|
Nike Of Callimachus
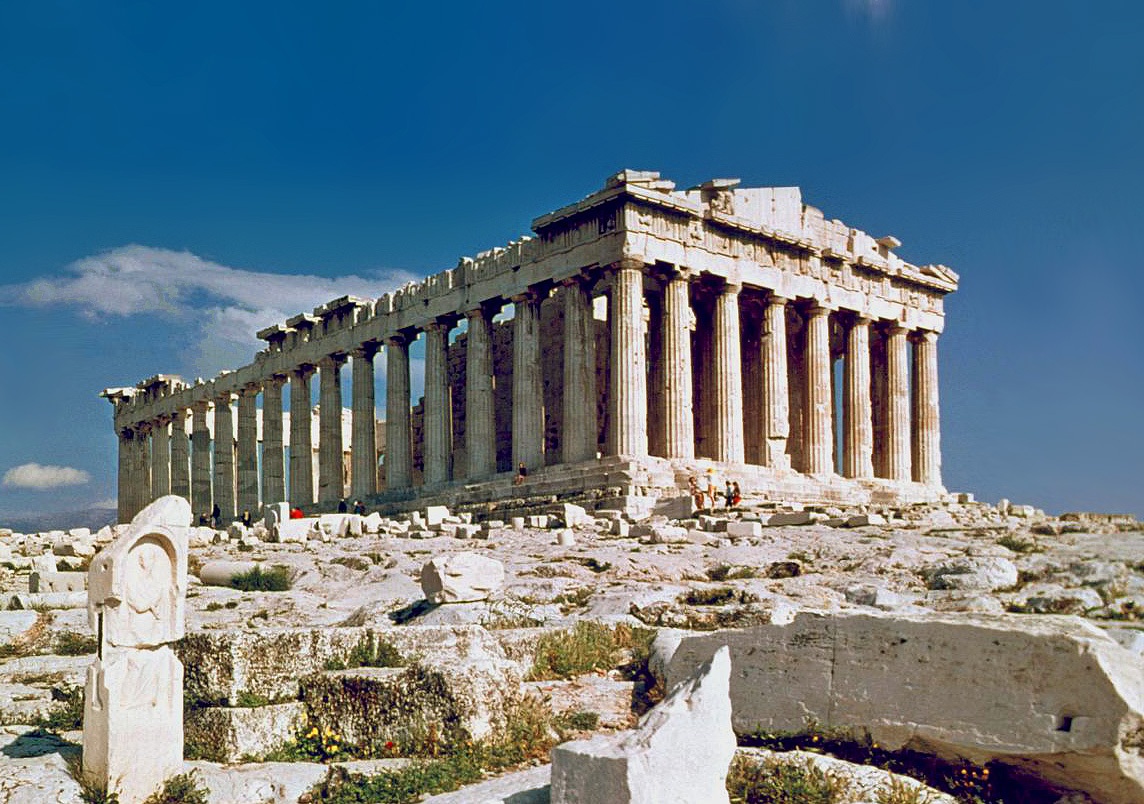
The Nike of Callimachus ( el, Nίκη του Καλλιμάχου ''Níki tou Kallimákhou'') also known as The Dedication of Callimachus, is a statue that the Athenians created in honour of Callimachus. History Callimachus was the Athenian polemarch at the Battle of Marathon at 490 BC. He had the last vote and voted in favour of a battle, when the ten strategoi were split evenly on the matter. He was killed at the battle and the Athenians erected the statue for him. The statue was erected in a prominent spot near the north-west corner of the Parthenon (not the Parthenon that we can see today, but the previous temple which was destroyed by the Persians) on the Acropolis of Athens. The statue was severely damaged by the Persians a decade later (480 BC) when they conquered Athens. They burned and destroyed the city and its monuments, including the Nike of Callimachus (Perserschutt). Statue The statue depicts Nike (Victory), in the form of a draped woman with wings running ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite. Marble is typically not Foliation (geology), foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphosed limestone, but its use in stonemasonry more broadly encompasses unmetamorphosed limestone. Marble is commonly used for Marble sculpture, sculpture and as a building material. Etymology The word "marble" derives from the Ancient Greek (), from (), "crystalline rock, shining stone", perhaps from the verb (), "to flash, sparkle, gleam"; Robert S. P. Beekes, R. S. P. Beekes has suggested that a "Pre-Greek origin is probable". This Stem (linguistics), stem is also the ancestor of the English language, English word "marmoreal," meaning "marble-like." While the English term "marble" resembles the French language, French , most other European languages (with words like "marmoreal") more closely resemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
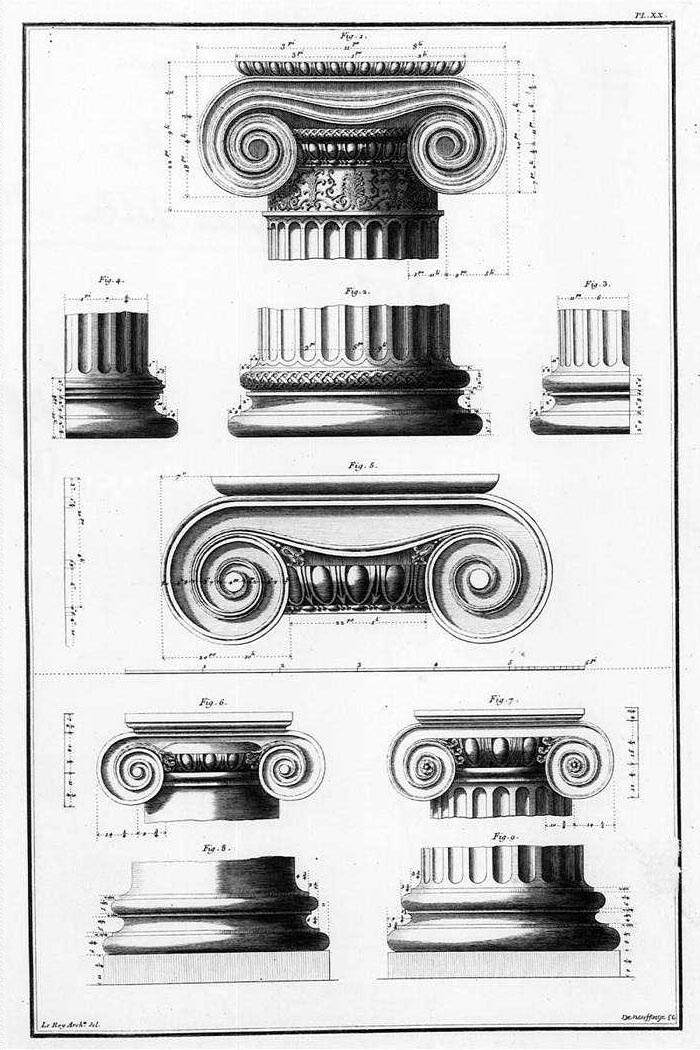
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Sculpture
The sculpture of ancient Greece is the main surviving type of fine ancient Greek art as, with the exception of painted ancient Greek pottery, almost no ancient Greek painting survives. Modern scholarship identifies three major stages in monumental sculpture in bronze and stone: the Archaic (from about 650 to 480 BC), Classical (480–323) and Hellenistic. At all periods there were great numbers of Greek terracotta figurines and small sculptures in metal and other materials. The Greeks decided very early on that the human form was the most important subject for artistic endeavour. Seeing their gods as having human form, there was little distinction between the sacred and the secular in art—the human body was both secular and sacred. A male nude of Apollo or Heracles had only slight differences in treatment to one of that year's Olympic boxing champion. The statue, originally single but by the Hellenistic period often in groups was the dominant form, though reliefs, often so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Culture
The culture of Greece has evolved over thousands of years, beginning in Minoan and later in Mycenaean Greece, continuing most notably into Classical Greece, while influencing the Roman Empire and its successor the Byzantine Empire. Other cultures and states such as the Frankish states, the Ottoman Empire, the Venetian Republic and Bavarian and Danish monarchies have also left their influence on modern Greek culture, but historians credit the Greek War of Independence with revitalising Greece and giving birth to a single entity of its multi-faceted culture. Greece is widely considered to be the cradle of Western culture and democracy. Modern democracies owe a debt to Greek beliefs in government by the people, trial by jury, and equality under the law. The ancient Greeks pioneered in many fields that rely on systematic thought, including biology, geometry, history, philosophy, and physics. They introduced such important literary forms as epic and lyric poetry, history, trage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Culture
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and other territories. Most of these regions were officially unified only once, for 13 years, under Alexander the Great's empire from 336 to 323 BC (though this excludes a number of Greek city-states free from Alexander's jurisdiction in the western Mediterranean, around the Black Sea, Cyprus, and Cyrenaica). In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Roughly three centuries after the Late Bronze Age collapse of Mycenaean Greece, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical Greec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Destruction Of Athens
The Achaemenid destruction of Athens was accomplished by the Achaemenid Army of Xerxes I during the Second Persian invasion of Greece, and occurred in two phases over a period of two years, in 480–479 BCE. First phase: Xerxes I (480 BCE) In 480 BCE, after the victory of Xerxes I at the Battle of Thermopylae, all of Boeotia fell to the Achaemenid Army. The two cities that had resisted Xerxes, Thespiae and Plataea, were captured and razed. Attica was also left open to invasion, and the remaining population of Athens was thus evacuated, with the aid of the Allied fleet, to Salamis Island, Salamis. The Peloponnesian Allies began to prepare a defensive line across the Isthmus of Corinth, building a wall, and demolishing the road from Megara, thereby abandoning Athens to the Persians. Athens fell a first time in September 480 BCE. The small number of Athenians who had barricaded themselves on the Acropolis of Athens, Acropolis were eventually defeated, and Xerxes then ordered Athens t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carian Coinage Device At The Time Of Artemisia I
The Carian language is an extinct language of the Luwic subgroup of the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family. The Carian language was spoken in Caria, a region of western Anatolia between the ancient regions of Lycia and Lydia, by the Carians, a name possibly first mentioned in Hittite sources. Carian is closely related to Lycian and Milyan (Lycian B), and both are closely related to, though not direct descendants of, Luwian. Whether the correspondences between Luwian, Carian, and Lycian are due to direct descent (i.e. a language family as represented by a tree-model), or are due to the effects of a sprachbund, is disputed. Sources Carian is known from these sources: * Nearly 40 inscriptions from Caria including five Carian-Greek bilinguals (however, only for two of them the connection between the Carian and Greek text is evident) * Two inscriptions from mainland Greece: a bilingual from Athens and a graffito from Thessaloniki * 60 funeral inscriptions of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miltiades
Miltiades (; grc-gre, Μιλτιάδης; c. 550 – 489 BC), also known as Miltiades the Younger, was a Greek Athenian citizen known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon, as well as for his downfall afterwards. He was the son of Cimon Coalemos, a renowned Olympic chariot-racer, and the father of Cimon, the noted Athenian statesman. Family Miltiades was a well-born Athenian, and considered himself a member of the Aeacidae, as well as a member of the prominent Philaid clan. He came of age during the tyranny of the Peisistratids. His family was prominent, due in good part to their success with Olympic chariot-racing.Creasy (1880) pg. 9 Plutarch claimed that Cimon, Miltiades' father, was known as "Coalemos", meaning "simpleton", because he had a reputation for being rough around the edges, but whose three successive chariot-racing victories at the Olympics made him popular, so popular in fact that, Herodotus claims, the sons of Peisistratos murdered him out of jeal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Culture And Tourism (Greece)
The Ministry of Culture and Sports ( el, Υπουργείο Πολιτισμού και Αθλητισμού) is the government department of Greece entrusted with preserving the country's cultural heritage, promoting the arts, and overseeing sport through the subordinate General Secretariat for Sports. The incumbent minister is Lina Mendoni. The Deputy Minister for Modern Culture is Nicholas Yatromanolakis, and the Deputy Minister for Sports is . History This ministry was established in 1971 as the Ministry of Culture and Sciences () and it was renamed the Ministry of Culture () on 26 July 1985. On 7 October 2009, it was merged with the Ministry of Touristic Development to form the Ministry of Culture and Tourism (). It ceased to exist on 21 June 2012, when the Ministry of Tourism was re-established and the culture portfolio was absorbed by the Ministry of Education, Lifelong Learning and Religious Affairs to form the Ministry of Education, Religious Affairs, Culture and Sports ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nike Callimachus
Nike often refers to: * Nike (mythology), a Greek goddess who personifies victory * Nike, Inc., a major American producer of athletic shoes, apparel, and sports equipment Nike may also refer to: People * Nike (name), a surname and feminine given name *Nike, daughter of Shahrbaraz Arts, entertainment, and media * Nike Award, a Polish language literature prize *''Nike of Samothrace'', an ancient statue of the goddess Nike *Nike of Callimachus, an ancient statue of the goddess Nike * "Nikes" (song), by Frank Ocean from the album ''Blonde'' (2016) Military * Project Nike, a US Army missile project ** MIM-3 Nike Ajax, a solid fuel–propelled surface-to-air missile ** MIM-14 Nike-Hercules, a solid fuel–propelled surface-to-air missile ** Nike (rocket stage) ** Various US sounding rockets named after the upper stage used, including: *** Nike Apache *** Nike-Asp *** Nike-Cajun *** Nike-Deacon *** Nike Hawk *** Nike Hydac *** Nike Iroquois *** Nike Javelin *** Nike Malemute *** Nike ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Olympus
Mount Olympus (; el, Όλυμπος, Ólympos, also , ) is the highest mountain in Greece. It is part of the Olympus massif near the Thermaic Gulf of the Aegean Sea, located in the Olympus Range on the border between Thessaly and Macedonia, between the regional units of Larissa and Pieria, about southwest from Thessaloniki. Mount Olympus has 52 peaks and deep gorges. The highest peak, Mytikas (Μύτικας ''Mýtikas''), meaning "nose", rises to . It is one of the highest peaks in Europe in terms of topographic prominence. In Greek mythology, Olympus is the home of the Greek gods, on Mytikas peak. The mountain has exceptional biodiversity and rich flora. It has been a National Park, the first in Greece, since 1938. It is also a World Biosphere Reserve. Every year, thousands of visitors admire its fauna and flora, tour its slopes, and climb its peaks. Organized mountain refuges and various mountaineering and climbing routes are available. The usual starting point for cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphidna
Aphidna ( grc, Ἄφιδνα) or Aphidnae or Aphidnai (Ἀφίδναι) was one of the twelve ancient towns of ancient Attica. It was celebrated in the mythical period as the place where Theseus deposited Helen of Troy, entrusting her to the care of his friend Aphidnus. When the Dioscuri invaded Attica in search of their sister, the inhabitants of Deceleia informed the Lacedaemonians where Helen was concealed, and showed them the way to Aphidna. The Dioscuri thereupon took the town, and carried off their sister. We learn, from a decree quoted by Demosthenes, that Aphidna was, in his time, a fortified town, and at a greater distance than 120 stadia from Athens. As an Attic deme, it belonged in succession to the tribes Aeantis, Leontis, Ptolemais, and Hadrianis. The site of Aphidna is located at Kotroni near the modern town of Afidnes. Archaeological excavations at Aphidia History of excavations The first Swedish fieldwork in Greece took place between June and August 1894 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)