|
New Testament People Named John
The name ''John'' (in Greek, ) is prominent in the New Testament and occurs numerous times. Among Jews of this period, the name was one of the most popular, borne by about five percent of men. Thus, it has long been debated which Johns are to be identified with which. Mentioned in narrative At least five unique Johns are mentioned in the texts of New Testament itself. For example, F.P. Dutripon's Latin Bible concordance (Paris 1838) identified 10 people named ''Joannes'' (John) in the Bible, 5 of whom featured in the New Testament: # John the Baptist # John the Apostle, son of Zebedee, whom Dutripon equated with John the Evangelist, John of Patmos, John the Presbyter, the Beloved Disciple and John of Ephesus # John, father of Simon Peter # John Mark, whom Dutripon distinguishes from Mark the Evangelist # John, son of Annas (Acts 4:6) John, father of Simon Peter Simon Peter is at times called “Simon, son of John”, though in Matthew the text has ''Simon Bariona''. The lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John (given Name)
John (; ') is a common male given name in the English language of Hebrew origin. The name is the English form of ''Iohannes'' and ''Ioannes'', which are the Latin forms of the Greek name Ioannis (Ιωάννης), originally borne by Hellenized Jews transliterating the Hebrew name ''Yochanan'' (), the contracted form of the longer name (), meaning "Yahweh is Gracious" or "Yahweh is Merciful". There are numerous forms of the name in different languages; these were formerly often simply translated as "John" in English, but are increasingly left in their native forms (see sidebar). It is among the most commonly given names in Anglophone, Arabic, European, Latin American, Persian and Turkish countries. Traditionally in the Anglosphere, it was the most common, although it has not been since the latter half of the 20th century. John owes its unique popularity to two highly revered saints, John the Baptist (forerunner of Jesus Christ) and the apostle John (traditionally considered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelve Apostles
In Christian theology and ecclesiology, the apostles, particularly the Twelve Apostles (also known as the Twelve Disciples or simply the Twelve), were the primary disciples of Jesus according to the New Testament. During the life and ministry of Jesus in the 1st century AD, the apostles were his closest followers and became the primary teachers of the gospel message of Jesus. There is also an Eastern Christian tradition derived from the Gospel of Luke of there having been as many as seventy apostles during the time of Jesus' ministry. The commissioning of the Twelve Apostles during the ministry of Jesus is described in the Synoptic Gospels. After his resurrection, Jesus sent eleven of them (as Judas Iscariot by then had died) by the Great Commission to spread his teachings to all nations. This event has been called the dispersion of the Apostles. In the Pauline epistles, Paul, although not one of the original twelve, described himself as an apostle, saying he was called b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel Of Mark
The Gospel of Mark), or simply Mark (which is also its most common form of abbreviation). is the second of the four canonical gospels and of the three synoptic Gospels. It tells of the ministry of Jesus from his baptism by John the Baptist to his death, burial, and the discovery of his empty tomb. There is no miraculous birth or doctrine of divine pre-existence, nor, in the original ending ( Mark 16:1–8), any post-resurrection appearances of Jesus. It portrays Jesus as a teacher, an exorcist, a healer, and a miracle worker. He refers to himself as the Son of Man. He is called the Son of God, but keeps his messianic nature secret; even his disciples fail to understand him. All this is in keeping with Christian interpretation of prophecy, which is believed to foretell the fate of the messiah as suffering servant. The gospel ends, in its original version, with the discovery of the empty tomb, a promise to meet again in Galilee, and an unheeded instruction to spread the good ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winkler Prins
The ''Winkler Prins'' is a Dutch-language encyclopedia, founded by the Dutch poet and clergyman Anthony Winkler Prins (1817–1908) and published by Elsevier. It has run through nine printed editions; the first, issued in 16 volumes from 1870 to 1882, and the last (the final in book form), numbering 26 volumes, from 1990 to 1993. ''Winkler Prins'' has been the most distinguished printed encyclopedia in the Dutch language. Publisher Elsevier collaborated with the Microsoft Corporation to put the 1993 version plus any new additions onto CD-ROM in 1997 as the Dutch-language version of ''Encarta.'' The online edition, initially titled 'De Grote Winkler Prins' (the Great Winkler Prins) is one of the most comprehensive works of its kind published so far in any country, containing more than 200,000 articles and references; such prominent scholars and journalists as Frits Staal Johan Frederik "Frits" Staal (3 November 1930 – 19 February 2012) was the department founder and Emeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encarta
''Microsoft Encarta'' is a discontinued digital multimedia encyclopedia published by Microsoft from 1993 to 2009. Originally sold on CD-ROM or DVD, it was also available on the World Wide Web via an annual subscription, although later articles could also be viewed for free online with advertisements. By 2008, the complete English version, ''Encarta Premium'', consisted of more than 62,000 articles, numerous photos and illustrations, music clips, videos, interactive content, timelines, maps, atlases and homework tools. Microsoft published similar encyclopedias under the ''Encarta'' trademark in various languages, including German, French, Spanish, Dutch, Italian, Portuguese and Japanese. Localized versions contained contents licensed from national sources and more or less content than the full English version. For example, the Dutch-language version had content from the Dutch ''Winkler Prins'' encyclopedia. In March 2009, Microsoft announced it was discontinuing both the ''Enc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
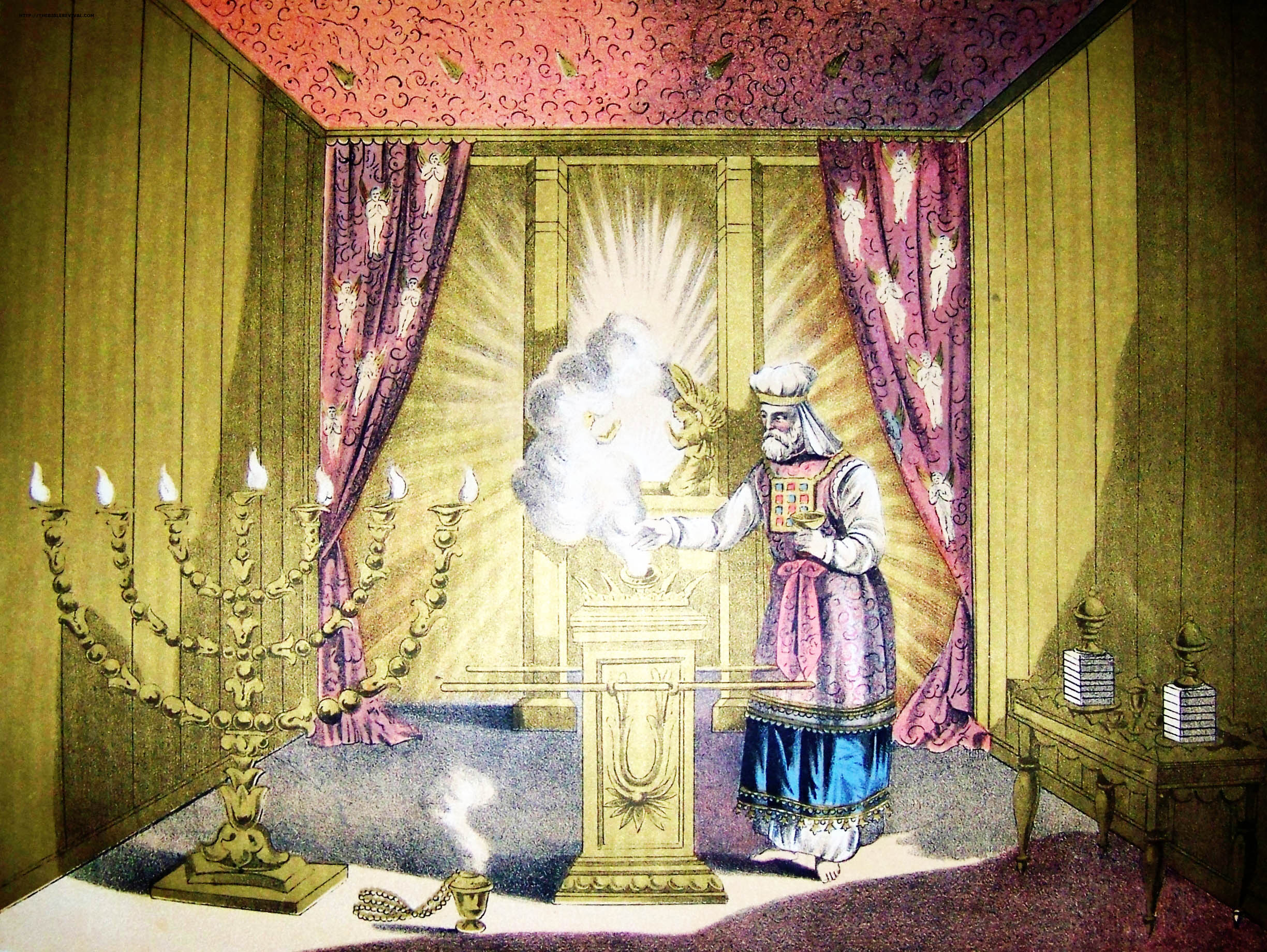
High Priest (Judaism)
High Priest ( he, כהן גדול, translit=Kohen Gadol or ; ) was the title of the chief religious official of Judaism from the early post- Exilic times until the destruction of the Second Temple in Jerusalem by the Romans in 70 CE. Previously, in the Israelite religion, including during the time of the kingdoms of Israel and Judah, other terms were used to designate the leading priests; however, as long as a king was in place, the supreme ecclesiastical authority lay with him. The official introduction of the term "high priest" went hand-in-hand with a greatly enhanced ritual and political significance bestowed upon the chief priest of the Israelites in the post-Exilic period, especially from 411 BCE onward due to the religious transformations brought about during the time of the Babylonian captivity and due to the lack of a Jewish king and kingdom. The high priests belonged to the Jewish priestly families that trace their paternal line back to Aaron—the first high priest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tzitz
The priestly crown or frontlet (צִיץ ''ṣîṣ''/''tsiyts'') was the golden plate or tiara worn by the Jewish High Priest on his mitre or turban whenever he would minister in the Tabernacle or the Temple in Jerusalem. Etymology The root ''tzitz'' (צִיץ) means “to blossom” or “a flower” and as such is employed by the picturesque metaphors in Isaiah 27:6, 28:1, 40:7-8, floral descriptions of Solomon’s temple (1 Kings 6:18-35) and the blooming of Aaron’s rod (Num. 17:23). This latter instance is particularly interesting, because just as a ''tzitz'' appeared on the Aaron’s rod so is the Aaronide high-priest supposed to wear a ''tzitz'' on his forehead. In addition to this, once in the Hebrew Bible, in Ezekiel 8:3, the word appears in the construction ''tzitzit rosh'' meaning “a mop of hair” and probably deriving from the metaphor of hair as the plants grown from skin. This is furthermore supported by a handful of rabbinic descriptions which compare the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycrates Of Ephesus
Polycrates of Ephesus (; el, Πολυκράτης; fl. c. 130 – 196) was an Early Christian bishop at Ephesus. Polycrates convened a synod to establish Quartodecimanism as the official position on Easter. His letter was written between 186-195 AD. Quartodeciman controversy When Pope Victor wanted to set an official practice of Easter on the whole Christian world, to celebrate Easter on Sunday, Polycrates writing in the name of the entire Asian church, argued that the apostles taught to celebrate Easter on the 14th day of Nisan. In his letter he appeals to the authority of Polycarp of Smyrna, Thraseas of Eumenia, Sagaris, Papirius and Melito Melito of Sardis ( el, Μελίτων Σάρδεων ''Melítōn Sárdeōn''; died ) was the bishop of Sardis near Smyrna in western Anatolia, and a great authority in early Christianity. Melito held a foremost place in terms of bishops in Asia ..., all of whom were Quartodecimans. Despite Polycrates convening a synod in Ephesus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel Of The Nazarenes
The Gospel of the Nazarenes (also ''Nazareans'', ''Nazaraeans'', ''Nazoreans'', or ''Nazoraeans'') is the traditional but hypothetical name given by some scholars to distinguish some of the references to, or citations of, non-canonical Jewish-Christian Gospels extant in patristic writings from other citations believed to derive from different Gospels. Collation into ''Gospel of the Nazarenes'' Due to contradictions in the account of the baptism of Jesus, and other reasons, most scholars in the 20th century consider that the ''Gospel of the Nazarenes'' is distinct from the ''Gospel of the Hebrews'' and '' Gospel of the Ebionites'', even though Jerome linked the Nazarenes to the Ebionites in their use of the ''Gospel of the Hebrews''. Text editions of ''Gospel of the Nazarenes'' The current standard critical edition of the text is found in Wilhelm Schneemelcher's ''New Testament Apocrypha'', where 36 verses, GN 1 to GN 36, are collated. GN 1 to GN 23 are mainly from Jerome, GN 24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caiaphas
Joseph ben Caiaphas (; c. 14 BC – c. 46 AD), known simply as Caiaphas (; grc-x-koine, Καϊάφας, Kaïáphas ) in the New Testament, was the Jewish high priest who, according to the gospels, organized a plot to kill Jesus. He famously presided over the Sanhedrin trial of Jesus. The primary sources for Caiaphas' life are the New Testament, and the writings of Josephus. Josephus records that he was made high priest by the Roman procurator Valerius Gratus after Simon ben Camithus had been deposed. Etymology The Babylonian Talmud (Yevamot 15B) gives the family name as Kuppai, while the Jerusalem Talmud (Yevamot 1:6) mentions ''Nekifi''. The ''Mishnah'', Parah 3:5, refers to the family name as hakKof (perhaps "the Monkey", a play on his name for opposing the Pharisees). The family name ''Caiaphas'' קַיָּפָה has three possible origins: * from קוּפָּה 'basket', 'tub', verbalized as קִיֵּף , whence קַיָּף meaning 'basket maker', or a worker utilizi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annas
Annas (also Ananus or Ananias;Goodman, Martin, "Rome & Jerusalem", Penguin Books, p.12 (2007) , ; grc-x-koine, Ἅννας, ; 23/22 BC – death date unknown, probably around AD 40) was appointed by the Roman legate Quirinius as the first High Priest of the newly formed Roman province of Judaea in AD 6 – just after the Romans had deposed Archelaus, Ethnarch of Judaea, thereby putting Judaea directly under Roman rule. Annas appears in the Gospels and Passion plays as a high priest before whom Jesus is brought for judgment, prior to being brought before Pontius Pilate. The sacerdotal family The terms of Annas, Caiaphas, and the five brothers are: Ananus (or Annas), son of Seth (6–15) Annas officially served as High Priest for ten years (AD 6–15), when at the age of 36 he was deposed by the procurator Valerius Gratus. Yet while having been officially removed from office, he remained as one of the nation's most influential political and social individuals, aided greatly by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papias Of Hierapolis
Papias ( el, Παπίας) was a Greek Apostolic Father, Bishop of Hierapolis (modern Pamukkale, Turkey), and author who lived c. 60 – c. 130 AD. He wrote the ''Exposition of the Sayings of the Lord'' ( el, Λογίων Κυριακῶν Ἐξήγησις) in five books. This work, which is lost apart from brief excerpts in the works of Irenaeus of Lyons () and Eusebius of Caesarea (), is an important early source on Christian oral tradition and especially on the origins of the canonical Gospels. Life Very little is known of Papias apart from what can be inferred from his own writings. He is described as "an ancient man who was a hearer of John and a companion of Polycarp" by Polycarp's disciple Irenaeus (c. 180).Irenaeus''Adv. Haer.'' 5.33.4. The original Greek is preserved apud Eusebius.1. Eusebius adds that Papias was Bishop of Hierapolis around the time of Ignatius of Antioch.Eusebius''Hist. Eccl.'' 3.36.2. In this office Papias was presumably succeeded by Abercius of H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |