|
New Zealand In World War II
The military history of New Zealand during World War II began when New Zealand entered the Second World War by declaring war on Nazi Germany with Great Britain. New Zealand's forces were soon serving across Europe and beyond, where their reputation was generally very good. In particular, the force of the New Zealanders who stationed in Northern Africa and Southern Europe was known for its strength and determination, and uniquely so on both sides. The state of war with Germany was officially held to have existed since 9:30 pm on 3 September 1939 (local time), simultaneous with that of Britain, but in fact New Zealand's declaration of war was not made until confirmation had been received from Britain that their ultimatum to Germany had expired. When Neville Chamberlain broadcast Britain's declaration of war, a group of New Zealand politicians (led by Peter Fraser because Prime Minister Michael Savage was terminally ill) listened to it on the shortwave radio in Carl Berendsen's room ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Cornish (judge)
Henry Cornish (died 1685) was a London alderman, executed in the reign of James II of England. Life He was a well-to-do merchant of London, and alderman of the ward of St Michael Bassishaw; in the ''London Directory'' for 1677 he is described as a factor residing in 'Cateaton Street, near Blackwelhall Gate.' He was a presbyterian in religion, and in politics was a strong whig. On 24 June 1680 he was chosen sheriff of London in conjunction with Slingsby Bethel. It was afterwards discovered that Cornish and his colleague had not taken the oath according to the Corporation Act, and the election was declared void. A second election was fixed for 17 July, when Cornish and Bethel took the oath under the Corporation Act, and claimed the appointment. Charles II decided to force on the city two sheriffs of his own choosing, named Box and Nicolson. The latter demanded a poll, which lasted until 22 July, and on the 29th Cornish and Bethel were declared elected. Cornish headed the poll with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Range Desert Group
)Gross, O'Carroll and Chiarvetto 2009, p.20 , patron = , motto = ''Non Vi Sed Arte'' (Latin: ''Not by Strength, but by Guile'') (unofficial) , colours = , colours_label = , march = , mascot = , equipment = Chevrolet or Ford trucks, Willys Jeep , equipment_label = , battles = Second World War * North African campaign * Battle of Kufra * Operation Caravan * Dodecanese Campaign * Battle of Leros * Albania * Yugoslavia * Italian Campaign , decorations = , battle_honours = , disbanded = 1 August 1945 , commander1 = , commander1_label = , commander2 = , commander2_label = , commander3 = , commander3_label = , notable_commanders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire. "Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 1926 Imperial Conference through the Balfour Declaration of 1926, recognising Great Britain and the Dominions as "autonomous within the British Empire, equal in status, in no way subordinate one to another in any aspect of their domestic or external affairs, though united by a common allegiance to the Crown and freely associated as members of the British Commonwealth of Nations". Their full legislative independence was subsequently confirmed in the 1931 Statute of Westminster. Later India, Pakistan, and Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) also became dominions, for short periods of time. With the dissolution of the British Empire after World War II and the formation of the Commonwealth of Nations, it was decided that the term ''Commonwealth country'' shou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Air Training Scheme
The British Commonwealth Air Training Plan (BCATP), or Empire Air Training Scheme (EATS) often referred to as simply "The Plan", was a massive, joint military aircrew training program created by the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia and New Zealand, during the Second World War.Hayter, Steven"History of the Creation of the British Commonwealth Air Training Plan." ''British Commonwealth Air Training Plan Museum,'' Retrieved: 18 October 2010. BCATP remains as one of the single largest aviation training programs in history and was responsible for training nearly half the pilots, navigators, bomb aimers, air gunners, wireless operators and flight engineers who served with the Royal Air Force (RAF), Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm (FAA), Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) and Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF) during the war. Under a parallel agreement, the Joint Air Training Scheme, South Africa trained 33,347 aircrew for the South African Air Force and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal New Zealand Air Force
The Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF) ( mi, Te Tauaarangi o Aotearoa, "The Warriors of the Sky of New Zealand"; previously ', "War Party of the Blue") is the aerial service branch of the New Zealand Defence Force. It was formed from New Zealand elements of the British Royal Air Force, becoming an independent force in 1923, although many RNZAF aircrew continued to serve in the Royal Air Force until the end of the 1940s. The RNZAF fought in World War II, Malaya, Korean War, Vietnam and the Gulf War as well as undertaking various United Nations peacekeeping missions. From a 1945 peak of over 1,000 combat aircraft the RNZAF has shrunk to a strength of around 48 aircraft in 2022, focusing on maritime patrol and transport duties in support of the Royal New Zealand Navy and the New Zealand Army. The RNZAF's air combat capability ended in 2001, under the Fifth Labour Government with the disbanding of the A-4 Skyhawk and Aermacchi MB-339 based squadrons. The Air Force is led by an Ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Crete
The Battle of Crete (german: Luftlandeschlacht um Kreta, el, Μάχη της Κρήτης), codenamed Operation Mercury (german: Unternehmen Merkur), was a major Axis airborne and amphibious operation during World War II to capture the island of Crete. It began on the morning of 20 May 1941, with a multiple German airborne landings on Crete. Greek and other Allied forces, along with Cretan civilians, defended the island. After only one day of fighting, the Germans had suffered heavy casualties and the Allied troops were confident that they would defeat the invasion. The next day, through communication failures, Allied tactical hesitation, and German offensive operations, Maleme Airfield in western Crete fell, enabling the Germans to land reinforcements and overwhelm the defensive positions on the north of the island. Allied forces withdrew to the south coast. More than half were evacuated by the British Royal Navy and the remainder surrendered or joined the Cretan resistance. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
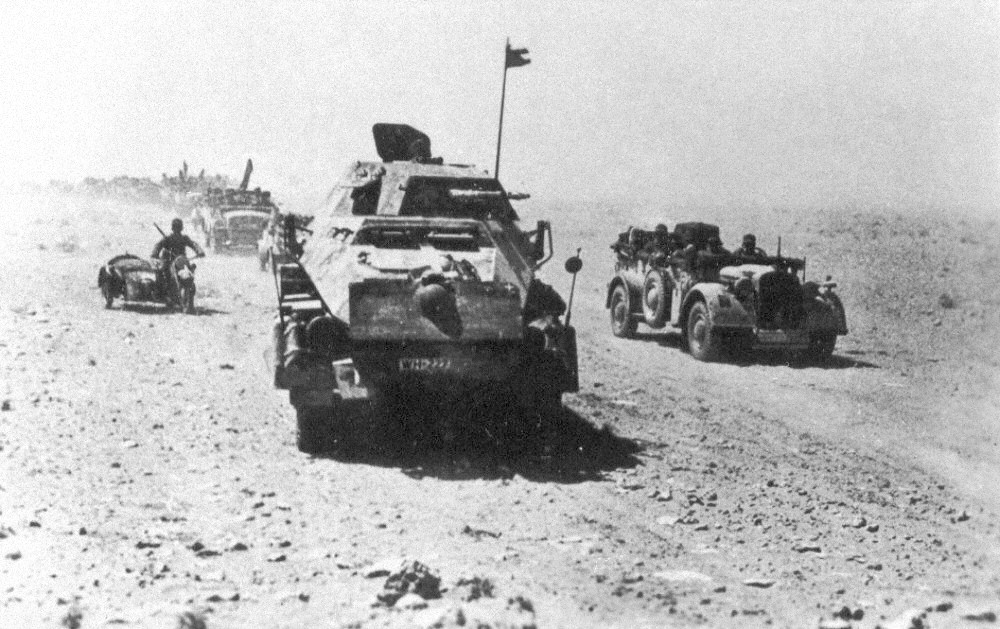
Battle Of El Alamein
There were two battles of El Alamein in World War II, both fought in 1942. The Battles occurred in North Africa, in Egypt, in and around an area named after a railway stop called El Alamein. * First Battle of El Alamein: 1–27 July 1942 * Second Battle of El Alamein: 23 October – 4 November 1942 In addition, the Battle of Alam el Halfa The Battle of Alam el Halfa took place between 30 August and 5 September 1942 south of El Alamein during the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. '' Panzerarmee Afrika'' (''Generalfeldmarschall'' Erwin Rommel), attempted an envelopme ... (30 August – 5 September 1942) was fought between both battles and in the same location. {{SIA ja:エル・アラメインの戦い ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of El Alamein
The Second Battle of El Alamein (23 October – 11 November 1942) was a battle of the Second World War that took place near the Egyptian Railway station, railway halt of El Alamein. The First Battle of El Alamein and the Battle of Alam el Halfa had prevented the Axis powers, Axis from advancing further into Egypt. In August 1942, General (United Kingdom), General Claude Auchinleck had been relieved as Commander-in-Chief Middle East Command and his successor, Lieutenant-General William Gott was killed on his way to replace him as commander of the Eighth Army (United Kingdom), Eighth Army. Lieutenant-general (United Kingdom), Lieutenant-General Bernard Montgomery was appointed and led the Eighth Army offensive. The British victory was the beginning of the end of the Western Desert Campaign, eliminating the Axis threat to Egypt, the Suez Canal and the Middle Eastern and Persian oil fields. The battle revived the morale of the Allies, being the first big success against the Axis sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of El Alamein
The First Battle of El Alamein (1–27 July 1942) was a battle of the Western Desert campaign of the Second World War, fought in Egypt between Axis (German and Italian) forces of the Panzer Army Africa—which included the under Field Marshal Erwin Rommel—and Allied (British Imperial and Commonwealth) forces of the Eighth Army under General Claude Auchinleck. The British prevented a second advance by the Axis forces into Egypt. Axis positions near El Alamein, only from Alexandria, were dangerously close to the ports and cities of Egypt, the base facilities of the Commonwealth forces and the Suez Canal. However, the Axis forces were too far from their base at Tripoli in Libya to remain at El Alamein indefinitely, which led both sides to accumulate supplies for more offensives, against the constraints of time and distance. The battle and the Second Battle of El Alamein three months later remain important to some of the countries that took part. In New Zealand, this is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fred Baker (soldier)
Lieutenant Colonel Frederick Baker DSO (19 June 1908 – 1 June 1958) was a New Zealand soldier who served in the Second World War, leading the 28th (Māori) Battalion from 13 July to 2 November 1942. He was injured at the commencement of the Second Battle of El Alamein and his wounds were such that he was repatriated back to New Zealand. He later worked in New Zealand's public service, leading the Rehabilitation Department which assisted servicemen returning from the war into civilian life, by providing them with finance, training and housing. Early life Frederick Baker was born in the Hokianga, in the north of the North Island of New Zealand, on 19 June 1908 to a bushman and his wife. Of Ngāpuhi descent (via his mother), he attended local schools in the area. Entering the public service after completion of his education, he worked for the Public Works Department based in Whangarei before moving to Hamilton in 1928. He became an accountant, qualifying in late 1931. He transfer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Freyberg, 1st Baron Freyberg
Lieutenant-General Bernard Cyril Freyberg, 1st Baron Freyberg, (21 March 1889 – 4 July 1963) was a British-born New Zealand soldier and Victoria Cross recipient, who served as the 7th Governor-General of New Zealand from 1946 to 1952. Freyberg served as an officer in the British Army during the First World War. He took part in the beach landings during the Gallipoli Campaign and was the youngest general in the British Army during the First World War, later serving on the Western Front, where he was decorated with the Victoria Cross and three Distinguished Service Orders, making him one of the most highly decorated British Empire soldiers of the First World War. He liked to be in the thick of the action: Winston Churchill called him "the Salamander" due to his ability to pass through fire unharmed. During the Second World War, he commanded the New Zealand Expeditionary Force in the Battle of Crete, the North African Campaign and the Italian Campaign. Freyberg was involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |