|
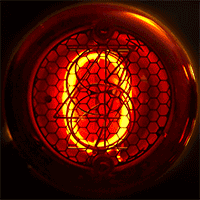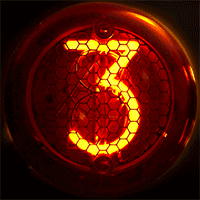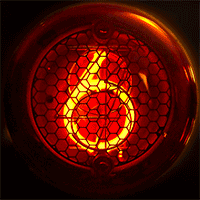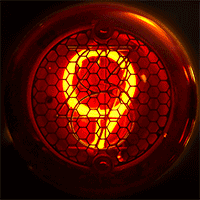
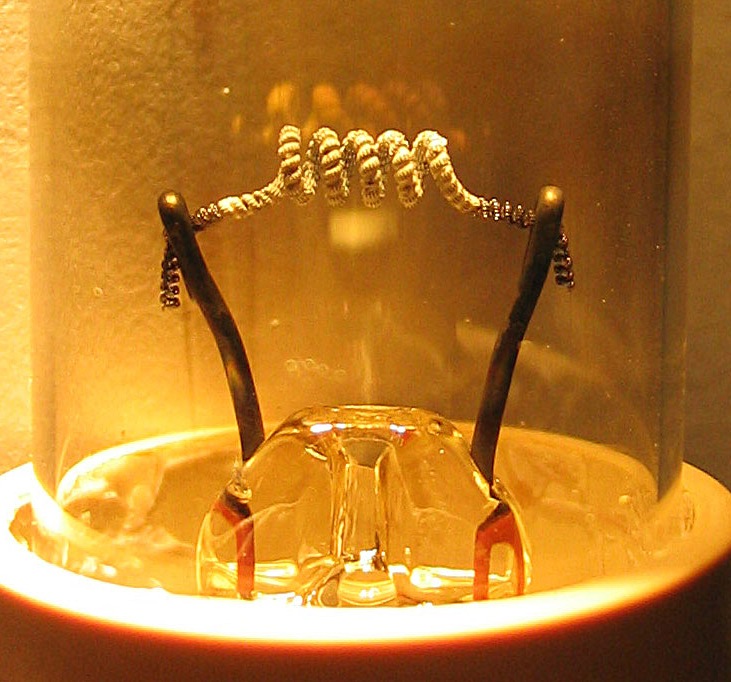
Nimo Tube
Nimo was the trademark of a family of small cathode-ray tube (CRTs) used for numerical displays. They were manufactured by Industrial Electronic Engineers (IEE) around the mid-1960s. The tube had ten electron guns with stencils that shaped the electron beam as digits. Details The Nimo tube operated on a similar principle as the charactron, but used a much simpler design. They were intended as single digit, simple displays, or as four or six digits by means of a special horizontal magnetic deflection system. Having only three electrode types (a filament, an anode and ten different grids), the driving circuit for this tube was very simple, and as the image was projected on the glass face, it allowed a much wider viewing angle than, for example, Nixie tubes, which Nimo tried to replace. The tube required 1750 volts direct current (DC) for the anode and also required 1.1 volts for the filaments, as well as a cathode bias for the filaments that enables or disables the display of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Grid
The control grid is an electrode used in amplifying thermionic valves (vacuum tubes) such as the triode, tetrode and pentode, used to control the flow of electrons from the cathode to the anode (plate) electrode. The control grid usually consists of a cylindrical screen or helix of fine wire surrounding the cathode, and is surrounded in turn by the anode. The control grid was invented by Lee De Forest, who in 1906 added a grid to the Fleming valve (thermionic diode) to create the first amplifying vacuum tube, the Audion (triode). Operation In a valve, the hot cathode emits negatively charged electrons, which are attracted to and captured by the anode, which is given a positive voltage by a power supply. The control grid between the cathode and anode functions as a "gate" to control the current of electrons reaching the anode. A more negative voltage on the grid will repel the electrons back toward the cathode so fewer get through to the anode. A less negative, or positive, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathode Ray Tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms ( oscilloscope), pictures (television set, computer monitor), radar targets, or other phenomena. A CRT on a television set is commonly called a picture tube. CRTs have also been used as memory devices, in which case the screen is not intended to be visible to an observer. The term ''cathode ray'' was used to describe electron beams when they were first discovered, before it was understood that what was emitted from the cathode was a beam of electrons. In CRT television sets and computer monitors, the entire front area of the tube is scanned repeatedly and systematically in a fixed pattern called a raster. In color devices, an image is produced by controlling the intensity of each of three electron beams, one for each additive primary color (red, green, and bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fran Blanche
Frantone Electronics is an American Philadelphia-based hand-made effects pedal manufacturer founded and run by Fran Blanche. Blanche operates a YouTube channel where she discusses the company's history and showcases various electronics projects. History Frantone Electronics was founded in 1994 in Lancaster, Pennsylvania by Fran Blanche, a self-taught electronic engineer. The company was one of the world's first boutique guitar effects companies. Over the years, the company's boutique pedals would be used by notable musicians including Lou Reed and R.E.M. The company's growth was never steady; Blanche moved Frantone repeatedly, being gentrified out of several NYC-area locations. In the early 1990s, Blanche built an effects pedal for herself named the "Fuzzy-Wuzzy". She subsequently founded Frantone and designed the Hep Cat, the company's first commercial product, which was followed by more pedal designs in the years to follow. Blanche took a hiatus from operating Frantone and wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charactron
Charactron was a U.S. registered trademark (number 0585950, 23 February 1954) of Consolidated Vultee Aircraft Corporation (Convair) for its shaped electron beam cathode ray tube. Charactron CRTs performed functions of both a display device and a read-only memory storing multiple characters and fonts. The similar Typotron was a U.S. registered trademark (23 November 1953) of Hughes Aircraft Corporation for its type of shaped electron beam storage tube with a direct-view bistable storage screen. The Charactron CRT used an electron beam to flood a specially patterned perforated anode that contained the stencil patterns for each of the characters that it could form. The first deflection positioning of the electron beam steered the beam to pass through one of the (typically 64 or 116) characters and symbols that could be formed. The beam, which then had the cross-section of the desired character, was re-centered along the axis of the tube and deflected to the desired position of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telefunken
Telefunken was a German radio and television apparatus company, founded in Berlin in 1903, as a joint venture of Siemens & Halske and the ''Allgemeine Elektrizitäts-Gesellschaft'' (AEG) ('General electricity company'). The name "Telefunken" appears in: * the product brand name "Telefunken"; * ''Gesellschaft für drahtlose Telegraphie m.b.H., System Telefunken'', founded 1903 in Berlin as a subsidiary of AEG and Siemens & Halske; * ''Telefunken, Gesellschaft für drahtlose Telegraphie m.b.H.'' (from 1923 to 1955 – since 1941 subsidiary of the AEG only); * ''Telefunken GmbH'' in 1955; * ''Telefunken Aktiengesellschaft (AG)'' in 1963; * Merger of AEG and Telefunken to form ''Allgemeine Elektrizitäts-Gesellschaft AEG-Telefunken'' (from 1967 to 1979); * AEG-TELEFUNKEN AG (from 1979 to 1985); * ''TELEFUNKEN Fernseh und Rundfunk GmbH'', Hanover (1972, subsidiary of AEG-TELEFUNKEN); * Telefunken electronic GmbH (a spin-off of AEG-Telefunken and DASA * the company (since 1992 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''current'' or ''voltage''. Direct current may be converted from an alternating current supply by use of a rectifier, which contains electronic elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be converted into alternating current via an inverter. Direct current has many uses, from the charging of batteries to large power sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nixie Tube
A Nixie tube ( ), or cold cathode display, is an electronic device used for displaying numerals or other information using glow discharge. The glass tube contains a wire-mesh anode and multiple cathodes, shaped like numerals or other symbols. Applying power to one cathode surrounds it with an orange glow discharge. The tube is filled with a gas at low pressure, usually mostly neon and often a little mercury or argon, in a Penning mixture. Although it resembles a vacuum tube in appearance, its operation does not depend on thermionic emission of electrons from a heated cathode. It is hence a cold-cathode tube (a form of gas-filled tube), and is a variant of the neon lamp. Such tubes rarely exceed even under the most severe of operating conditions in a room at ambient temperature. Vacuum fluorescent displays from the same era use completely different technology—they have a heated cathode together with a control grid and shaped phosphor anodes; Nixies have no heater or control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ACID, for "anode current into device". The direction of conventional current (the flow of positive charges) in a circuit is opposite to the direction of electron flow, so (negatively charged) electrons flow out the anode of a galvanic cell, into an outside or external circuit connected to the cell. For example, the end of a household battery marked with a "-" (minus) is the anode. In both a galvanic cell and an electrolytic cell, the anode is the electrode at which the oxidation reaction occurs. In a galvanic cell the anode is the wire or plate having excess negative charge as a result of the oxidation reaction. In an electrolytic cell, the anode is the wire or plate upon which excess positive charge is imposed. As a result of this, anion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathode-ray Tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms (oscilloscope), pictures (television set, computer monitor), radar targets, or other phenomena. A CRT on a television set is commonly called a picture tube. CRTs have also been used as memory devices, in which case the screen is not intended to be visible to an observer. The term ''cathode ray'' was used to describe electron beams when they were first discovered, before it was understood that what was emitted from the cathode was a beam of electrons. In CRT television sets and computer monitors, the entire front area of the tube is scanned repeatedly and systematically in a fixed pattern called a raster. In color devices, an image is produced by controlling the intensity of each of three electron beams, one for each additive primary color (red, green, and blue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Cathode
In vacuum tubes and gas-filled tubes, a hot cathode or thermionic cathode is a cathode electrode which is heated to make it emit electrons due to thermionic emission. This is in contrast to a cold cathode, which does not have a heating element. The heating element is usually an electrical filament heated by a separate electric current passing through it. Hot cathodes typically achieve much higher power density than cold cathodes, emitting significantly more electrons from the same surface area. Cold cathodes rely on field electron emission or secondary electron emission from positive ion bombardment, and do not require heating. There are two types of hot cathode. In a ''directly heated cathode'', the filament is the cathode and emits the electrons. In an ''indirectly heated cathode'', the filament or ''heater'' heats a separate metal cathode electrode which emits the electrons. From the 1920s to the 1960s, a wide variety of electronic devices used hot-cathode vacuum tubes. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charactron
Charactron was a U.S. registered trademark (number 0585950, 23 February 1954) of Consolidated Vultee Aircraft Corporation (Convair) for its shaped electron beam cathode ray tube. Charactron CRTs performed functions of both a display device and a read-only memory storing multiple characters and fonts. The similar Typotron was a U.S. registered trademark (23 November 1953) of Hughes Aircraft Corporation for its type of shaped electron beam storage tube with a direct-view bistable storage screen. The Charactron CRT used an electron beam to flood a specially patterned perforated anode that contained the stencil patterns for each of the characters that it could form. The first deflection positioning of the electron beam steered the beam to pass through one of the (typically 64 or 116) characters and symbols that could be formed. The beam, which then had the cross-section of the desired character, was re-centered along the axis of the tube and deflected to the desired position of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |