|
Nikolski Air Station
Nikolski Air Station is an unattended airport located in Nikolski on Umnak Island in the Aleutians West Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska. This former military airport is now owned by The Aleut Corporation. Scheduled commercial airline passenger service is subsidized by the Essential Air Service program. Current service to Nikolski is provided by Grant Aviation from Unalaska. As per Federal Aviation Administration records, the airport had 165 passenger boardings (enplanements) in calendar year 2008, 219 enplanements in 2009, and 160 in 2010. History The airport was built in 1958 to support Nikolski Air Force Station, a Cold War United States Air Force Distant Early Warning Line radar station on Umnak Island. The station was operated by Detachment 1, 714th Aircraft Control and Warning Squadron based at Cold Bay Air Force Station, near Cold Bay, Alaska. The radar station was inactivated in September 1969, ending military use of the airport. The Air Force remediated the site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
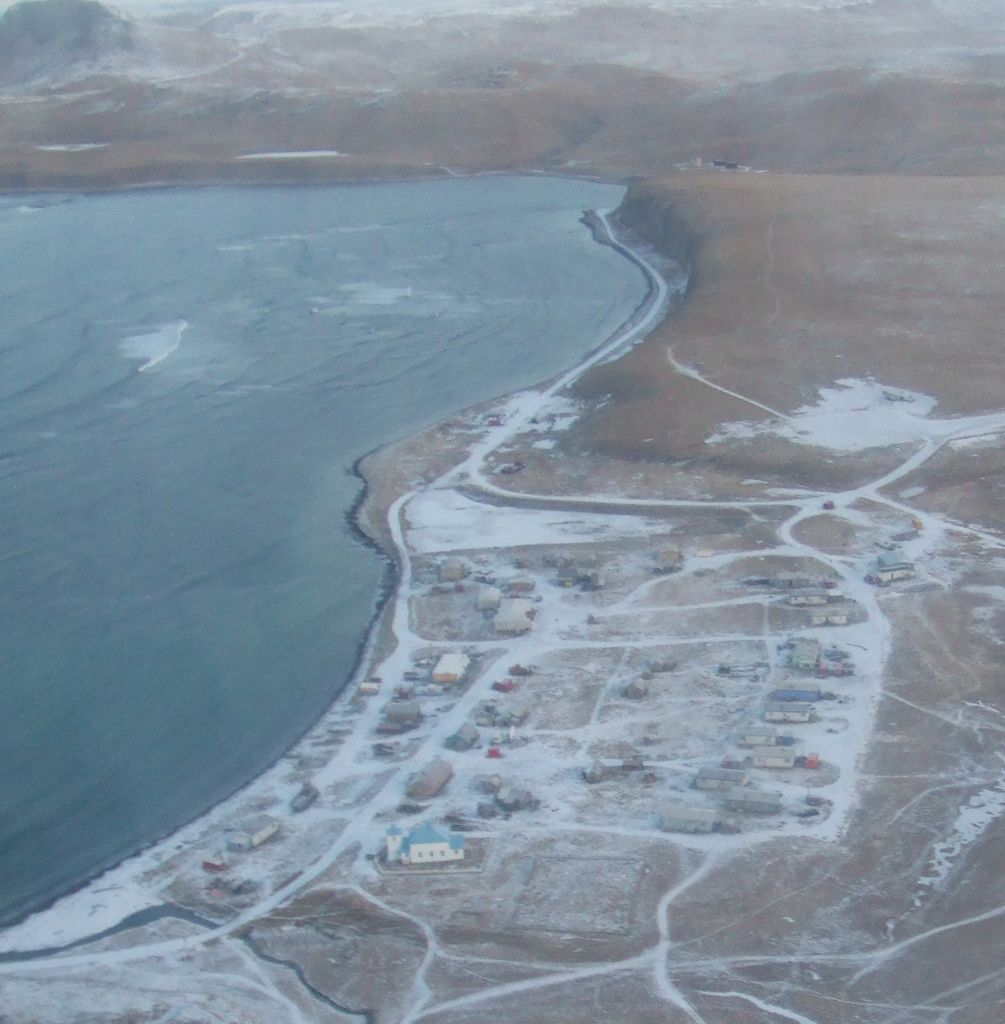
Nikolski, Alaska
Nikolski (''Chalukax̂'' in Aleut; russian: Никольский) is a census-designated place (CDP) on Umnak Island in Aleutians West Census Area, Alaska, United States. The population was 39 at the 2020 census, up from 18 in 2010. Nikolski is on Nikolski Bay, off the southwest end of the island. It is 116 air miles west of Unalaska, and 900 air miles from Anchorage. Residents are known as Unangan, and Aleut is spoken in most of the remaining homes. History The Aleutian Pribilof Islands Association reports that Nikolski is thought to be one of the oldest continuously-occupied communities in the world. Archaeological evidence from Ananiuliak Island, 5 km offshore in Nikolski Bay, dates human habitation to 8,500 years ago. A site known as Chaluka in Nikolski shows 4,000 years of virtually continuous occupation. Subsistence activities, sheep and cattle raising, and fishing are the main livelihoods and the latter has been traced back thousands of years by archaeologists, thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Bay, Alaska
Cold Bay ( ale, Udaamagax,; Sugpiaq language, Sugpiaq: ''Pualu'') is a city in Aleutians East Borough, Alaska, United States. As of the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census, the population was 108, but at the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census this had reduced to 50. Cold Bay is one of the main commercial centers of the Alaska Peninsula, which extends west towards the Aleutian Islands, and is home to Cold Bay Airport. History There is evidence of prehistoric occupation by Aleuts and later Russian encampments. Cold Bay's significance to American history began with the Japanese invasion of the Aleutians in World War II. General Simon Bolivar Buckner, Jr. ordered the creation of Fort Randall (Alaska), Fort Randall, an airbase on the shores of Cold Bay, in 1942 as a part of a general expansion of American assets in the Aleutians. It (along with Otter Point) served as a base for the 11th Air Force to provide protection to the only deep water port in the Aleutians at the time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Installations Of The United States Air Force In Alaska ) or political one
{{disambig ...
Installation may refer to: * Installation (computer programs) * Installation, work of installation art * Installation, military base * Installation, into an office, especially a religious (Installation (Christianity) Installation is a Christian liturgical act that formally inducts an incumbent into a new role at a particular place such as a cathedral. The term arises from the act of symbolically leading the incumbent to their stall or throne within the cathedra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airports In The Aleutians West Census Area, Alaska
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Operating airports is extremely complicated, with a complex system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for tourism and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
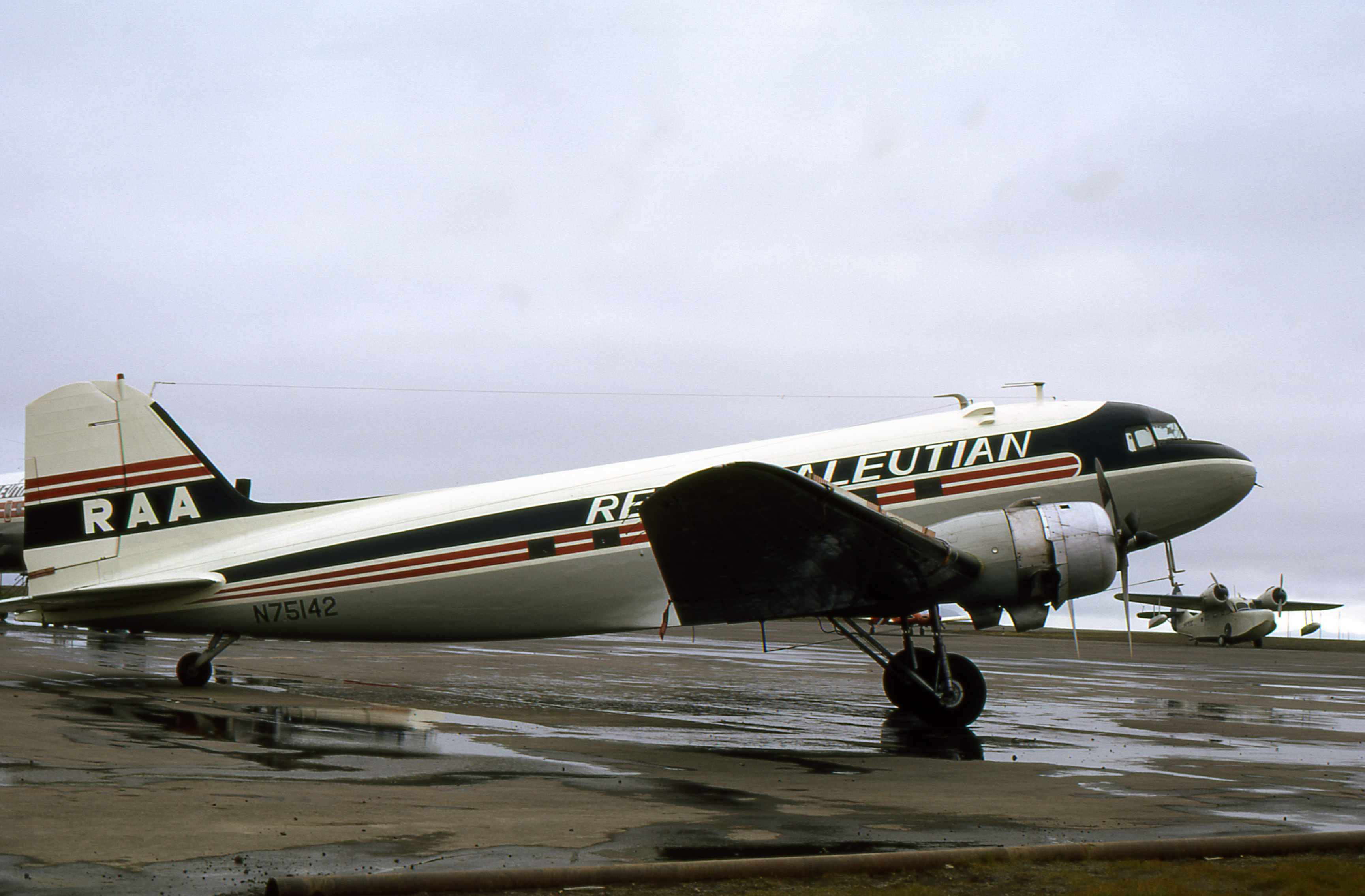
Douglas C-47A
The Douglas C-47 Skytrain or Dakota (RAF, RAAF, RCAF, RNZAF, and SAAF designation) is a military transport aircraft developed from the civilian Douglas DC-3 airliner. It was used extensively by the Allies during World War II and remained in front-line service with various military operators for many years.Parker 2013, pp. 13, 35, 37, 39, 45-47. Design and development The C-47 differed from the civilian DC-3 by way of numerous modifications, including being fitted with a cargo door, hoist attachment and strengthened floor - along with a shortened tail cone for glider-towing shackles, and an astrodome in the cabin roof.Wilson, Stewart. ''Aircraft of WWII''. Fyshwick, ACT, Australia: Aerospace Publications Pty Ltd., 1998. . During World War II, the armed forces of many countries used the C-47 and modified DC-3s for the transport of troops, cargo, and wounded. The U.S. naval designation was R4D. More than 10,000 aircraft were produced in Long Beach and Santa Monica, California, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reeve Aleutian Airways
Reeve Aleutian Airways was an airline headquartered in Anchorage, Alaska, United States. It ceased operations on December 5, 2000. History Founding In February 1946, Bob Reeve received a call informing him that some ex USAAF C-47s and Douglas DC-3s were for sale (the C-47 being the military version of the DC-3). Reeve bought his first DC-3 for $20,000 with $3,000 down and the balance payable over 3 years. The cost of conversion to civilian standard was quoted at $50,000 but Reeve did the work himself at a cost of $5,000. A strike by sailors on steamships operating between Seattle and Anchorage started on April 6, 1946. Reeve, along with Merritt Boyle and Bill Borland began flying between Seattle and Anchorage, with stops at Juneau, Yakutat or Annette Island. Each trip carried a full load of 21 passengers and took an average of hours. In 53 days, 26 round trips were made. Reeve would work all night on inspections and maintenance of the plane at Spokane, and then fly back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unalaska Airport
Tom Madsen (Dutch Harbor) Airport is a state-owned public-use airport in City of Unalaska, on Amaknak Island in the Aleutian Islands, off the coast of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located near the Bering Sea coast of Unalaska Island, southwest of Anchorage and from Seattle. The official name of the City of Unalaska's port is Dutch Harbor. That name is also applied to the portion of Unalaska on Amaknak Island, which is located across a bridge from the rest of the city on Unalaska Island. Therefore, the airport is sometimes referred to as Dutch Harbor Airport. In 2002, the State of Alaska renamed it Tom Madsen Airport in honor of Charles Thomas Madsen Sr., a bush pilot who was killed in an airplane accident that year. However, the Federal Aviation Administration still refers to it as Unalaska Airport. Scheduled commercial airline service was provided by PenAir, a code share partner of Alaska Airlines until October 2019, and prior to that Alaska Airlines operated Boeing 737-20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grant Aviation
Grant Aviation is a regional airline that serves the town of Kenai, the Yukon-Kuskokwim Delta, Bristol Bay, and the Aleutian Chain in Alaska, United States. The airline was formed in 1971 as Delta Air Services based in Emmonak, Alaska, Emmonak. The current owners are Bruce McGlasson and Mark "Woody" Richardson, who purchased the airline in 2004. The company slogan is "Fly Easy, Fly Grant." History Grant Aviation was established in 1971 as Delta Air Services in Emmonak. The name was changed to Grant Aviation in 1993. Throughout the company's early years, before organizations like LifeMed Alaska, Grant provided medevac services for many of the villages of the Yukon Kuskokwim Delta. Villages would call Grant for medevac services and Grant would then transport patients to receive emergency medical care. In October 1994, the village of Emmonak gave a Native owl mask to Grant Aviation in appreciation for numerous life-saving efforts in the villages of the Yukon River Delta. Later th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravel
Gravel is a loose aggregation of rock fragments. Gravel occurs naturally throughout the world as a result of sedimentary and erosive geologic processes; it is also produced in large quantities commercially as crushed stone. Gravel is classified by particle size range and includes size classes from granule- to boulder-sized fragments. In the Udden-Wentworth scale gravel is categorized into granular gravel () and pebble gravel (). ISO 14688 grades gravels as fine, medium, and coarse, with ranges 2–6.3 mm to 20–63 mm. One cubic metre of gravel typically weighs about 1,800 kg (or a cubic yard weighs about 3,000 lb). Gravel is an important commercial product, with a number of applications. Almost half of all gravel production is used as aggregate for concrete. Much of the rest is used for road construction, either in the road base or as the road surface (with or without asphalt or other binders.) Naturally occurring porous gravel deposits have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
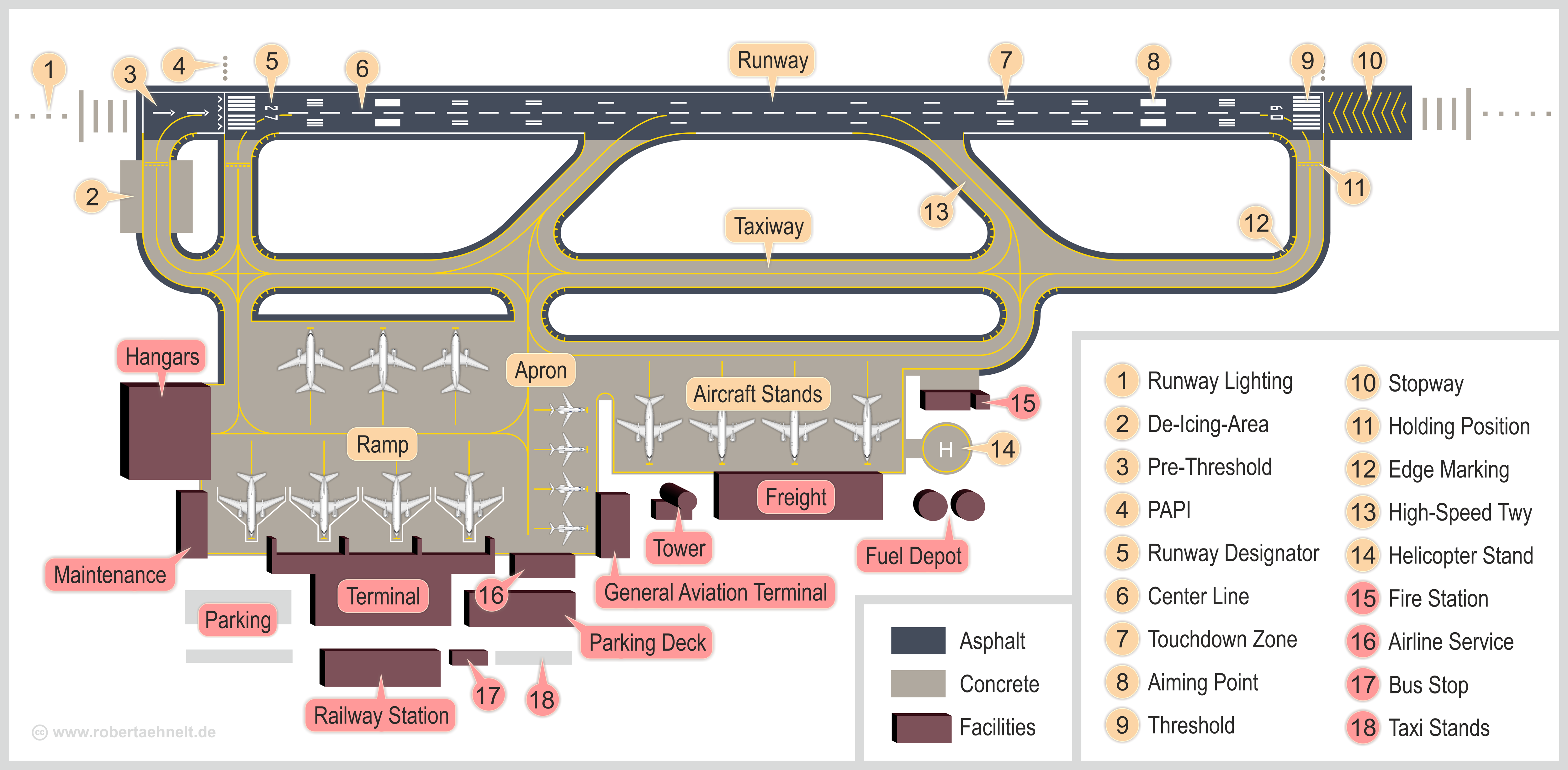
Runway
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt concrete, asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface (sod, grass, soil, dirt, gravel, ice, sand or road salt, salt). Runways, as well as taxiways and Airport apron, ramps, are sometimes referred to as "tarmac", though very few runways are built using Tarmacadam, tarmac. Takeoff and landing areas defined on the surface of water for seaplanes are generally referred to as waterways. Runway lengths are now International Civil Aviation Organization#Use of the International System of Units, commonly given in meters worldwide, except in North America where feet are commonly used. History In 1916, in a World War I war effort context, the first concrete-paved runway was built in Clermont-Ferrand in France, allowing local company Michelin to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Sea Level
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ..., especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value (magnitude (mathematics), magnitude and sign (mathematics), sign) of a given data set. For a data set, the ''arithmetic mean'', also known as "arithmetic average", is a measure of central tendency of a finite set of numbers: specifically, the sum of the values divided by the number of values. The arithmetic mean of a set of numbers ''x''1, ''x''2, ..., x''n'' is typically denoted using an overhead bar, \bar. If the data set were based on a series of observations obtained by sampling (statistics), sampling from a statistical population, the arithmetic mean is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

