|
Niuatahi
Niuatahi or also called Volcano O is a submarine volcano located in the far northern territory of Tonga. Since the cone in the middle is named Motutahi, the volcano is sometimes referred to as Niuatahi-Motutahi. Despite not having any record of any eruption, Niuatahi does have a record of recent hydrothermal activity. Etymology Niuatahi was named by the Tonga Ministry of Lands, Environment, Climate Change and Natural Resources. In the Tongan language, Niuatahi means ''sea''. The name Motutahi means ''island in the sea'' in the Tongan language. Geography The volcano can be found approximately northwest of Niuatoputapu and southwest of the Samoan Islands. It is also located southwest of the far more known and more active West Mata submarine volcano, located in the same volcanic group as Niuatahi. An active ridge can also be found just west of the caldera walls. Structure Niuatahi is a submarine volcano mostly known for its' circular shape and enormous width. It is in diameter an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niuatahi
Niuatahi or also called Volcano O is a submarine volcano located in the far northern territory of Tonga. Since the cone in the middle is named Motutahi, the volcano is sometimes referred to as Niuatahi-Motutahi. Despite not having any record of any eruption, Niuatahi does have a record of recent hydrothermal activity. Etymology Niuatahi was named by the Tonga Ministry of Lands, Environment, Climate Change and Natural Resources. In the Tongan language, Niuatahi means ''sea''. The name Motutahi means ''island in the sea'' in the Tongan language. Geography The volcano can be found approximately northwest of Niuatoputapu and southwest of the Samoan Islands. It is also located southwest of the far more known and more active West Mata submarine volcano, located in the same volcanic group as Niuatahi. An active ridge can also be found just west of the caldera walls. Structure Niuatahi is a submarine volcano mostly known for its' circular shape and enormous width. It is in diameter an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Mata
West Mata, located in the far northern portion of Tonga, is an active submarine volcano. Known for the deepest recorded volcanic eruption to date, West Mata does not have a very long recorded history since it was recently discovered in 2008 along with another group of volcanoes nearby. Compared to the other Mata group volcanoes, West Mata is the most hydrothermally active one and its' activity is not disputed. Geography West Mata can be found in the northeastern portion of Tonga, in between Fiji and Samoa. It is located approximately southwest of the Samoan Islands and around northeast of the Lau Islands of Fiji. Structure With data from bathymetry, bathymetric surveys, the structure of the West Mata volcano was made more clear. The West Mata vent has a common structure with most volcanic structures in the area, mostly dominated by a prominent rift zone that extends away from the summit, which is the peak of a conical structure with a circular base on the seafloor. Therefore, me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast Lau Basin Volcanoes
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, Radius, radially arrayed compass directions (or Azimuth#In navigation, azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each separated by 90 degree (angle), degrees, and secondarily divided by four ordinal (intercardinal) directions—northeast, southeast, southwest, and northwest—each located halfway between two cardinal directions. Some disciplines such as meteorology and navigation further divide the compass with additional azimuths. Within European tradition, a fully defined compass has 32 'points' (and any finer subdivisions are described in fractions of points). Compass points are valuable in that they allow a user to refer to a specific azimuth in a Colloquialism, colloquial fashion, without having to compute or remember degrees. Designations The names of the compass point directions follow these rules: 8-wind compass rose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
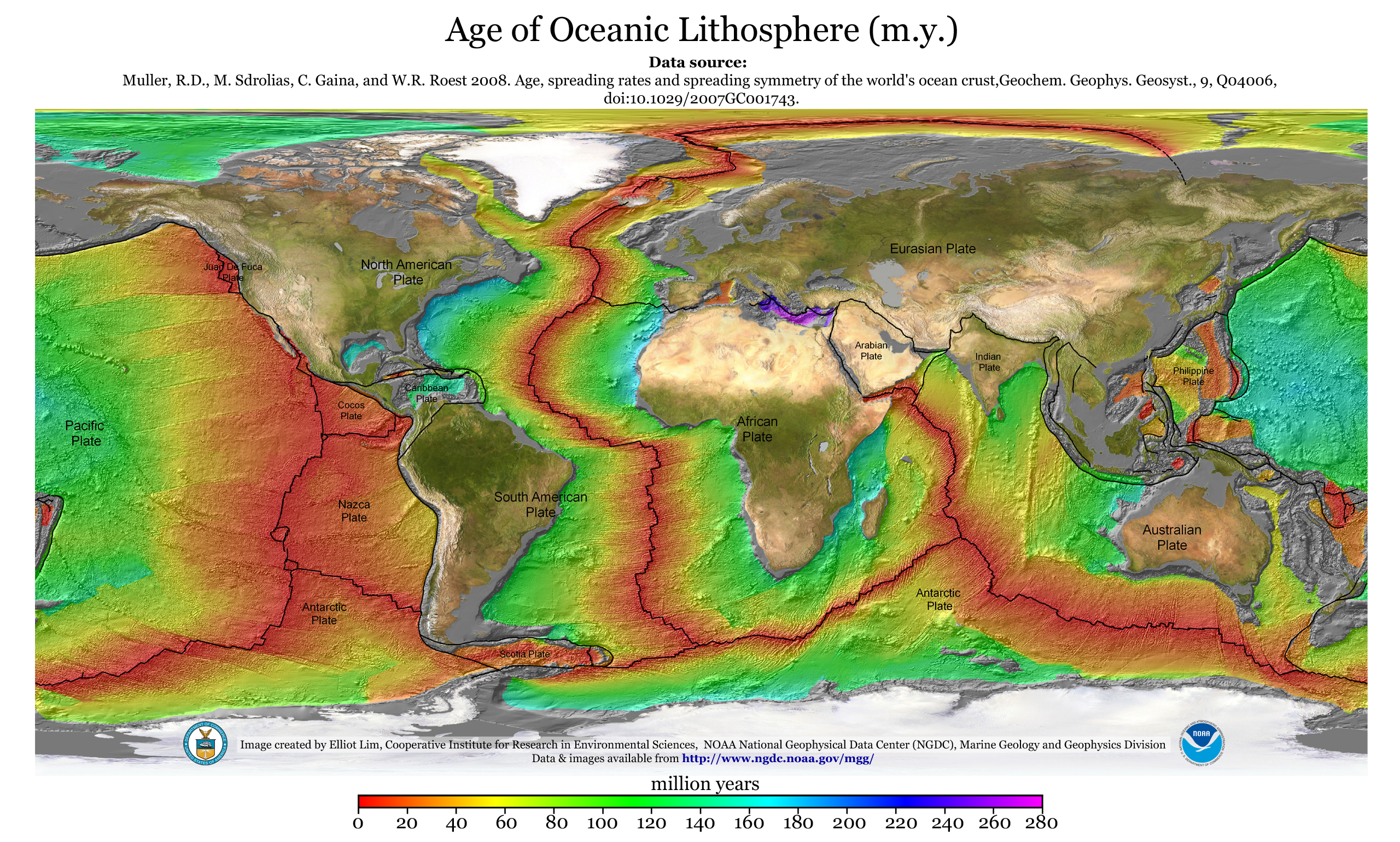
Oceanic Crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic cumulates. The crust overlies the rigid uppermost layer of the mantle. The crust and the rigid upper mantle layer together constitute oceanic lithosphere. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium. It is thinner than continental crust, or sial, generally less than 10 kilometers thick; however, it is denser, having a mean density of about 3.0 grams per cubic centimeter as opposed to continental crust which has a density of about 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter. The crust uppermost is the result of the cooling of magma derived from mantle material below the plate. The magma is injected into the spreading center, which consists mainly of a partly solidified crystal mush derived from earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial planet, rocky planet or natural satellite, moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of volcanism on Venus, Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar mare, lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Fiji Basin
The North Fiji Basin (NFB) is an oceanic basin west of Fiji in the south-west Pacific Ocean. It is an actively spreading back-arc basin delimited by the Fiji islands to the east, the inactive Vitiaz Trench to the north, the Vanuatu/New Hebrides island arc to the west, and the Hunter fracture zone to the south. Roughly triangular in shape with its apex located at the northern end of the New Hebrides Arc, the basin is actively spreading southward and is characterised by three spreading centres and an oceanic crust younger than 12 . The opening of the NFB began when a slab roll-back was initiated beneath the New Hebrides and the island arc started its clockwise rotation. The opening of the basin was the result of the collision between the Ontong Java Plateau and the Australian Plate along the now inactive Solomon–Vitiaz subduction system north of the NFB. The NFB is the largest and most developed back-arc basin of the south-west Pacific. It is opening in a complex geologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Plate
The Australian Plate is a major tectonic plate in the eastern and, largely, southern hemispheres. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, Australia remained connected to India and Antarctica until approximately when India broke away and began moving north. Australia and Antarctica began rifting and completely separated roughly . The Australian plate later fused with the adjacent Indian Plate beneath the Indian Ocean to form a single Indo-Australian Plate. However, recent studies suggest that the two plates have once again split apart and have been separate plates for at least 3 million years and likely longer. The Australian Plate includes the continent of Australia, including Tasmania, as well as portions of New Guinea, New Zealand and the Indian Ocean basin. Scope The continental crust of this plate covers the whole of Australia, the Gulf of Carpentaria, southern New Guinea, the Arafura Sea, the Coral Sea. The continental crust also includes northwestern N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate. The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and Izanagi Plates. The Pacific Plate subsequently grew to where it underlies most of the Pacific Ocean basin. This reduced the Farallon Plate to a few remnants along the west coast of North America and the Phoenix Plate to a small remnant near the Drake Passage, and destroyed the Izanagi Plate by subduction under Asia. The Pacific Plate contains an interior hot spot forming the Hawaiian Islands. Boundaries The north-eastern side is a divergent boundary with the Explorer Plate, the Juan de Fuca Plate and the Gorda Plate forming respectively the Explorer Ridge, the Juan de Fuca Ridge and the Gorda Ridge. In the middle of the eastern side is a transform boundary with the North American Plate along the San Andreas Fault, and a boundary with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forearc
Forearc is a plate tectonic term referring to a region between an oceanic trench, also known as a subduction zone, and the associated volcanic arc. Forearc regions are present along a convergent margins and eponymously form 'in front of' the volcanic arcs that are characteristic of convergent plate margins. A back-arc region is the companion region behind the volcanic arc. Many forearcs have an accretionary wedge which may form a topographic ridge known as an outer arc ridge that parallels the volcanic arc. Between the accretionary wedge and the volcanic arc a forearc basin, sometimes referred to as an outer arc trough, may be present and can accumulate thick deposits of sediment. Due to tectonic stresses as one tectonic plate rides over another, forearc regions are sources for great thrust earthquakes. Formation During subduction, an oceanic plate is thrust below another tectonic plate, which may be oceanic or continental. Water and other volatiles in the down-going plat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |