|
Nimatnama-i-Nasiruddin-Shahi
The ''Ni'matnāmah Naṣir al-Dīn Shāhī'' ( Naskh: ; ) (c. 1500) is a medieval Indian cookbook, written in Persian language using Naskh script, of delicacies and recipes, and some accompanying paintings illustrating the preparation of the recipes. It was started for Ghiyath Shah (r. 1469–1500), the ruler of the Malwa Sultanate in central India. After he was forced to abdicate, it was completed for his son 'Abd al-Muzaffar Nasir Shah. (r. 1500–10). Some of the illustrations have women painted wearing men's various types of Persian and Indian garments and turbans, including a specific style of turban which is also featured in Turkman style paintings of 1470s. The style of the surrounding landscape are influenced by the Turkmen style of the last third of the 15th century. The Manuscript is in the British Library, London. It was first written about by Robert Skelton, museum curator and scholar of Indian art (1929–2022), in 1959. At least two artists collaborated in illustrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghiyath Shah
Ghiyath Shah, also known as Ghiyas-ud-Din Shah or Ghiyasuddin, was a Sultan of the Malwa Sultanate in the fifteenth century. The son of his predecessor Mahmud Shah I, he reigned from 1469 to 1500. A military leader before his accession, he was known during his reign for his religious devotion and cultural life. During his reign, the Nimatnama-i-Nasiruddin-Shahi was written and illustrated. His court was known for having over 12,000 women, including entertainers and scholars. His exiled son Nasir-ud-Din Shah revolted and took the throne in October 1500. Ghiyasuddin was found dead four months later and is believed to have been poisoned by his son and successor. Biography The eldest son of Mahmud, Ghiyath served his father as a military leader. He was made Shah at the death of his father in 1469. According to Firishta, shortly after his accession, he held a grand feast at which he announced that after thirty-four years on the field he was yielding his military rule to his son. He w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
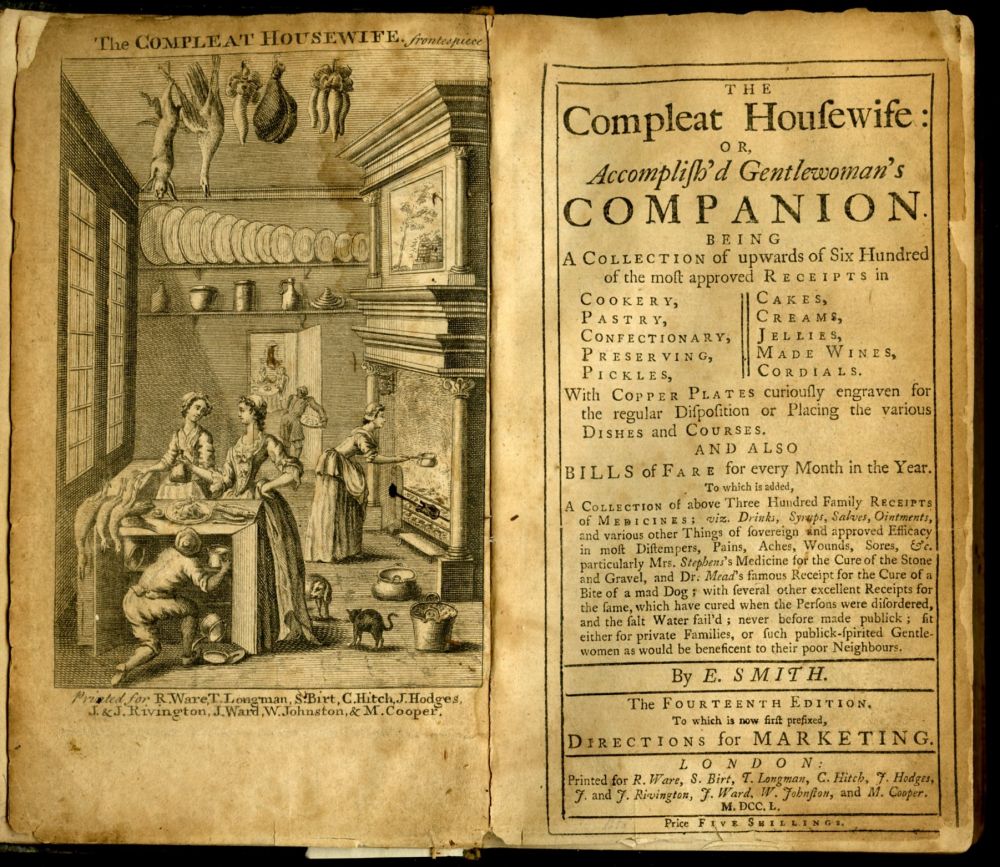
Samosa
A samosa () or singara is a fried Indian pastry with a savory filling, including ingredients such as spiced potatoes, onions, and peas. It may take different forms, including triangular, cone, or half-moon shapes, depending on the region. Samosas are often accompanied by chutney, and have origins in medieval times or earlier. Samosas are a popular entrée, appetizer, or snack in the cuisines of South Asia, the Middle East, Central Asia, East Africa and their South Asian diasporas. The English word ''samosa'' derives from Hindi word '' ( hi, समोसा), traceable to the Middle Persian word ()Lovely triangles '''', 23 August 2008. 'triangular pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Library
The British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom and is one of the largest libraries in the world. It is estimated to contain between 170 and 200 million items from many countries. As a legal deposit library, the British Library receives copies of all books produced in the United Kingdom and Ireland, including a significant proportion of overseas titles distributed in the UK. The Library is a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport. The British Library is a major research library, with items in many languages and in many formats, both print and digital: books, manuscripts, journals, newspapers, magazines, sound and music recordings, videos, play-scripts, patents, databases, maps, stamps, prints, drawings. The Library's collections include around 14 million books, along with substantial holdings of manuscripts and items dating as far back as 2000 BC. The library maintains a programme for content acquis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naskh (script)
Naskh ( ar, , qalam an-naskh, from the verb , , 'to copy', from n-s-kh root (ن-س-خ)) is a smaller, round script of Islamic calligraphy. Naskh is one of the first scripts of Islamic calligraphy to develop, commonly used in writing administrative documents and for transcribing books, including the Qur’an, because of its easy legibility. In his 1617 ''Grammatica Arabica'', Thomas van Erpe defined naskhī characters as the "noblest and true writing style". Origin Naskh style of writing can be found as early as within the first century of the Islamic calendar. Round scripts became the most popular in the eleventh, twelfth and thirteenth centuries, due to their use by scribes. Ibn Muqla is credited with standardizing the "Six Pens" of Islamic calligraphy, also including , , , , and . These are known as "the proportioned scripts" () or "the six scripts" (). Kufic is commonly believed to predate naskh, but historians have traced the two scripts as coexisting long before their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval India
Medieval India refers to a long period of Post-classical history of the Indian subcontinent between the "ancient period" and "modern period". It is usually regarded as running approximately from the breakup of the Gupta Empire in the 6th century CE to the start of the Early modern period in 1526 with the start of the Mughal Empire, although some historians regard it as both starting and finishing later than these points. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Medieval and Late Medieval eras. In the Early Medieval period, there were more than 40 different states on the Indian subcontinent, which hosted a variety of cultures, languages, writing systems, and religions. At the beginning of the time period, Buddhism was predominant throughout the area, with the short-lived Pala Empire on the Indo Gangetic Plain sponsoring the Buddhist faith's institutions. One such institution was the Buddhist Nalanda University in modern-day Bihar, India, a centre of scholars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Language
Persian (), also known by its endonym Farsi (, ', ), is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964) and Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate history in the cultural sphere of Greater Iran. It is written officially within Iran and Afghanistan in the Persian alphabet, a derivation of the Arabic script, and within Tajikistan in the Tajik alphabet, a der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malwa Sultanate
The Malwa Sultanate ( fa, ) (Pashto: ; ''lit: Mālwā Salṭanat'') was a late medieval Islamic sultanate in the Malwa, Malwa region, covering the present day Indian states of Madhya Pradesh and south-eastern Rajasthan from 1392 to 1562. It was founded by Dilawar Khan, an Afghan (ethnonym), Afghan governor of the Delhi Sultanate. Dilawar Khan had ceased to pay tribute to Delhi after 1392. Following Timur's invasion and the disintegration of the Delhi Sultanate, in 1401/2, Dilawar Khan made Malwa an independent realm. History The sultanate of Malwa was founded by Dilawar Khan, Dilawar Khan Ghuri, the governor of Malwa for the Delhi Sultanate, who asserted his independence in 1392, but did not actually assume the ensigns of royalty till 1401. Initially Dhar was the capital of the new kingdom, but soon it was shifted to Mandu, Madhya Pradesh, Mandu, which was renamed Shadiabad (the city of joy). After his death, he was succeeded by his son Hoshang Shah of Malwa, Alp Khan, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kheer
Kheer, also known as payasam, is a sweet dish and a type of wet pudding popular in the Indian subcontinent, usually made by boiling milk, sugar or jaggery, and rice, although rice may be substituted with one of the following: daals, bulgur wheat, millet, tapioca, vermicelli, or sweet corn. It is typically flavoured with desiccated coconut, cardamom, raisins, saffron, cashews, pistachios, almonds, or other dry fruits and nuts, and recently pseudograins are also gaining popularity. It is typically served as a dessert. Etymology The word ''kheer'' is derived from the Sanskrit word for milk, ''ksheer'' (क्षीर). Kheer is also the archaic name for sweet rice pudding. Origin Kheer was a part of the ancient Indian diet. According to the food historian K. T. Achaya, kheer or ''payas'', as it is known in southern India, was a popular dish in ancient India According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subconti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th-century Indian Books
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The 16th century is regarded by historians as the century which saw the rise of Western civilization and the Islamic gunpowder empires. The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a champion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cookbooks Of The Medieval Islamic World
A cookbook or cookery book is a kitchen reference containing recipes. Cookbooks may be general, or may specialize in a particular cuisine or category of food. Recipes in cookbooks are organized in various ways: by course (appetizer, first course, main course, dessert), by main ingredient, by cooking technique, alphabetically, by region or country, and so on. They may include illustrations of finished dishes and preparation steps; discussions of cooking techniques, advice on kitchen equipment, ingredients, and substitutions; historical and cultural notes; and so on. Cookbooks may be written by individual authors, who may be chefs, cooking teachers, or other food writers; they may be written by collectives; or they may be anonymous. They may be addressed to home cooks, to professional restaurant cooks, to institutional cooks, or to more specialized audiences. Some cookbooks are didactic, with detailed recipes addressed to beginners or people learning to cook particular dishes or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian-language Books
Persian (), also known by its endonym Farsi (, ', ), is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964) and Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate history in the cultural sphere of Greater Iran. It is written officially within Iran and Afghanistan in the Persian alphabet, a derivation of the Arabic script, and within Tajikistan in the Tajik alphabet, a derivatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Art
Persian art or Iranian art () has one of the richest art heritages in world history and has been strong in many media including architecture, painting, weaving, pottery, calligraphy, metalworking and sculpture. At different times, influences from the art of neighbouring civilizations have been very important, and latterly Persian art gave and received major influences as part of the wider styles of Islamic art. This article covers the art of Persia up to 1925, and the end of the Qajar dynasty; for later art see Iranian modern and contemporary art, and for traditional crafts see arts of Iran. Rock art in Iran is its most ancient surviving art. Iranian architecture is covered at that article. From the Achaemenid Empire of 550 BC–330 BC for most of the time a large Iranian-speaking state has ruled over areas similar to the modern boundaries of Iran, and often much wider areas, sometimes called Greater Iran, where a process of cultural Persianization left enduring results even w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |









.jpg)