|
Niiname-no-Matsuri
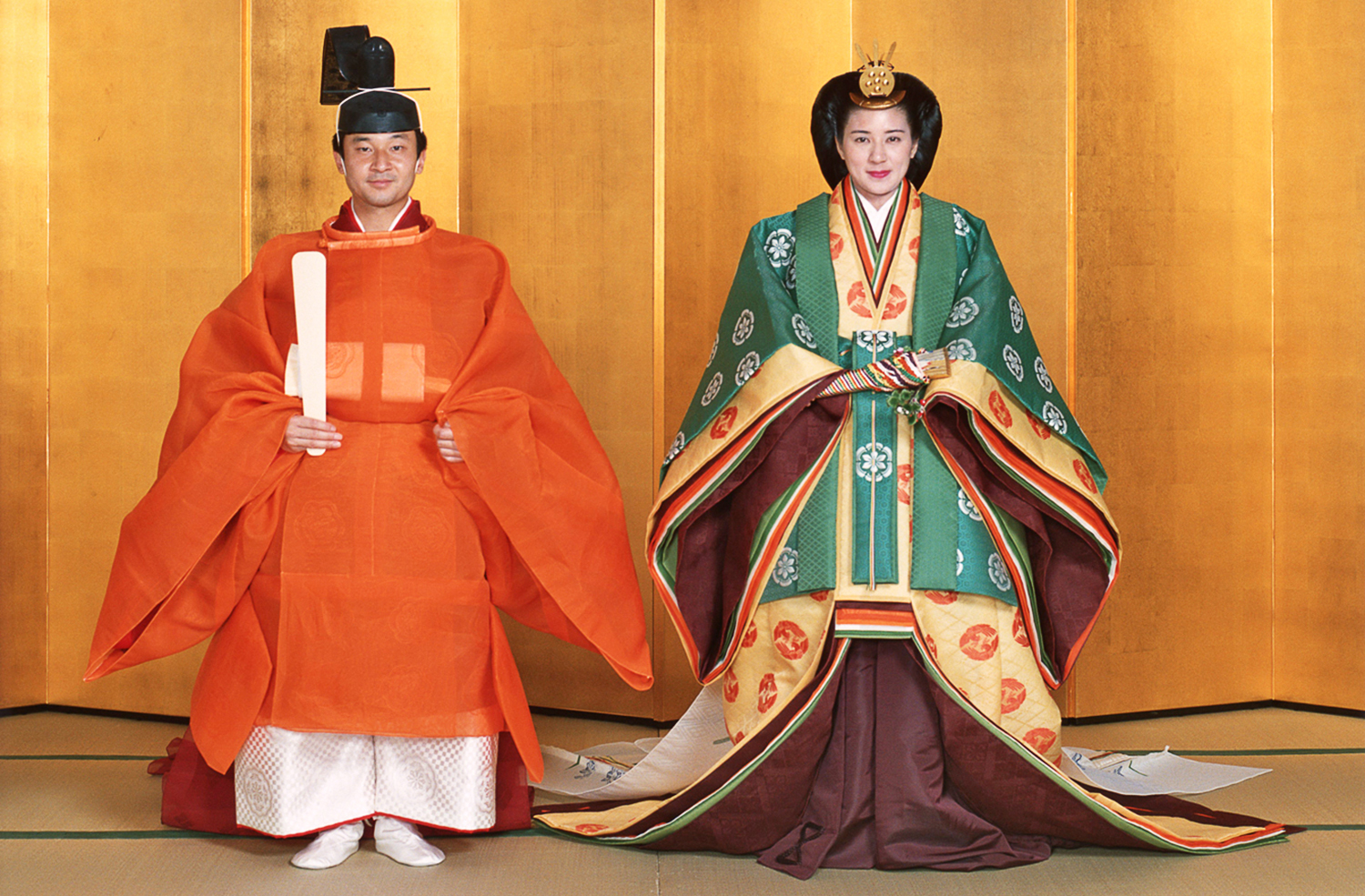
The Niiname-sai (新嘗祭, also read Shinjō-sai and Niiname-no-Matsuri) is a Japanese harvest festival, harvest ritual. The ritual is celebrated by the Emperor of Japan, who thanks the Shinto deities for a prosperous year and prays for a fruitful new year. It takes place near the Three Palace Sanctuaries of in the imperial palace and several large Shinto shrines. The first Niiname-sai for a new emperor is known as the Daijō-sai (大嘗祭), and is part of his Enthronement of the Japanese emperor, enthronement ceremonies. In pre-modern Japan, the date of the Niiname-sai was moveable, taking place on the last rabbit (zodiac), Day of the Rabbit of the eleventh month of the old Japanese lunar calendar, but in the Meiji period the date was fixed at November 23, and this date became a national holiday, Labor Thanksgiving Day, in the Shōwa period after World War II. Ceremony During the Niiname-sai, an ancient Shinto ritual that says thanks for the crops of the previous year and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvest Festival
A harvest festival is an annual celebration that occurs around the time of the main harvest of a given region. Given the differences in climate and crops around the world, harvest festivals can be found at various times at different places. Harvest festivals typically feature feasting, both family and public, with foods that are drawn from crops. In Britain, thanks have been given for successful harvests since pagan times. Harvest festivals are held in September or October depending on local tradition. The modern Harvest Festival celebrations include singing hymns, praying, and decorating churches with baskets of fruit and food in the festival known as Harvest Festival, Harvest Home, Harvest Thanksgiving or Harvest Festival of Thanksgiving. In British and English-Caribbean churches, chapels and schools, and some Canadian churches, people bring in produce from the garden, the allotment or farm. The food is often distributed among the poor and senior citizens of the loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbit (zodiac)
The rabbit ( 兔) is the fourth in the twelve-year cycle of animals that appear in the Chinese zodiac related to the Chinese calendar. The Year of the Rabbit is associated with the Earthly Branch symbol 卯. In the Vietnamese zodiac and the Gurung zodiac, the cat takes the place of the rabbit. In the Malay zodiac, the mousedeer takes the place of the rabbit. Years and elements People born within these date ranges can be said to have been born in the "Year of the Rabbit", while also bearing the following elemental sign: Basic astrological associations See also *Rabbit *Niiname-no-Matsuri The Niiname-sai (新嘗祭, also read Shinjō-sai and Niiname-no-Matsuri) is a Japanese harvest ritual. The ritual is celebrated by the Emperor of Japan, who thanks the Shinto deities for a prosperous year and prays for a fruitful new year. It ta ... References External links * {{Chinese Zodiac Chinese astrological signs Mythological rabbits and hares de:Chinesische Astrologie# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labor Thanksgiving Day
is an annual public holiday in Japan celebrated on November 23 of each year, unless that day falls on a Sunday, in which case the holiday is moved to Monday. The law establishing the holiday cites it as an occasion to respect labor, to celebrate production, and citizens give each other thanks. Events are held throughout Japan, one such being the Nagano Ebisuko Fireworks Festival (長野えびす講煙火大会), which had 400,000 attendees in 2017. History Labor Thanksgiving Day is the modern name for an ancient harvest festival known as , celebrating the harvest of the Five Cereals. The classical chronicle the '' Nihon Shoki'' mentions a harvest ritual having taken place during the reign of the legendary Emperor Jimmu (660–585 BC), as well as more formalized harvest celebrations during the reign of Emperor Seinei (480–484 AD). Modern scholars can date the basic forms of ''niiname-sai'' to the time of Emperor Tenmu (667–686 AD). Traditionally, it celebrated the year's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Calendar
Japanese calendar types have included a range of official and unofficial systems. At present, Japan uses the Gregorian calendar together with year designations stating the year of the reign of the current Emperor. The written form starts with the year, then the month and finally the day, coinciding with the ISO 8601 standard. For example, February 16, 2003 can be written as either 2003年2月16日 or 平成15年2月16日 (the latter following the regnal year system). 年 reads ''nen'' and means "year", 月 reads ''gatsu'' or 「がつ」and means "month" and finally 日 (usually) reads ''nichi'' (its pronunciation depends on the number that precedes it, see below) and means "day". Prior to the introduction of the Gregorian calendar in 1873, the reference calendar was based on the lunisolar Chinese calendar. History The lunisolar Chinese calendar was introduced to Japan via Korea in the middle of the sixth century. After that, Japan calculated its calendar using various Chine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogakukan
is a Japanese publisher of dictionaries, literature, comics (manga), non-fiction, DVDs, and other media in Japan. Shogakukan founded Shueisha, which also founded Hakusensha. These are three separate companies, but are together called the Hitotsubashi Group, one of the largest publishing groups in Japan. Shogakukan is headquartered in the Shogakukan Building in Hitotsubashi, part of Kanda, Chiyoda, Tokyo, near the Jimbocho book district. The corporation also has the other two companies located in the same ward. International operations In the United States Shogakukan, along with Shueisha, owns Viz Media, which publishes manga from both companies in the United States. Shogakukan's licensing arm in North America was ShoPro Entertainment; it was merged into Viz Media in 2005. Shogakukan's production arm is Shogakukan-Shueisha Productions (previously Shogakukan Productions Co., Ltd.) In March 2010 it was announced that Shogakukan would partner with the American comics publish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daijisen
The is a general-purpose Japanese dictionary published by Shogakukan in 1995 and 1998. It was designed as an "all-in-one" dictionary for native speakers of Japanese, especially high school and university students. History Shogakukan intended for the to directly compete with Iwanami's popular desktop dictionary, which was a bestseller through three editions (1955, 1969 and 1983). The followed upon the success of two other competitors, Sanseido's ("Great forest of words", 1988, 1995, 2006) and Kōdansha's color-illustrated ("Great dictionary of Japanese", 1989, 1995). All of these dictionaries weigh around and have about 3000 pages. The 1st edition of the (1995) included over 220,000 entries and 6000 all-color illustrations and photographs. The chief editor was also chief editor of the directly-competing dictionary. Other editors included , , and . Shogakukan also released a CD-ROM version (1997) of the 1st edition. The "enlarged and revised" edition (1998) was more of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc
An encyclopedia (American English) or encyclopædia (British English) is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge either general or special to a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles or entries that are arranged alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on '' factual information'' concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammatical forms.Béjoint, Henri (2000)''Modern Lexicography'', pp. 30–31. Oxford University Press. Encyclopedias have existed for around 2,000 years and have evolved considerably during that time as regards language (written in a major international or a verna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Imperial Rituals
Rituals of the Imperial Family describes various Rituals related to the Emperor (the Emperor and the Imperial Family). Of these, ceremonies related to the Emperor can be divided into two categories: national acts as stipulated in Article 7 of the Japanese Constitution, and official acts that do not fall under this category. Pregnancy-Birth Gochaku obi A ceremony held on the day of the dog, the ninth month of pregnancy, for female members of the Imperial Family who have conceived a child, to pray for a safe delivery. In the case of Empress Masako, the Emperor presented her with a red and white silk sash, which was then delivered to the expectant female royal family member by a palace official sent by the sash's parent, followed by a Gochaku Shinken no Gi. Sanctuaries, Three Palaces, and takes it back to the Palace to worship on behalf of the couple. The sash is then taken by the head priest to the Three Palace Sanctuaries for substitute worship. The obi is offered to the temple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Man'yōshū
The is the oldest extant collection of Japanese (poetry in Classical Japanese), compiled sometime after AD 759 during the Nara period. The anthology is one of the most revered of Japan's poetic compilations. The compiler, or the last in a series of compilers, is today widely believed to be Ōtomo no Yakamochi, although numerous other theories have been proposed. The chronologically last datable poem in the collection is from AD 759 ( 4516). It contains many poems from a much earlier period, with the bulk of the collection representing the period between AD 600 and 759. The precise significance of the title is not known with certainty. The contains 20 volumes and more than 4,500 poems, and is divided into three genres: , songs at banquets and trips; , songs about love between men and women; and songs to mourn the death of people. These songs were written by people of various statuses, such as the Emperor, aristocrats, junior officials, soldiers ( songs), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in polar and temperate climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Different cultures define different dates as the start of winter, and some use a definition based on weather. When it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere, it is summer in the Southern Hemisphere, and vice versa. In many regions, winter brings snow and freezing temperatures. The moment of winter solstice is when the Sun's elevation with respect to the North or South Pole is at its most negative value; that is, the Sun is at its farthest below the horizon as measured from the pole. The day on which this occurs has the shortest day and the longest night, with day length increasing and night length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice. The earliest sunset and latest sunrise dates outside the polar regions differ from the date of the winte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |