molybdenum alloys Titanium alloys Beryllium alloys Antiferromagnetic alloys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, opacity (optics), opacity, and lustre (mineralogy), luster, but may have properties that differ from those of the pure metals, such as increased strength or hardness. In some cases, an alloy may reduce the overall cost of the material while preserving important properties. In other cases, the mixture imparts synergistic properties to the constituent metal elements such as corrosion resistance or mechanical strength. Alloys are defined by a metallic bonding character. The alloy constituents are usually measured by mass percentage for practical applications, and in Atomic ratio, atomic fraction for basic science studies. Alloys are usually classified as substitutional or interstitial alloys, depending on the atomic arrangement that forms the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |