|
Nikolsburg
Mikulov (; german: Nikolsburg; yi, ניקאלשבורג, ''Nikolshburg'') is a town in Břeclav District in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 7,400 inhabitants. The historic centre of Mikulov is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban monument reservation. Administrative parts Mikulov is made up of one administrative part. Geography Mikulov is located about northwest of Břeclav, on the border with Austria. It borders the Austrian municipality of Drasenhofen. Mikulov lies mostly in the Mikulov Highlands, but the municipal territory also extends into the Lower Morava Valley on the east and into the Dyje–Svratka Valley on the west. The highest point is the hill Turold with an elevation of . Most of the territory lies within the Pálava Protected Landscape Area. The Mušlovský and Včelínek streams flow through the territory and supply a set of ponds, the largest of them are Nový with an area of and Šibeník with . Other notable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasidic Dynasty
A Hasidic dynasty is a dynasty led by Hasidic Jewish spiritual leaders known as rebbes, and usually has some or all of the following characteristics: * Each leader of the dynasty is often known as an ''ADMOR'' (abbreviation for '' ADoneinu MOreinu veRabeinu'' – "our master, our teacher, and our rabbi"), or simply as ''Rebbe'' (or "the Rebbe"), and at times called the "Rav" ("rabbi"), and sometimes referred to in English as a "Grand Rabbi"; * The dynasty continues beyond the initial leader's lifetime by succession (usually by a family descendant); * The dynasty is usually named after a key town in Eastern Europe where the founder may have been born or lived, or where the group began to grow and flourish; * The dynasty has (or once had) followers who, through time, continue following successive leaders (rebbes), or may even continue as a group without a leader by following the precepts of a deceased leader. A Hasidic group has the following characteristics: * It was founded by a le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anabaptists
Anabaptism (from New Latin language, Neo-Latin , from the Greek language, Greek : 're-' and 'baptism', german: Täufer, earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re-baptizers"), considering it biased. The term (translation: "Baptizers") is now used, which is considered more impartial. From the perspective of their persecutors, the "Baptizers" baptized for the second time those "who as infants had already been baptized". The denigrative term Anabaptist, given to them by others, signifies rebaptizing and is considered a polemical term, so it has been dropped from use in modern German. However, in the English-speaking world, it is still used to distinguish the Baptizers more clearly from the Baptists, a Protestant sect that developed later in England. Compare their self-designation as "Brethren in Christ" or "Church of God": . is a Protestantism, Protestant List of Christian movements, Christian movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balthasar Hubmaier
Balthasar Hubmaier (1480 – 10 March 1528; la , Pacimontanus) was an influential German Anabaptist leader. He was one of the most well-known and respected Anabaptist theologians of the Reformation. Early life and education He was born in Friedberg, Bavaria in 1480. Information on his parentage is lacking. He attended Latin School at Augsburg, and entered the University of Freiburg on 1 May 1503. Insufficient funds caused him to leave the university and teach for a time at Schaffhausen, Switzerland. He returned to Freiburg in 1507 and received both a bachelor's and a master's degree in 1511. In 1512, he received a doctor's degree from the University of Ingolstadt under John Eck, and became the university's vice-rector by 1515. Hubmaier's fame as a pulpiteer was widespread. He left the University of Ingolstadt for a pastorate of the Roman Catholic church at Regensburg in 1516. After Maximilian I's death in 1519, Hubmaier helped orchestrate a violent pogrom against Regensburg' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely Family Of Liechtenstein
The House of Liechtenstein, from which the principality takes its name, is the family which reigns by hereditary right over the principality of Liechtenstein. Only dynastic members of the family are eligible to inherit the throne. The dynasty's membership, rights and responsibilities are defined by a law of the family, which is enforced by the reigning prince and may be altered by vote among the family's dynasts, but which may not be altered by the Government or Parliament of Liechtenstein.Princely House of Liechtenstein. House Laws' History The family originates from Liechtenstein Castle in Lower Austria (near Vienna), which the family possessed from at least 1140 to the 13th century, and from 1807 onwards. Heinrich I von Liechtenstein (d. 1265) was lord of Nikolsburg, Liechtenstein and Petronell. Through the centuries, the dynasty acquired vast swathes of land, predominantly in Moravia, Lower Austria, Silesia and Styria, though in all cases, these territories were held in fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
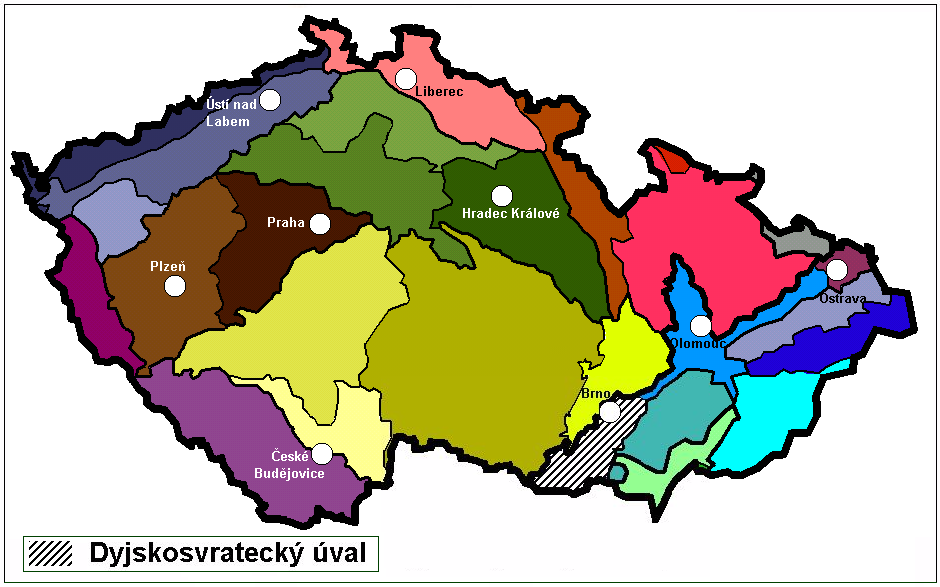
Dyje–Svratka Valley
The Dyje–Svratka Valley ( cs, Dyjsko-svratecký úval, german: Thaya-Schwarza Talsenke) is a geomorphological feature (a special type of vale) in South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. History The Dyje–Svratka Valley has been a natural pass between the Vienna Basin (Carpathians) and the Vyškov Gate, the Upper Morava Valley, Moravian Gate and later, the North European Plain (Poland - Lower Silesia - Galicia) since ancient times. It served as an arm of several important trade routes from southern Europe to the Baltic Sea such as the Amber Road, as well as routes from Moravia to Upper Silesia and Lesser Poland. The Emperor Ferdinand Northern Railway from Břeclav to Brno traverses the Dyje–Svratka Valley. Geography The floodplains of several rivers end in the Dyje–Svratka Valley, including Svratka, Jihlava, Svitava, Thaya, Jevišovka and Litava. Many towns are located within it, including the southern districts of Brno, Slavkov u Brna, Židlochovice, Pohořel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Swiss Confederacy
The Old Swiss Confederacy or Swiss Confederacy (German language, Modern German: ; historically , after the Swiss Reformation, Reformation also , "Confederation of the Swiss") was a loose confederation of independent small states (, German or In the charters of the 14th century described as "communities" (, ), the German term ''Orte'' becomes common in the early 15th century, used alongside "estate" after the Reformation. The French term is used in Fribourg in 1475, and after 1490 is increasingly used in French and Italian documents. It only enters occasional German usage after 1648, and only gains official status as synonym of with the Act of Mediation of 1803. ), initially within the Holy Roman Empire. It is the precursor of the modern state of Switzerland. It formed during the 14th century, from a foundation of the Old Swiss Confederacy, nucleus in what is now Central Switzerland, growth of the Old Swiss Confederacy, expanding to include the cities of Zürich and Bern by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Bohemians
German Bohemians (german: Deutschböhmen und Deutschmährer, i.e. German Bohemians and German Moravians), later known as Sudeten Germans, were ethnic Germans living in the Czech lands of the Bohemian Crown, which later became an integral part of Czechoslovakia. Before 1945, over three million German Bohemians constituted about 23% of the population of the whole country and about 29.5% of the population of Bohemia and Moravia. Ethnic Germans migrated into the Kingdom of Bohemia, an electoral territory of the Holy Roman Empire, from the 11th century, mostly in the border regions of what was later called the "Sudetenland", which was named after the Sudeten Mountains. The process of German expansion was known as ''Ostsiedlung'' ("Settling of the East"). The name "Sudeten Germans" was adopted during rising nationalism after the fall of Austria-Hungary after the First World War. After the Munich Agreement, the so-called Sudetenland became part of Germany. After the Second World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Rights
A market town is a settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rural towns with a hinterland of villages are still commonly called market towns, as sometimes reflected in their names (e.g. Downham Market, Market Rasen, or Market Drayton). Modern markets are often in special halls, but this is a recent development, and the rise of permanent retail establishments has reduced the need for periodic markets. Historically the markets were open-air, held in what is usually called (regardless of its actual shape) the market square (or "Market Place" etc), and centred on a market cross ( mercat cross in Scotland). They were and are typically open one or two days a week. History The primary purpose of a market town is the provision of goods and services to the surrounding locality. Although market towns were k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
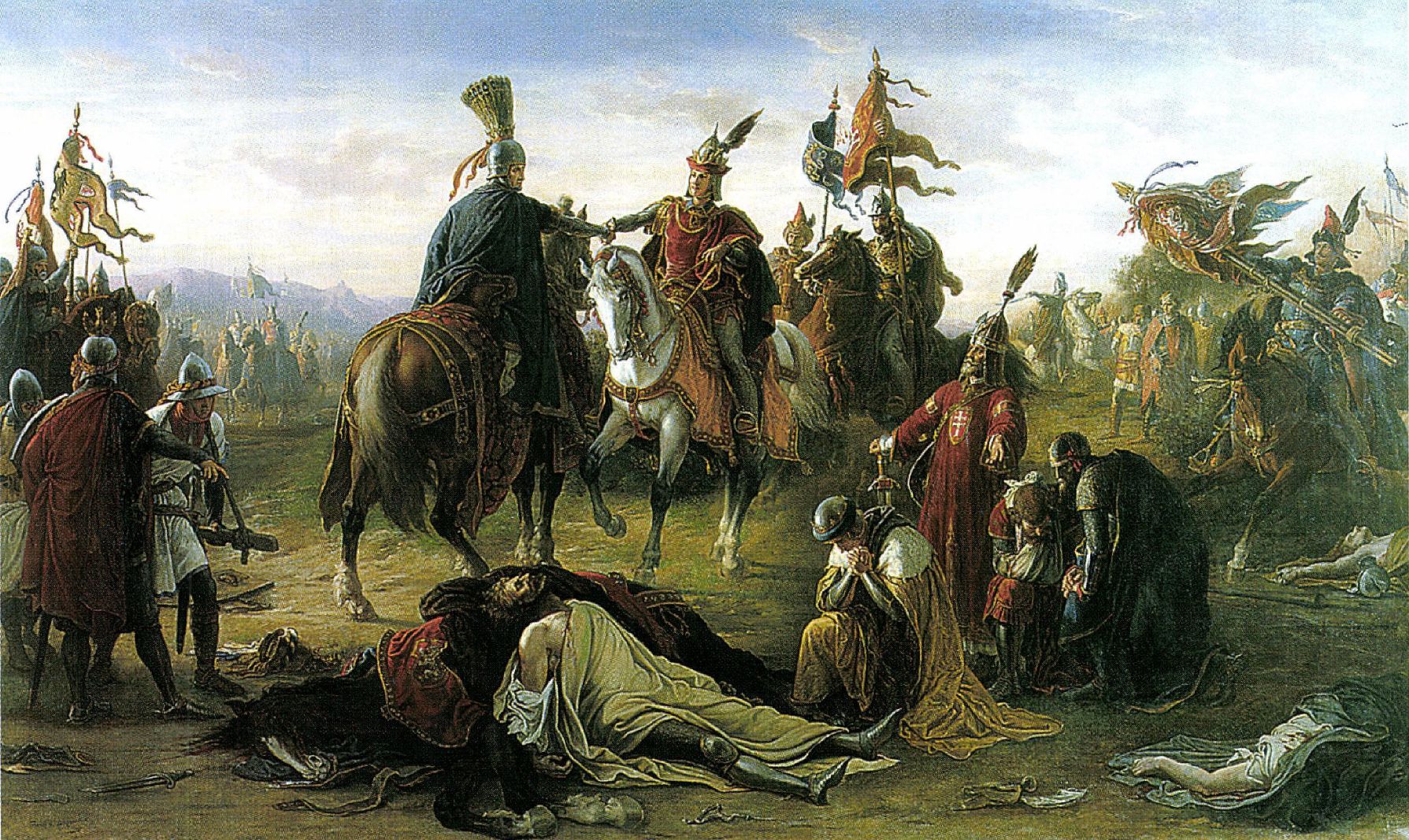
Battle On The Marchfeld
The Battle on the Marchfeld (''i.e. Morava Field''; german: Schlacht auf dem Marchfeld; cs, Bitva na Moravském poli; hu, Morvamezei csata) at Dürnkrut and Jedenspeigen took place on 26 August 1278 and was a decisive event for the history of Central Europe for the following centuries. The opponents were a Bohemian (Czech) army led by the Přemyslid king Ottokar II of Bohemia and the German army under the German king Rudolph I of Habsburg in alliance with King Ladislaus IV of Hungary. With 15,300 mounted troops, it was one of the largest cavalry battles in Central Europe during the Middle Ages. The Hungarian cavalry played a significant role in the outcome of the battle. King Ottokar II of Bohemia expanded his territories considerably from 1250 to 1273, but suffered a devastating defeat in November 1276, when the newly elected German king Rudolph I of Habsburg imposed the Imperial ban on Ottokar, declaring him an outlaw and took over Ottokar's holdings in Austria, Carinthia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf I Of Germany
Rudolf I (1 May 1218 – 15 July 1291) was the first King of Germany from the House of Habsburg. The first of the count-kings of Germany, he reigned from 1273 until his death. Rudolf's election marked the end of the Great Interregnum which had begun after the death of the Hohenstaufen Emperor Frederick II in 1250. Originally a Swabian count, he was the first Habsburg to acquire the duchies of Austria and Styria in opposition to his mighty rival, the Přemyslid king Ottokar II of Bohemia, whom he defeated in the 1278 Battle on the Marchfeld. The territories remained under Habsburg rule for more than 600 years, forming the core of the Habsburg monarchy and the present-day country of Austria. Rudolf played a vital role in raising the comital House of Habsburg to the rank of Imperial princes. Early life Rudolf was born on 1 May 1218 at Limburgh Castle near Sasbach am Kaiserstuhl in the Breisgau region of present-day southwestern Germany. He was the son of Count Albert IV of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Austria
The Duchy of Austria (german: Herzogtum Österreich) was a medieval principality of the Holy Roman Empire, established in 1156 by the ''Privilegium Minus'', when the Margraviate of Austria (''Ostarrîchi'') was detached from Bavaria and elevated to a duchy in its own right. After the ruling dukes of the House of Babenberg became extinct in male line, there was as much as three decades of rivalry on inheritance and rulership, until the German king Rudolf I took over the dominion as the first monarch of the Habsburg dynasty in 1276. Thereafter, Austria became the patrimony and ancestral homeland of the dynasty and the nucleus of the Habsburg monarchy. In 1453, the archducal title of the Austrian rulers, invented by Duke Rudolf IV in the forged ''Privilegium Maius'' of 1359, was officially acknowledged by the Habsburg emperor Frederick III. Geography Initially, the duchy was comparatively small in area, roughly comprising the modern-day Austrian state of Lower Austria. As a forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottokar II Of Bohemia
Ottokar II ( cs, Přemysl Otakar II.; , in Městec Králové, Bohemia – 26 August 1278, in Dürnkrut, Lower Austria), the Iron and Golden King, was a member of the Přemyslid dynasty who reigned as King of Bohemia from 1253 until his death in 1278. He also held the titles of Margrave of Moravia from 1247, Duke of Austria from 1251, and Duke of Styria from 1260, as well as Duke of Carinthia and landgrave of Carniola from 1269. With Ottokar's rule, the Přemyslids reached the peak of their power in the Holy Roman Empire. His expectations of the imperial crown, however, were never fulfilled. Ottokar was the second son of King Wenceslaus I of Bohemia (reigned 1230–1253). Through his mother, Kunigunde, daughter of Philip of Swabia, he was related to the Holy Roman Emperors of the Hohenstaufen dynasty, which became extinct in the male line upon the execution of King Conradin of Sicily in 1268. Named after his grandfather King Přemysl Ottokar I, he was originally educate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_c1640_Rudolf_I.jpg)
.png)
