|
Nichollsemys
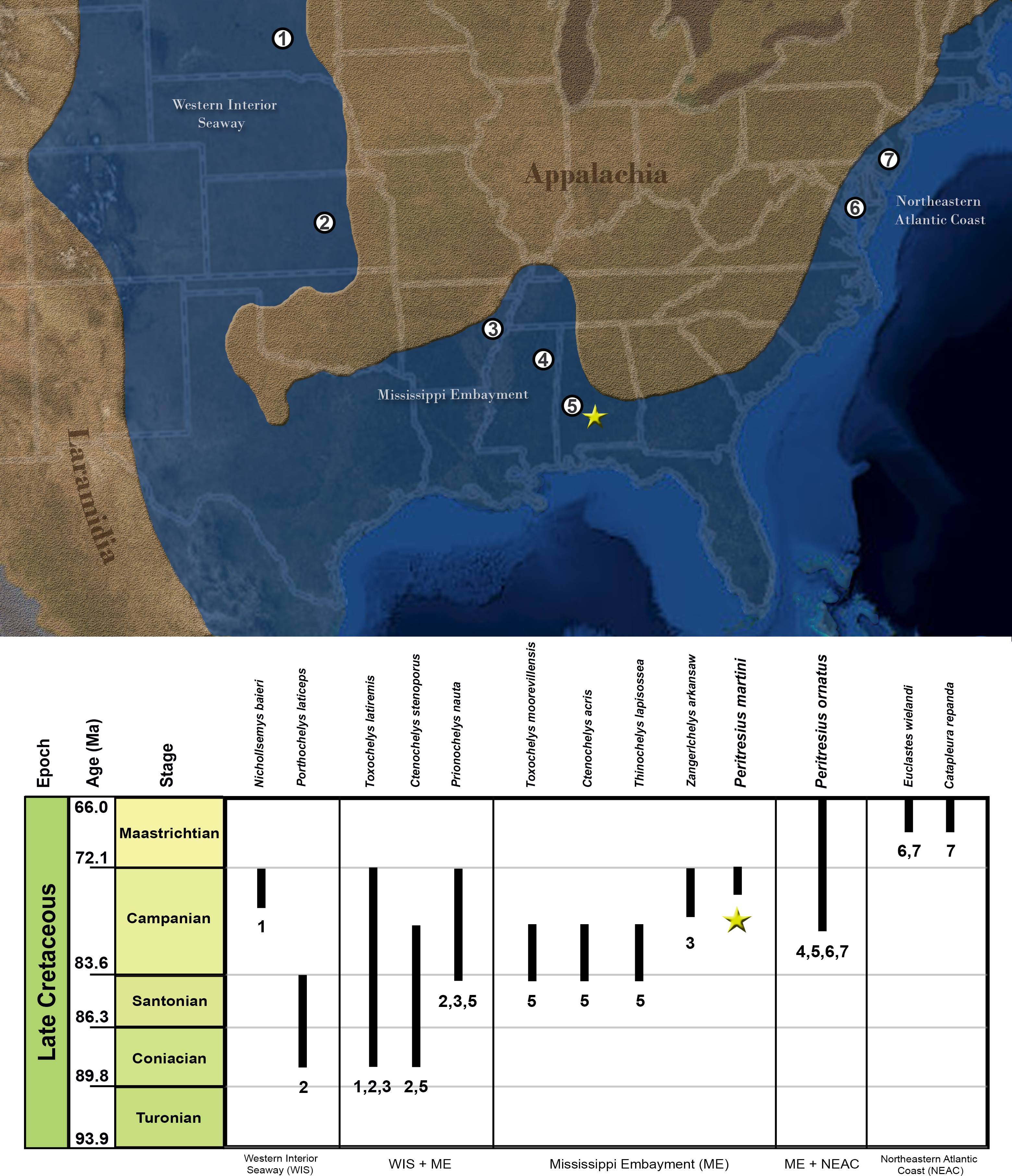
''Nichollsemys'' is a genus of extinct sea turtles. The only known species is ''Nichollsemys baieri''. Taxonomy Fossils of the ''Nichollsemys'' have been found in Alberta, Canada, by Donald Brinkman. The fossils found are all skulls. The name of ''Nichollsemys'' is a tribute to Elizabeth Nicholls, a paleontologist from Canada who studied marine reptiles from the Triassic period. She had previously done work with Brinkman when they found the ichthyosaur genus Pattinatator. Evolution Description The full length of the ''Nichollsemys'' is unknown, but Brinkman made a chart of the length of some parts of the specimen. The length from the basioccipital to the premaxilla measures 11.4 cm, the width of all the quadrates measures 9.8 cm, the depth at level of the quadrates measures 7.1 cm, the intraorbital width measures 2 cm, and the length measures 3.6 cm. The cranium has many things in common with that of Toxochelys ''Toxochelys'' () is an extinct genus of marine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelonioidea
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead, Kemp's ridley, and olive ridley sea turtles. All six of the sea turtle species present in US waters (all of those listed above except the flatback) are listed as endangered and/or threatened under the Endangered Species Act. The seventh sea turtle species is the flatback, which exists in the waters of Australia, Papua New Guinea and Indonesia. Sea turtles can be separated into the categories of hard-shelled (cheloniid) and leathery-shelled ( dermochelyid).Wyneken, J. 2001. The Anatomy of Sea Turtles. U.S Department of Commerce NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFSC-470, 1-172 pp. There is only one dermochelyid species which is the leatherback sea turtle. Description For each of the seven types of sea turtles, females and males are the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead, Kemp's ridley, and olive ridley sea turtles. All six of the sea turtle species present in US waters (all of those listed above except the flatback) are listed as endangered and/or threatened under the Endangered Species Act. The seventh sea turtle species is the flatback, which exists in the waters of Australia, Papua New Guinea and Indonesia. Sea turtles can be separated into the categories of hard-shelled (cheloniid) and leathery-shelled ( dermochelyid).Wyneken, J. 2001. The Anatomy of Sea Turtles. U.S Department of Commerce NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFSC-470, 1-172 pp. There is only one dermochelyid species which is the leatherback sea turtle. Description For each of the seven types of sea turtles, females and males are the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Nicholls
Elizabeth (Betsy) Laura Nicholls (January 31, 1946 – October 18, 2004) was an American-Canadian paleontology, paleontologist who specialized in Triassic marine reptiles. She was a paleontologist at the Royal Tyrrell Museum in Alberta, Canada. Early life and education Nicholls was born in Oakland, California, and received her undergraduate degree in 1968 from the University of California, Berkeley and her graduate degrees, an M.Sc. in 1972 and a Ph.D. in 1989, from the University of Calgary, working under Samuel Paul Welles. Nichollsemys was also named in her honor. Career She was the co-editor with American vertebrate paleontologist Jack Murff Callaway of the book ''Ancient Marine Reptiles''. ''Latoplatecarpus nichollsae'' was named in her honor. Nicholls was a 2000 Rolex Awards for Enterprise laureate for exploration for her leadership in excavating the remains of a large ichthyosaur, ''Shonisaurus sikanniensis'' (Nicholls & Manabe, 2004), from the Late Triassic, Upper T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermochelyidae
Dermochelyidae is a family of turtles which has seven extinct genera and one extant genus, including the largest living sea turtles. Classification of known genera The following list of dermochelyid species was published by Hirayama and Tong in 2003, unless otherwise noted. * ''Arabemys crassiscutata'' * †''Eosphargis breineri'' * ''Mesodermochelys undulatus'' *Subfamily Dermochelyinae ** †''Cosmochelys'' ** ''Dermochelys coriacea'' – leatherback sea turtle ** †''Psephophorus ''Psephophorus'' is an extinct genus of sea turtle that lived from the Oligocene to the Pliocene. Its remains have been found in Europe, Africa, North America, and New Zealand. It was first named by Hermann von Meyer in 1847, and contains seve ...'' Phylogeny Evers et al. (2019): References Bibliography * External linksFamily Dermochelyidae (Leatherback turtles) from Turtles of the World by C.H. Ernst, R.G.M. Altenburg & R.W. Barbour {{Taxonbar, from=Q2738058 Taxa named by Leopo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panchelonioidea
Panchelonioidea is a clade of marine turtles that includes the sea turtle Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhe ...s and related taxa. Phylogeny Evers et al. (2019): References Cryptodira {{Turtle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabindachelys
''Cabindachelys'' is a genus of extinct sea turtles. The only known species is ''Cabindachelys landanensis''. Fossils A partial skull of the ''Cabindachelys'' has been found in Cabinda, Angola, by Timothy S. Myers, Michael J. Polcyn, Octávio Mateus, Diana P. Vineyard, A. O. Gonçalves, Louis L. Jacobs. Habitat ''Cabindachelys'' lived in deep subtidal indents of the shores of Cabinda, Angola. Etymology The name of ''Cabindachelys'' is a mixture of Cabinda the place where it lived and the Greek name for turtle Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked tu .... Phylogeny References Chelonioidea Prehistoric turtle genera Paleocene turtles Fossil taxa described in 2017 {{paleo-turtle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allopleuron
''Allopleuron'' is a genus of extinct sea turtle, which measured long in life. The type species is ''Allopleuron hofmanni''. It is a basal member of the clade Pancheloniidae, closely related to ''Protosphargis''. Similar to ''Protosphargis'', it was characterized by shell reduction. Fossil history ''Allopleuron'' lived from the Early Cretaceous (Cenomanian age, 94.3 Ma) to the Oligocene (Rupelian age, 28.4 Ma), therefore surviving the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event. Fossils have been found from Germany, the Netherlands, Kazakhstan and the United States. Life history ''Allopleuron'' was believed to have used the Laurasian-Holarctic The Holarctic realm is a biogeographic realm that comprises the majority of habitats found throughout the continents in the Northern Hemisphere. It corresponds to the floristic Boreal Kingdom. It includes both the Nearctic zoogeographical region ... southern continental shelf as a breeding area. The modern day location of the breeding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argillochelys
''Argillochelys'' is an extinct genus of sea turtle from the middle to lower Eocene in what is now Britain. It was first named by Lydekker in 1889. A species, ''A. africana'', was found in Morocco, and described in 2008 by Tong & Hirayama. References External links ''Argillochelys''at the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale ... www.ppne.co.uk Eocene turtles Chelonioidea Eocene reptiles of Europe Eocene reptiles of Africa Prehistoric turtle genera Taxa named by Richard Lydekker Fossil taxa described in 1889 {{paleo-turtle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procolpochelys
''Procolpochelys'' is an extinct genus of sea turtle from the Miocene of what is now Maryland, Virginia, and New Jersey. Its fossils have been found in the Calvert Formation. It was first named by Hay in 1908. References External links ''Procolpochelys''at the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale ... www.scistp.org Cryptodira Fossils of the United States Miocene turtles Prehistoric turtle genera Taxa named by Oliver Perry Hay Extinct turtles {{paleo-turtle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eochelone
''Eochelone'' is an extinct genus of sea turtle from the late Eocene. It was first named by Dollo in 1903. Its type species is ''E. brabantica''. References Professor Paul's Guide to Reptiles''Eochelone''in the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale ... * * Chelonioidea Eocene turtles Fossils of Denmark Prehistoric turtle genera Monotypic prehistoric reptile genera {{paleo-turtle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma. Geology Proposals for the exact age of the Barremian-Aptian boundary ranged from 126 to 117 Ma until recently (as of 2019), but based on drillholes in Svalbard the defining early Aptian Oceanic Anoxic Event 1a (OAE1a) was carbon isotope dated to 123.1±0.3 Ma, limiting the possible range for the boundary to c. 122–121 Ma. There is a possible link between this anoxic event and a series of Early Cretaceous large igneous provinces (LIP). The Ontong Java-Manihiki-Hikurangi large igneous province, emplaced in the South Pacific at c. 120 Ma, is by far the largest LIP in Earth's history. The Ontong Java Plateau today covers an area of 1,860,000 km2. In the Indian Ocean another LIP began to form at c. 120 Ma, the Kerguelen P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puppigerus
''Puppigerus'' is an extinct genus of sea turtle from the Eocene. It is known from finds in the United States, the United Kingdom, Belgium, Denmark, and Uzbekistan. Taxonomy ''Puppigerus'' was described by Edward Drinker Cope in 1870. As of 1997, ''P. camperi'' and ''P. crassicostata'' were considered the two valid species. ''P. camperi'' was later thought to be the sole species of the genus until the 2005 discovery of ''P. nessovi'' from Uzbekistan. Description Fossils show that ''Puppigerus'' was around long, and its weight has been estimated as being somewhere around . Although cheloniids such as ''Puppigerus'' first appeared during the Cretaceous, several traits of this genus give it more of a resemblance to modern cheloniids: its "huge" eyes pointed sideways rather than upward, unlike more primitive cheloniids, and its shell was completely ossified. The pygal (rearmost plate of the upper shell) also lacked the notch seen in earlier cheloniids. It was a herbivore, living ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |