|
Nicanor (Syrian General)
Nicanor (; el, Nικάνωρ ''Nīkā́nōr''; died 161 BC) was a Syrian-Seleucid General under the kings Antiochus Epiphanes and Demetrius Soter. Early military career The son of Patroclus and one of the king's "chief friends" ( 2 Macc 8:9), After the defeat of Seron by Judas Maccabeus at the Battle of Beth Horon, Epiphanes entrusted his chancellor Lysias with the destruction of Judea ( 1 Macc 3:34). Nicanor was one of the three generals commissioned by Lysias; the others being Ptolemy, son of Dorymenes, and Gorgias (1 Macc 3:38). The campaign began in 166 BC; the Syrians were defeated at Emmaus (1 Macc 3:57), while Gorgias at a later stage gained a victory at Jamnia over a group of Jews who disobeyed Judas Maccabeus (1 Macc 5:58). The account given in 2 Maccabees differs considerably, both in omissions and in additions (2 Macc 8:9). There Nicanor, not Gorgias, is the chief in command. The battle of Emmaus is not mentioned, but "the thrice-accursed Nicanor," having in overwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire originally founded by Alexander the Great. After receiving the Mesopotamian region of Babylonia in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Persian Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that had covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, and what are now modern Iraq, Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide variet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacchides (general)
Bacchides ( el, Βακχίδης) was a Hellenistic Greek general; friend of the Syrian-Greek king Demetrius; and "ruler in the country beyond the river"—Euphrates. Demetrius sent him in 161 BCE to Judea with a large army, in order to invest Alcimus with the office of High Priest of Israel (''I Macc.'' vii. 8, 9). The peaceable Assideans credulously expected friendship from him; but, contrary to oath and covenant, he cruelly slew sixty of them (ib. vii. 16). Leaving Jerusalem, he made a slaughter-house of Bezeth (Bethzecha), and after handing the country over to Alcimus, returned to the king (ib. vii. 19, 20). Demetrius sent Bacchides back to Judea. A Greek army, under General Nicanor, had been defeated by Judas Maccabeus (ib. vii. 26–50) at the Battle of Adasa. Nicanor had been killed near Adasa. Bacchides was sent with Alcimus and an army of twenty thousand infantry and two thousand cavalry. Bacchides met Judas at The Battle of Elasa (Laisa). Judas was killed and his a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid People In The Books Of The Maccabees
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire originally founded by Alexander the Great. After receiving the Mesopotamian region of Babylonia in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Persian Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that had covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, and what are now modern Iraq, Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide variet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
161 BC Deaths
Year 161 ( CLXI) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Aurelius (or, less frequently, year 914 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 161 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * March 7 – Emperor Antoninus Pius dies, and is succeeded by Marcus Aurelius, who shares imperial power with Lucius Verus, although Marcus retains the title Pontifex Maximus. * Marcus Aurelius, a Spaniard like Trajan and Hadrian, is a stoical disciple of Epictetus, and an energetic man of action. He pursues the policy of his predecessor and maintains good relations with the Senate. As a legislator, he endeavors to create new principles of morality and humanity, particularly favoring women and slaves. * Aurelius reduces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Maccabaeus
Simon Thassi ( he, ''Šīməʿōn haTassī''; died 135) was the second son of Mattathias and thus a member of the Hasmonean family. Names The name "Thassi" has a connotation of "the Wise", a title which can also mean "the Director", "the Guide", "the Man of Counsel", and "the Zealous". This Simon is also sometimes distinguished as , , or (from Latin) . History Simon took a prominent part in the Jewish revolt against the Seleucid Empire led by his brothers, Judas Maccabaeus and Jonathan Apphus. The successes of the Jews rendered it expedient for the Seleucid leaders in Syria to show them special favour. Therefore, Antiochus VI appointed Simon ''strategus'', or military commander, of the coastal region stretching from the Ladder of Tyre to Egypt. As ''strategus'', Simon conquered the cities of Beth-zur and Joppa, garrisoning them with Jewish troops and built the fortress of Adida. After the capture of Jonathan by the Seleucid general, Diodotus Tryphon, Simon was elected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purim
Purim (; , ; see Name below) is a Jewish holiday which commemorates the saving of the Jews, Jewish people from Haman, an official of the Achaemenid Empire who was planning to have all of Persia's Jewish subjects killed, as recounted in the Book of Esther (usually dated to the 5th century BCE). Haman was the royal vizier to Persian king Ahasuerus (Xerxes I or Artaxerxes I; "Khshayarsha" and "Artakhsher" in Old Persian, respectively). His plans were foiled by Mordecai of the tribe of Benjamin, and Esther, Mordecai's cousin and adopted daughter who had become queen of Persia after her marriage to Ahasuerus. The day of deliverance became a day of feasting and rejoicing among the Jews. According to the Scroll of Esther, "they should make them days of feasting and gladness, and of sending portions one to another, and gifts to the poor". Purim is celebrated among Jews by: *Exchanging gifts of food and drink, known as *Donating charity to the poor, known as *Eating a celebratory me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mordecai
Mordecai (; also Mordechai; , IPA: ) is one of the main personalities in the Book of Esther in the Hebrew Bible. He is described as being the son of Jair, of the tribe of Benjamin. He was promoted to Vizier after Haman was killed. Biblical account Mordecai resided in Susa (Shushan or Shoushan),Esther 2:5–6 of the Bible ( New International Version): : Now there was in the citadel of Susa a Jew of the tribe of Benjamin, named Mordecai son of Jair, the son of Shimei, the son of Kish, who has been carried into exile from Jerusalem by Nebuchadnezzar king of Babylon, among those taken captive with Jeconiah king of Judah. the metropolis of Persia (now Iran). He adopted his orphaned cousin (Esther 2:7), Hadassah (Esther), whom he brought up as if she were his own daughter. When "young virgins" were sought, she was taken into the presence of King Ahasuerus and was made queen in the place of the exiled queen Vashti. Subsequently, Mordecai discovered a plot of the king's chamberlains Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Adasa
The Battle of Adasa was fought during the Maccabean revolt on the 13th of the month Adar (late winter, equivalent to March), 161 BC at Adasa ( he, חדשה), near Beth-horon. It was a battle between the rebel Maccabees of Judas Maccabeus (Judah Maccabee) and the Seleucid Empire, whose army was led by Nicanor. The Maccabees won the battle after killing Nicanor early in the fighting. The battle came after a period of political maneuvering over several months where the peace deal established a year earlier by Lysias was tested by new High Priest Alcimus, new military governor Nicanor, and Maccabee leader Judas Maccabeus. The date of the battle in the Hebrew calendar, 13 Adar, was celebrated as ''Yom Nicanor'' (Day of Nicanor) to commemorate the victory. Primary sources Nicanor's military governance of Judea, the Battle of Caphar-salama, and the Battle of Adasa are recorded in the book of 1 Maccabees (), the book of 2 Maccabees (, ), and in Josephus's ''Antiquities of the Jews'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adar
Adar ( he, אֲדָר ; from Akkadian ''adaru'') is the sixth month of the civil year and the twelfth month of the religious year on the Hebrew calendar, roughly corresponding to the month of March in the Gregorian calendar. It is a month of 29 days. Names and Leap Years The month's name, like all the others from the Hebrew calendar, was adopted during the Babylonian captivity. In the Babylonian calendar the name was Araḫ Addaru or Adār ('Month of Adar'). In leap years, it is preceded by a 30-day intercalary month named Adar Aleph ( he, אדר א׳, Aleph being the first letter of the Hebrew alphabet), also known as "Adar Rishon" (''First Adar'') or "Adar I", and it is then itself called Adar Bet ( he, אדר ב׳, Bet being the second letter of the Hebrew alphabet, also known as "Adar Sheni" (''Second Adar'' or "Adar II"). Occasionally instead of Adar I and Adar II, "Adar" and "Ve'Adar" are used (Ve means 'and' thus: And-Adar). Adar I and II occur during February–March o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adasa
Adasa ( grc, Αδασά) is a city referred to in 1 Maccabees, being the site of the Syrian-Seleucid General Nicanor's death and Judah Maccabee's post in the battle of Adasa (during the Maccabean Revolt). It is said to be less than four miles from Beth-Horon Bethoron ( he, בֵית־חוֹרֹ֔ן, lit=house of Horon; grc, Ὡρωνείν), also Beth-Horon, was the name of two adjacent ancient towns strategically located on the Gibeon-Aijalon road, guarding the "ascent of Beth-Horon". The towns are ... ( 1 Macc 7:39). References Places in the deuterocanonical books Books of the Maccabees {{Jewish-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
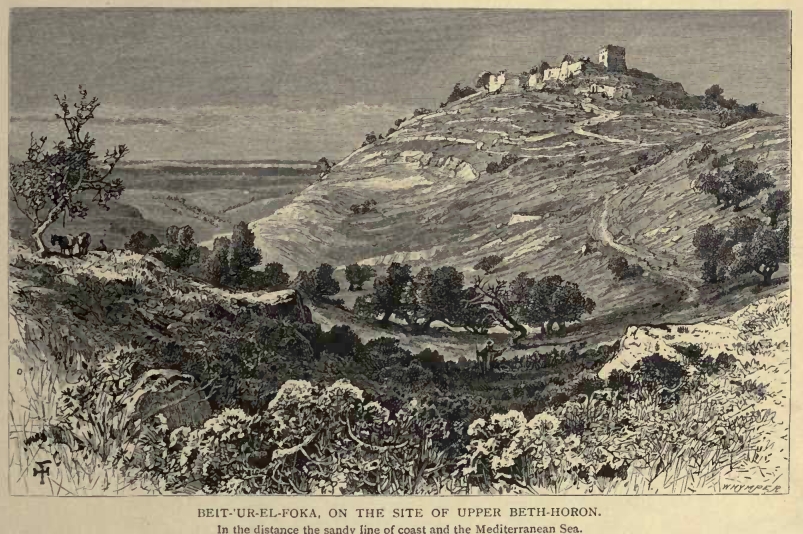
Beth-horon
Bethoron ( he, בֵית־חוֹרֹ֔ן, lit=house of Horon; grc, Ὡρωνείν), also Beth-Horon, was the name of two adjacent ancient towns strategically located on the Gibeon-Aijalon road, guarding the "ascent of Beth-Horon". The towns are mentioned in the Hebrew Bible and in other ancient sources: Upper Bethoron appears in ''Joshua'' and Lower Bethoron in ''Joshua'' and '' 1 Chronicles'' and I Maccabees 3:16. The ancient towns of Upper Bethoron and Lower Bethoron are identified respectively with the present day Palestinian Arab villages of Beit Ur al-Fauqa and Beit Ur al-Tahta, which are believed to preserve the ancient names. Etymology The Hebrew name Bethoron (Beit Horon, ) is derived from the name of an Egypto- Canaanite deity, ''Horon'', mentioned in Ugaritic literature. The city is mentioned among the cities and towns smitten by Sheshonq I in his inscription at the Temple of Karnak as Batae Houarn. History Upper Bethoron is mentioned several times in the Hebrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megillat Taanit
''Megillat Taanit'' (Hebrew: ), lit. ''"the Scroll of Fasting,"'' is an ancient text, in the form of a chronicle, which enumerates 35 eventful days on which the Jewish nation either performed glorious deeds or witnessed joyful events. These days were celebrated as feast-days. Public mourning was forbidden on 14 of them, and public fasting on all. History of the feast days The events described therein date to several time periods: the pre-Hasmonean period, the Hasmonean era, the early Roman period and the period of the Great War against Rome, with the majority of the entries relating to the Hasmonean period. Almost half of theses events cannot be conclusively identified. Nearly all commemorate victories in battle, especially those events centered around the Hasmonean period. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |