|
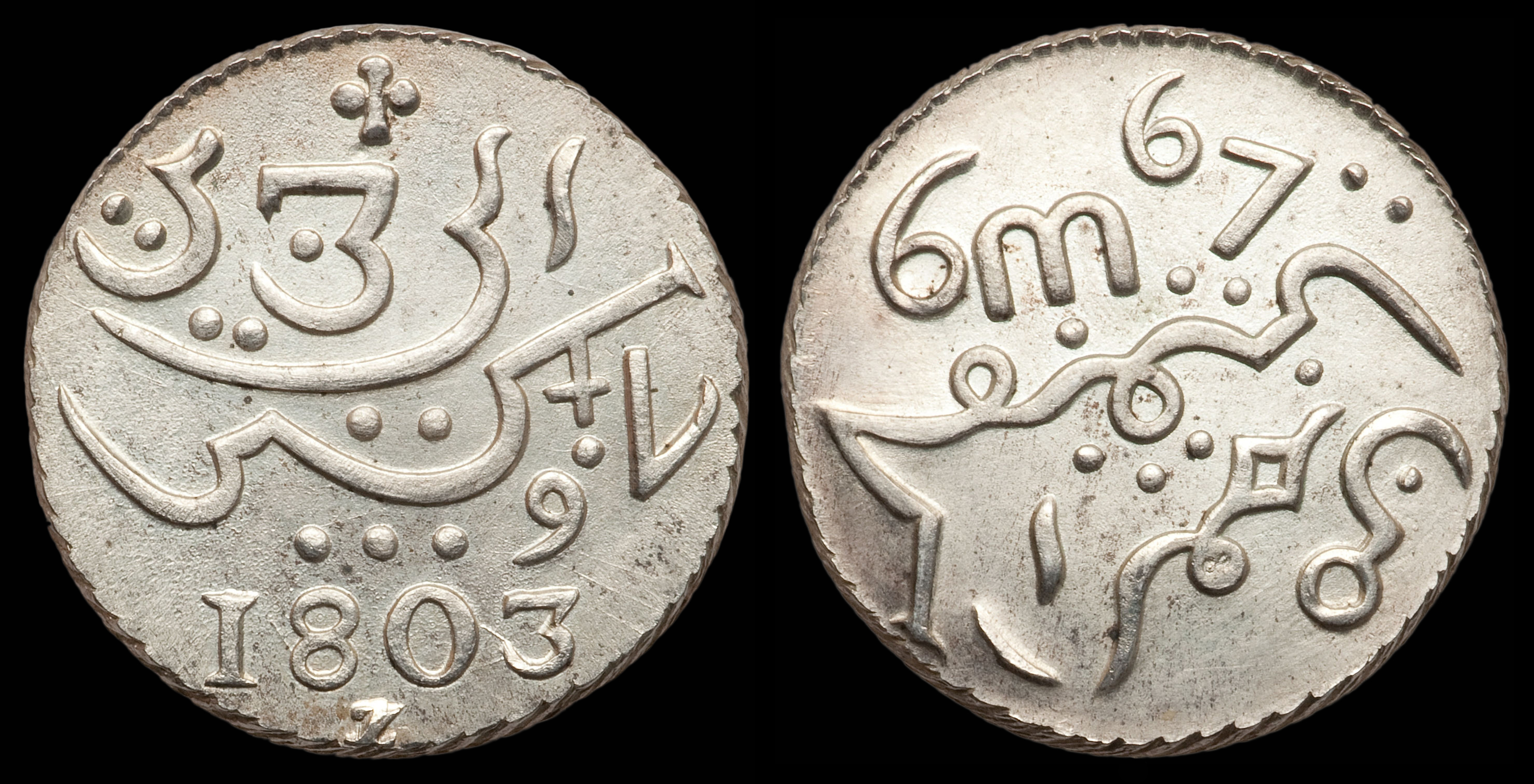
Ng (Arabic Letter)
Turkic ng or (Ng or Naf) is an additional letter of the Arabic script, derived from kāf () with the addition of three dots above the letter. It is used in Arabic as used in Morocco for (or by ), but is used to represent a velar when writing Turkic languages. In Turkic dialects, it represented the velar . An example is the word دݣز (däŋiz, “sea”), compare deniz in modern Turkish, and deñiz in Kyrgyz, Turkmen, Uyghur and Uzbek. It is also used in Sindhi and Saraiki, as ڳ. Turkic languages The letter is used or has been used to write: * Chagatai * Kazakh * Kirghiz * Azerbaijani *Ottoman Turkish * Uyghur Xiao'erjing The Xiao'erjing script variant is used to spell in Sinitic languages such as Mandarin (especially the Lanyin, Zhongyuan and Northeastern dialects) or the Dungan language. Southeast Asian ng The letter derived from , is used in many languages when using the Arabic script to represent in: * Jawi script to write: ** Acehnese ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used writing system in the world by number of countries using it or a script directly derived from it, and the third-most by number of users (after the Latin and Chinese scripts). The script was first used to write texts in Arabic, most notably the Quran, the holy book of Islam. With the religion's spread, it came to be used as the primary script for many language families, leading to the addition of new letters and other symbols. Such languages still using it are: Persian (Farsi/Dari), Malay ( Jawi), Uyghur, Kurdish, Punjabi (Shahmukhi), Sindhi, Balti, Balochi, Pashto, Lurish, Urdu, Kashmiri, Rohingya, Somali and Mandinka, Mooré among others. Until the 16th century, it was also used for some Spanish texts, and—prior to the language reform in 1928—it was the writing system of Turkish. The script is written from right to left in a cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirghiz Language
Kyrgyz (; autonym: , tr. ''Kyrgyz tili'', ) is a Turkic language of the Kipchak branch spoken in Central Asia. Kyrgyz is the official language of Kyrgyzstan and a significant minority language in the Kizilsu Kyrgyz Autonomous Prefecture in Xinjiang, China and in the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region of Tajikistan. There is a very high level of mutual intelligibility between Kyrgyz, Kazakh, and Altay. A dialect of Kyrgyz known as Pamiri Kyrgyz is spoken in Afghanistan and Pakistan. Kyrgyz is also spoken by many ethnic Kyrgyz through the former Soviet Union, Afghanistan, Turkey, parts of northern Pakistan, and Russia. Kyrgyz was originally written in Göktürk script, gradually replaced by the Perso-Arabic alphabet (in use until 1928 in the USSR, still in use in China). Between 1928 and 1940 a Latin-script alphabet, the Uniform Turkic Alphabet, was used. In 1940, Soviet authorities replaced the Latin script with the Cyrillic alphabet for all Turkic countries. When Kyrgyz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerinci Language
Kerinci (Kinci or Kincai) is a Malayic language spoken in Jambi Province, Sumatra especially in Kerinci Regency and Sungai Penuh city. It has a high dialectical diversity, with dialects Ulu, Mamaq, Akit, Talang and Sakei. Van Reijn (1974) notes that Kerinci shares many phonological similarities with Austroasiatic languages, such as sesquisyllabic Primarily in Austroasiatic languages (also known as Mon–Khmer), in a typical word a minor syllable is a reduced (minor) syllable followed by a full tonic or stressed syllable. The minor syllable may be of the form or , with a reduced vowel, as ... word structure and vowel inventory. References Bibliography *Van Reijn, E.O. (1974).Some Remarks on the Dialects of North Kerintji: A link with Mon-Khmer Languages" ''Journal of the Malaysian Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society'', 31, 2: 130-138. Further reading * Ernanda. (2011). On the loss of the phrasal alternation in Pondok Tinggi dialect of Kerinci: A Stochastic Optimality T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banjar Language
The Banjar or Banjarese (; ) is an Austronesian language predominantly spoken by the Banjarese—an indigenous ethnic group native to Banjar regions— in the southeastern Kalimantan of Indonesia. The Banjarese language is the lingua franca for various indigenous community especially in South Kalimantan, as well as Central Kalimantan (notably in Seruyan Regency and Sukamara Regency) and East Kalimantan in general. Apart from the native Banjarese in Indonesia, the Banjarese language also spoken by little Banjarese diaspora abroad (such as in Brunei, Malaysia (notably in Sabah and Perak), and Singapore); however, they tend to not use it as their primary language, and their fluency degree is questionable. Dialects There are at least three divisions of dialects within the Banjarese language: #Batangbanyu Banjarese #Kuala Banjarese #Pahuluan Banjarese According to Cense,A.A.Cee - E.M. Uhienbeck, Critical Survey of Studies on the Language of Borneo, 'S-Gravenhage-Martin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acehnese Language
Acehnese or Achinese (Jawi alphabet, Jawi: بهسا اچيه) is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language natively spoken by the Acehnese people in Aceh, Sumatra, Indonesia. This language is also spoken by Acehnese descendants in some parts of Malaysia like Yan, Kedah, Yan, in Kedah. Name As of 1988, "Acehnese" is the modern English language, English name spelling and the bibliographical standard, and Acehnese people use the spelling "Acehnese" when writing in English. "Achinese" is an antiquated spelling of the English language tradition. "Atjehnese" is the Dutch language, Dutch spelling and an outdated Indonesian language, Indonesian one. The spelling "Achehnese" originates from a 1906 English translation of the Dutch language ''Studien over atjesche klank- en schriftleer. Tijdschrift voor Indische Taal-, Land- en Volkenkunde 35.346-442'' by Christiaan Snouck Hurgronje, 1892. In Acehnese the language is called ''Basa/Bahsa Acèh''. In Indonesian it is called ''Bahasa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jawi Script
Jawi (; ace, Jawoë; Kelantan-Pattani Malay, Kelantan-Pattani: ''Yawi''; ) is a writing system used for writing several languages of Southeast Asia, such as Acehnese language, Acehnese, Banjar language, Banjarese, Kerinci language, Kerinci, Maguindanao language, Maguindanaon, Malay language, Malay, Minangkabau language, Minangkabau, Tausug language, Tausūg, and Ternate language, Ternate. Jawi is based on the Arabic script, consisting of all of the original 31 Arabic letters, and six additional letters constructed to fit the phonemes native to Malay, and an additional phoneme used in foreign loanwords, but not found in Classical Arabic, which are ''ca'' ( ), ''nga'' ( ), ''pa'' ( ), ''ga'' ( ), ''va'' ( ), and ''nya'' ( ). Jawi was developed from the Spread of Islam in Southeast Asia, advent of Islam in the Maritime Southeast Asia, supplanting the earlier Brahmic scripts used during Hindu-Buddhist era. The oldest evidence of Jawi writing can be found on the 14th century Tere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dungan Language
Dungan ( or ) is a Sinitic language spoken primarily in Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan by the Dungan people, an ethnic group related to the Hui people of China. Although it is derived from the Central Plains Mandarin of Gansu and Shaanxi, it is written in Cyrillic (or Xiao'erjing) and contains loanwords and archaisms not found in other modern varieties of Mandarin. History The Dungan people of Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan (with smaller groups living in other post-Soviet states) are the descendants of several groups of the Hui people that migrated to the region in the 1870s and the 1880s after the defeat of the Dungan revolt in Northwestern China. The Hui of Northwestern China (often referred to as "Dungans" or "Tungani" by the 19th-century western writers as well as by members of Turkic nationalities in China and Central Asia) would normally speak the same Mandarin dialect as the Han people in the same area Dru C. Gladney, ''Muslim Chinese: Ethnic Nationalism in the People's Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
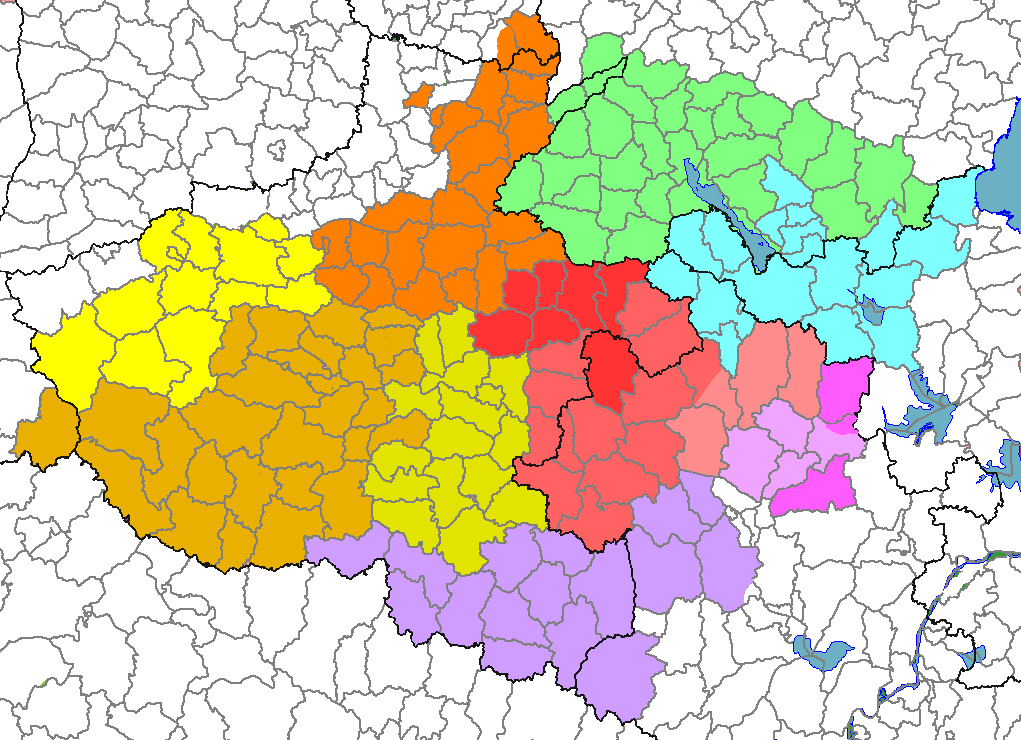
Northeastern Mandarin
Northeastern Mandarin ( or / ''Dōngběiguānhuà'' "Northeast Mandarin") is the subgroup of Mandarin varieties spoken in Northeast China with the exception of the Liaodong Peninsula and few enclaves along Amur and Ussuri rivers. The classification of Northeastern Mandarin as a separate dialect group from Beijing Mandarin was first proposed by Li Rong, author of the ''Language Atlas of China'', in 1989. However, many researchers do not accept the distinction. Geographical distribution Northeastern Mandarin varieties are spoken in the northeastern part of China, in the provinces of Liaoning (except its southern part from Dalian to Dandong where Jiaoliao Mandarin is spoken), Jilin and Heilongjiang, and in some northern parts of Inner Mongolia. The number of speakers was estimated in 1987 as 82 million. The ''Language Atlas of China'' divided Northeastern Mandarin into three subgroups, following a classification be Hè Wēi based on the occurrence of nasal initials in words h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhongyuan Mandarin
Central Plains Mandarin, or ''Zhongyuan'' Mandarin (), is a variety of Mandarin Chinese spoken in the central and southern parts of Shaanxi, Henan, southwestern part of Shanxi, southern part of Gansu, far southern part of Hebei, northern Anhui, northern parts of Jiangsu, southern Xinjiang and southern Shandong. The archaic dialect in Peking opera is a form of Zhongyuan Mandarin. Among Hui people, Zhongyuan Mandarin is sometimes written with the Arabic alphabet, called Xiao'erjing ("Children's script"). Subdialects * Zheng-Kai (鄭開) region: e.g. Kaifeng (開封) dialect, Zhengzhou (鄭州) dialect * Luo-Song (洛嵩) region: e.g. Luoyang dialect (洛陽話) * Nan-Lu (南魯) region: e.g. Nanyang (南陽) dialect * Luo-Xiang (漯項) region: e.g. Zhumadian (駐馬店) dialect * Shang-Fu (商阜) region: e.g. Shangqiu (商丘) dialect, Fuyang (阜陽) dialect * Xin-Beng (信蚌) region: e.g. Xinyang (信陽) dialect, Bengbu (蚌埠) dialect * Yan-He (兗菏) region: e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanyin Mandarin
Lan–Yin Mandarin (Lanyin) () is a branch of Mandarin Chinese traditionally spoken throughout Gansu province and in the northern part of Ningxia. In recent decades it has expanded into northern Xinjiang. It forms part of Northwestern Mandarin, together with Central Plains Mandarin (). The name is a compound of the capitals of the two former provinces where it dominates, Lanzhou and Yinchuan, which are also two of its principal subdialects. Among Chinese Muslims, it was sometimes written in the Arabic alphabet instead of Chinese characters. The 14th Dalai Lama, Tenzin Gyatso, spoke the Xining dialect as his first language: he has said that his first language was "a broken Xining language which was (a dialect of) the Chinese language", a form of Central Plains Mandarin, and his family speak neither Amdo Tibetan nor Lhasa Tibetan Lhasa Tibetan (), or Standard Tibetan, is the Tibetan dialect spoken by educated people of Lhasa, the capital of the Tibetan Autonomous Region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin (; ) is a group of Chinese (Sinitic) dialects that are natively spoken across most of northern and southwestern China. The group includes the Beijing dialect, the basis of the phonology of Standard Chinese, the official language of China. Because Mandarin originated in North China and most Mandarin dialects are found in the north, the group is sometimes referred to as Northern Chinese (). Many varieties of Mandarin, such as those of the Southwest (including Sichuanese) and the Lower Yangtze, are not mutually intelligible with the standard language (or are only partially intelligible). Nevertheless, Mandarin as a group is often placed first in lists of languages by number of native speakers (with nearly one billion). Mandarin is by far the largest of the seven or ten Chinese dialect groups; it is spoken by 70 percent of all Chinese speakers over a large geographical area that stretches from Yunnan in the southwest to Xinjiang in the northwest and Heilongjiang in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinitic Languages
The Sinitic languages (漢語族/汉语族), often synonymous with "Chinese languages", are a group of East Asian analytic languages that constitute the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. It is frequently proposed that there is a primary split between the Sinitic languages and the rest of the family (the Tibeto-Burman languages). This view is rejected by a number of researchers but has found phylogenetic support among others. The Greater Bai languages, whose classification is difficult, may be an offshoot of Old Chinese and thus Sinitic; otherwise Sinitic is defined only by the many varieties of Chinese unified by a common writing system, and usage of the term "Sinitic" may reflect the linguistic view that Chinese constitutes a family of distinct languages, rather than variants of a single language. Population The total speakers of the Chinese macrolanguage is 1,521,943,700, of which about 73.5% (1,118,584,040) speak a Mandarin variety. The estimated number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |