|
Nitrogen Oxide
Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds: Charge-neutral *Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen(II) oxide, or nitrogen monoxide * Nitrogen dioxide (), nitrogen(IV) oxide * Nitrogen trioxide (), or nitrate radical *Nitrous oxide (), nitrogen(0,II) oxide * Dinitrogen dioxide (), nitrogen(II) oxide dimer * Dinitrogen trioxide (), nitrogen(II,IV) oxide *Dinitrogen tetroxide (), nitrogen(IV) oxide dimer * Dinitrogen pentoxide (), nitrogen(V) oxide, or nitronium nitrate * Nitrosyl azide (), nitrogen(−I,0,I,II) oxide *Nitryl azide () * Oxatetrazole () * Trinitramide ( or ), nitrogen(0,IV) oxide Anions * Nitroxide () * Nitrite ( or ) * Nitrate () * Peroxynitrite ( or ) *Peroxynitrate ( or ) * Orthonitrate (, analogous to phosphate ) * Hyponitrite ( or ) * Trioxodinitrate or hyponitrate ( or ) * Nitroxylate ( or ) * Dinitramide ( or ) Cations *Nitrosonium ( or ) *Nitronium ( or ) Atmospheric sciences In atmospheric chemistry: * (or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Compound
In materials chemistry, a binary phase or binary compound is a chemical compound containing two different elements. Some binary phase compounds are molecular, e.g. carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). More typically binary phase refers to extended solids. Famous examples zinc sulfide, which contains zinc and sulfur, and tungsten carbide Tungsten carbide (chemical formula: WC) is a chemical compound (specifically, a carbide) containing equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. In its most basic form, tungsten carbide is a fine gray powder, but it can be pressed and formed into ..., which contains tungsten and carbon. Phases with higher degrees of complexity feature more elements, e.g. three elements in ternary phases, four elements in quaternary phases. References Chemical compounds {{chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
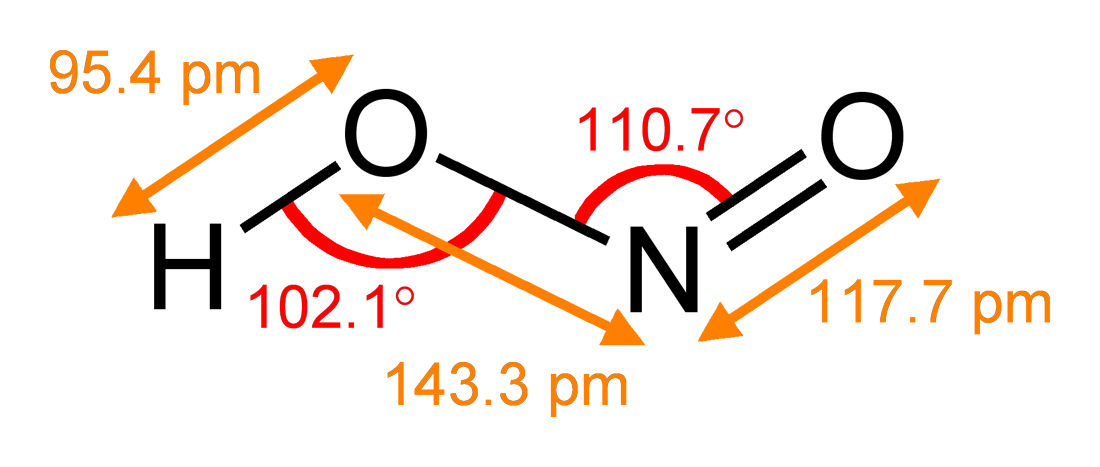
Nitrite
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid. Production Sodium nitrite is made industrially by passing a mixture of nitrogen oxides into aqueous sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate solution: : The product is purified by recrystallization. Alkali metal nitrites are thermally stable up to and beyond their melting point (441 °C for KNO2). Ammonium nitrite can be made from dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3, which is formally the anhydride of nitrous acid: :2 NH3 + H2O + N2O3 → 2 NH4NO2 Structure The nitrite ion has a symmetrical structure (C2v symmetry), with both N–O bonds having equal length and a bond angle of about 115°. In valence bond theory, it is described as a resonance hybrid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is one of several nitrogen oxides. is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year for use primarily in the production of fertilizers. At higher temperatures it is a reddish-brown gas. It can be fatal if inhaled in large quantities. Nitrogen dioxide is a paramagnetic, bent molecule with C2v point group symmetry. It is included in the NOx family of atmospheric pollutants. Properties Nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas with a pungent, acrid odor above , becomes a yellowish-brown liquid below , and converts to the colorless dinitrogen tetroxide () below . The bond length between the nitrogen atom and the oxygen atom is 119.7 pm. This bond length is consistent with a bond order between one and two. Unlike ozone, O3, the ground electronic state of nitrogen dioxide is a doublet state, since nitrogen has one unpaired electron, which decreases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula (•N=O or •NO). Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a class of molecules whose study spawned early modern theories of chemical bonding. An important intermediate in industrial chemistry, nitric oxide forms in combustion systems and can be generated by lightning in thunderstorms. In mammals, including humans, nitric oxide is a signaling molecule in many physiological and pathological processes. It was proclaimed the "Molecule of the Year" in 1992. The 1998 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded for discovering nitric oxide's role as a cardiovascular signalling molecule. Nitric oxide should not be confused with nitrogen dioxide (NO2), a brown gas and major air pollutant, or with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Chemistry
Atmospheric chemistry is a branch of atmospheric science in which the chemistry of the Earth's atmosphere and that of other planets is studied. It is a multidisciplinary approach of research and draws on environmental chemistry, physics, meteorology, computer modeling, oceanography, geology and volcanology and other disciplines. Research is increasingly connected with other areas of study such as climatology. The composition and chemistry of the Earth's atmosphere is of importance for several reasons, but primarily because of the interactions between the atmosphere and living organisms. The composition of the Earth's atmosphere changes as result of natural processes such as volcano emissions, lightning and bombardment by solar particles from corona. It has also been changed by human activity and some of these changes are harmful to human health, crops and ecosystems. Examples of problems which have been addressed by atmospheric chemistry include acid rain, ozone depletion, photo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitronium
The nitronium ion, , is a cation. It is an onium ion because its nitrogen atom has +1 charge, similar to ammonium ion . It is created by the removal of an electron from the paramagnetic nitrogen dioxide molecule , or the protonation of nitric acid (with removal of ). It is stable enough to exist in normal conditions, but it is generally reactive and used extensively as an electrophile in the nitration of other substances. The ion is generated '' in situ'' for this purpose by mixing concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid according to the equilibrium: : Structure The nitronium ion is isoelectronic with carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide, and has the same linear structure and bond angle of 180°. For this reason it has a similar vibrational spectrum to carbon dioxide. Historically, the nitronium ion was detected by Raman spectroscopy, because its symmetric stretch is Raman-active but infrared-inactive. The Raman-active symmetrical stretch was first used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrosonium
The nitrosonium ion is , in which the nitrogen atom is bonded to an oxygen atom with a bond order of 3, and the overall diatomic species bears a positive charge. It can be viewed as nitric oxide with one electron removed. This ion is usually obtained as the following salts: , ( nitrosylsulfuric acid, more descriptively written ) and . The and salts are slightly soluble in acetonitrile . NOBF4 can be purified by sublimation at 200–250 °C and . is isoelectronic with CO, and . It arises via protonation of nitrous acid: :HONO + H+ NO+ + H2O Chemical properties Hydrolysis reacts readily with water to form nitrous acid: : For this reason, nitrosonium compounds must be protected from water or even moist air. With base, the reaction generates nitrite: : As a diazotizing agent reacts with aryl amines, , to give diazonium salts, . The resulting diazonium group is easily displaced (unlike the amino group) by a variety of nucleophiles. As an oxidizing agent , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Dinitramide
Ammonium dinitramide (ADN) is the ammonium salt of dinitraminic acid. ADN decomposes under heat to leave only nitrogen, oxygen, and water. The ions are the ammonium ion NH4+ and the dinitramide N(NO2)2−. It makes an excellent solid rocket oxidizer with a slightly higher specific impulse than ammonium perchlorate and more importantly, does not leave corrosive hydrogen chloride fumes. This property is also of military interest because halogen-free smoke is harder to detect. It decomposes into low-molecular-mass gases so it contributes to higher performance without creating excessive temperatures if used in gun or rocket propellants. The salt is prone to detonation under high temperatures and shock more so than the perchlorate. The EURENCO Bofors company produced LMP-103S as a 1-to-1 substitute for hydrazine by dissolving 65% ammonium dinitramide, NH4N(NO2)2, in 35% water solution of methanol and ammonia. LMP-103S has 6% higher specific impulse and 30% higher impulse densi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitroxylate
Nitroxylic acid or hydronitrous acid is an unstable reduced oxonitrogen acid. It has formula H4N2O4 containing nitrogen in the +2 oxidation state. The corresponding anion called nitroxylate is or . The first clue that nitroxylic acid exists was when Edward Bedford Maxted electrolysed sodium nitrite dissolved in liquid ammonia. A bright yellow substance deposited on the cathode. He called this disodium nitrite. The disodium nitrite could also be made by mixing ammonia solutions of sodium and sodium nitrite in the complete absence of water. Disodium nitrite reacts with water to form sodium nitrite, sodium hydroxide and hydrogen. Other ways to make the disodium nitrite include reacting sodium with ammonium nitrate or electrolysing sodium nitrate solution. Note that the disodium nitrite is very explosive, and experimenters often had their apparatus destroyed when making it. Disodium nitrite reacts with oxygen and carbon dioxide explosively. The substance is nowadays called sodium n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trioxodinitrate
Angeli's salt, sodium trioxodinitrate, is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2 2O3 It contains nitrogen in an unusual reduced state. It is a colorless, water-soluble solid, a salt. In research, this salt is used as a source of the metastable nitroxyl (HNO), which is a signalling molecule in nature. It is also known by the name sodium trioxodinitrate(II) monohydrate. Preparation and properties As first reported by Angelo Angeli in 1896, the salt is prepared by combining hydroxylamine and an organic nitrate, as a source of nitronium (): :NH2OH + RONO2 + 2 NaOR′ → ROH + 2 R′OH + Na2N2O3 The structure of the hydrate has been confirmed by X-ray crystallography. The anion is planar. Starting from the ONN end, the bond distances are 1.35 Å (N−O), 1.26 Å (N−N), 1.31 Å (N−O), and 1.32 Å (N−-O). The negative charge is on the oxygen atoms at opposite ends of the molecule. The angles are 112.9° (Osingle−N−N), 118.4° ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyponitrite
In chemistry, hyponitrite may refer to the anion ( N=NOsup>2−), or to any ionic compound that contains it. In organic chemistry, it may also refer to the group −O−N=N−O−, or any organic compound with the generic formula R1−O−N=N−O−R2, where R1 and R2 are organic groups.M. N. Hughes (1968), "Hyponitrites". Quarterly Reviews of the Chemical Society, volume 22, issue 1, pages 1–13. . Such compounds can be viewed as salts and esters of respectively hyponitrous acid or HON=NOH. An acid hyponitrite is an ionic compound with the anion ( ON=NOsup>−). Hyponitrite ion Hyponitrite exhibits cis–trans isomerism.Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) ''Inorganic Chemistry'', Elsevier The ''trans'' (''E'') form is generally found in hyponitrite salts such as sodium hyponitrite () and silver(I) hyponitrite (). The ''cis'' (''Z'') form of sodium hyponitrite can be obtained too, and it is more reactive than the ''trans'' form. The ''cis'' hyponitrite anion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthonitrate
Orthonitrate is a tetrahedral oxoanion of nitrogen with the formula . It was first identified in 1977 and is currently known in only two compounds, sodium orthonitrate (Na3NO4) and potassium orthonitrate (K3NO4). The corresponding oxoacid, orthonitric acid (H3NO4), is hypothetical and has never been observed. Sodium and potassium orthonitrate can be prepared by fusion of the nitrate and metal oxide under high temperatures and ideally high pressures (several GPa). :NaNO3 + Na2O → Na3NO4 (300 °C for 3 days) The resulting orthonitrates are white solids which are extremely sensitive to moisture and CO2, decomposing within minutes to sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, and sodium nitrate upon exposure to air. :Na3NO4 + CO2 → NaNO3 + Na2CO3 :Na3NO4 + H2O → NaNO3 + 2 NaOH The orthonitrate ion is tetrahedral with N–O bond lengths of 139 pm, which is unexpectedly short, indicating that polar interactions are shortening the bond. This short bond length parallels that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |