|
New Historian
The New Historians ( he, ההיסטוריונים החדשים, ''HaHistoryonim HaChadashim'') are a loosely defined group of Israeli historians who have challenged traditional versions of Israeli history, including Israel's role in the 1948 Palestinian exodus and Arab willingness to discuss peace. The term was coined in 1988 by Benny Morris, one of the leading New Historians. According to Ethan Bronner of ''The New York Times'', the New Historians have sought to advance the peace process in the region.Bronner, Ethan"The New New Historians" ''The New York Times'', 9 November 2003. Much of the primary source material used by the group comes from Israeli government papers that were newly available as a result of being declassified thirty years after the founding of Israel. The perception of a new historiographical current emerged with the publications of four scholars in the 1980s: Benny Morris, Ilan Pappé, Avi Shlaim and Simha Flapan. Subsequently, many other historians and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
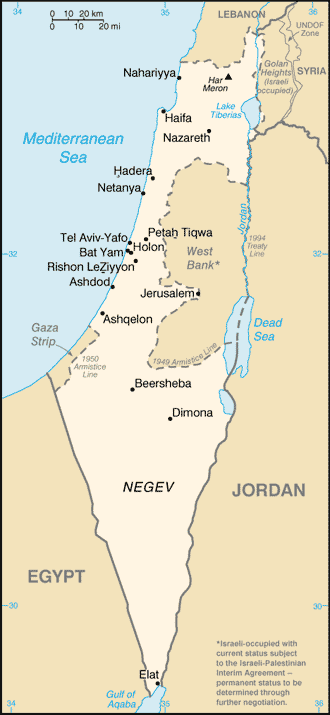
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the Canaanites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-Zionism
Post-Zionism refers to the opinions of some Israelis, diaspora Jews and others, particularly in academia, that Zionism fulfilled its ideological mission with the formation of the modern State of Israel in 1948, and that Zionist ideology should therefore be considered at an end. Right-wing Jews also use the term to refer to the left wing of Israeli politics in light of the Oslo Accords of 1993 and 1995. Some critics associate post-Zionism with anti-Zionism; proponents strenuously deny this association. Characteristic of the perceptions of post-Zionism Post-Zionism is a term associated with a variety of perceptions and different positions, behind which stands criticism of the core beliefs of Zionist groups. Post-Zionists raise many questions about Zionism and the state of Israel, among them: * Is the State of Israel indeed a safe shelter for the Jewish nation? Are there any other places in the world in which the Jews' conditions are better from a historical point of view? (Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anita Shapira
Anita Shapira ( he, אניטה שפירא, born 1940) is an Israeli historian. She is the founder of the Yitzhak Rabin Center, professor emerita of Jewish history at Tel Aviv University, and former head of the Weizmann Institute for the Study of Zionism at Tel Aviv University. She received the Israel Prize for History in 2008. Biography Shapira was born in Warsaw, Poland, in 1940, immigrated to Mandatory Palestine in 1947 and grew up in Tel Aviv. The family lived on Yavneh Street sharing a kitchen and bathroom with other families. Later, they moved to Yad Eliyahu. She studied general and Jewish history at Tel Aviv University, completing her Ph.D. in 1974 under Professor Daniel Carpi. Her dissertation, "The Struggle for Hebrew Labor, 1929-1939," indicated her interest in the history of the Labor Zionist movement, which was to be a continuing focus of her research. In 1985 she was appointed full professor at Tel Aviv University, serving in 1990-95 as dean of the Faculty of Humani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haganah
Haganah ( he, הַהֲגָנָה, lit. ''The Defence'') was the main Zionist paramilitary organization of the Jewish population ("Yishuv") in Mandatory Palestine between 1920 and its disestablishment in 1948, when it became the core of the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). Formed out of previous existing militias, its original purpose was to defend Jewish settlements from Arab attacks, such as the riots of 1920, 1921, 1929 and during the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine. It was under the control of the Jewish Agency, the official governmental body in charge of Palestine's Jewish community during the British Mandate. Until the end of the Second World War, Haganah's activities were moderate, in accordance with the policy of havlaga ("self-restraint"), which caused the splitting of the more radical Irgun and Lehi. The group received clandestine military support from Poland. Haganah sought cooperation with the British in the event of an Axis invasion of Palestine through N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; he, צְבָא הַהֲגָנָה לְיִשְׂרָאֵל , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the Israel, State of Israel. It consists of three service branches: the Israeli Ground Forces, the Israeli Air Force, and the Israeli Navy. It is the sole military wing of the Israeli security forces, Israeli security apparatus, and has no civilian jurisdiction within Israel. The IDF is headed by the Chief of the General Staff (Israel), Chief of the General Staff, who is subordinate to the Ministry of Defense (Israel), Israeli Defense Minister. On the orders of David Ben-Gurion, the IDF was formed on 26 May 1948 and began to operate as a Conscription in Israel, conscript military, drawing its initial recruits from the already-existing paramilitaries of the Yishuv—namely Haganah, the Irgun, and Lehi (militant group), Lehi. Since its formation shortly after the Israeli Declaration of Independen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efraim Karsh
Efraim Karsh ( he, אפרים קארש; born 1953) is an Israeli–British historian who is the founding director and emeritus professor of Middle East and Mediterranean Studies at King's College London. Since 2013, he has served as professor of political studies at Bar-Ilan University (where he also directs the Begin-Sadat Center for Strategic Studies). He is also a principal research fellow and former director of the Middle East Forum, a Philadelphia-based think tank. He is a vocal critic of the New Historians, a group of Israeli scholars who have questioned the traditional Israeli narrative of the Arab–Israeli conflict. Early life and education Born and raised in Israel to Jewish immigrants to the Palestine Mandate, Karsh graduated in Arabic and Modern Middle East History from the Hebrew University in Jerusalem, and obtained an MA and PhD in International Relations from Tel Aviv University. After acquiring his first academic degree in modern Middle Eastern history, he wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli–Palestinian Peace Process
The Israeli–Palestinian peace process refers to the intermittent discussions held by various parties and proposals put forward in an attempt to resolve the ongoing Israeli–Palestinian conflict. Since the 1970s, there has been a parallel effort made to find terms upon which peace can be agreed to in both the Arab–Israeli conflict and in the Palestinian–Israeli conflict. Some countries have signed peace treaties, such as the Egypt–Israel (1979) and Jordan–Israel (1994) treaties, whereas some have not yet found a mutual basis to do so. William B. Quandt, in the introduction of his book ''Peace Process'', says: Sometime in the mid-1970s the term peace process became widely used to describe the American-led efforts to bring about a negotiated peace between Israel and its neighbors. The phrase stuck, and ever since it has been synonymous with the gradual, step-by-step approach to resolving one of the world's most difficult conflicts. In the years since 1967 the emphasis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avi Beker
Avi Beker ( he, אבי בקר; May 3, 1951 – June 4, 2015) was an Israeli writer, statesman, and academic. Beker served as secretary-general of the World Jewish Congress from 4 October 2001 to 14 October 2003. Born in Tel Aviv in 1951, Avi Beker served in the Israel Defense Forces and rose to the rank of captain. He graduated from Tel Aviv University and obtained a Ph.D. in political science from City University of New York. He was a member of the Permanent Mission of Israel to the United Nations (1977–1982) and a delegate to five United Nations General Assemblies and two special sessions of the General Assembly on disarmament, in 1978 and 1982 respectively. World Jewish Congress Beker served as secretary-general of the World Jewish Congress from 2001 to 2003, following stints as the organization's international relations director (from 1998 to 2001) and as executive director of the WJC Israel office (from 1985 to 2001). He worked with several governments on ownership of prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perspectives On Politics
''Perspectives on Politics'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal covering political science. It was established in 2003 and is published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of the American Political Science Association. The editor-in-chief is Michael Bernhard (University of Florida) and the associate/book review editor is Daniel I. O'Neill (University of Florida); the founding editor was Jennifer Hochschild. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Social Sciences Citation Index and Current Contents/Social & Behavioral Sciences. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2016 impact factor of 3.234, ranking it 8th out of 165 journals in the category "Political Science". See also * List of political science journals This is a list of political science journals presenting representative academic journals in the field of political science. A *''Acta Politica'' *''African Affairs'' *''American Journal of Pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab–Israeli Conflict
The Arab–Israeli conflict is an ongoing intercommunal phenomenon involving political tension, military conflicts, and other disputes between Arab countries and Israel, which escalated during the 20th century, but had mostly faded out by the early 21st century. The roots of the Arab–Israeli conflict have been attributed to the support by Arab League member countries for the Palestinians, a fellow League member, in the ongoing Israeli–Palestinian conflict; this in turn has been attributed to the simultaneous rise of Zionism and Arab nationalism towards the end of the 19th century, though the two national movements had not clashed until the 1920s. Part of the Palestine–Israel conflict arose from the conflicting claims by these movements to the land that formed the British Mandatory Palestine, which was regarded by the Jewish people as their ancestral homeland, while at the same time it was regarded by the Pan-Arab movement as historically and currently belonging to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestinian Refugee
Palestinian refugees are citizens of Mandatory Palestine, and their descendants, who fled or were expelled from their country over the course of the 1947–49 Palestine war ( 1948 Palestinian exodus) and the Six-Day War ( 1967 Palestinian exodus). Most Palestinian refugees live in or near 68 Palestinian refugee camps across Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. In 2019 more than 5.6 million Palestinian refugees were registered with the United Nations. In 1949, the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA) defined Palestinian refugees to refer to the original "Palestine refugees" as well as their patrilineal descendants. However, UNRWA's assistance is limited to Palestine refugees residing in UNRWA's areas of operation in the Palestinian Territories, Lebanon, Jordan and Syria. As of 2019, more than 5.6 million Palestinians were registered with UNRWA as refugees, of which more than 1.5 million live in UNRWA-run ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestinian People
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=none, ), are an ethnonational group descending from peoples who have inhabited the region of Palestine over the millennia, and who are today culturally and linguistically Arab. Despite various wars and exoduses, roughly one half of the world's Palestinian population continues to reside in the territory of former British Palestine, now encompassing the West Bank and the Gaza Strip (the Palestinian territories) as well as Israel. In this combined area, , Palestinians constituted 49 percent of all inhabitants, encompassing the entire population of the Gaza Strip (1.865 million), the majority of the population of the West Bank (approximately 2,785,000 versus some 600,000 Israeli settlers, which includes about 200,000 in East Jerusalem), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |