|
New Beckenham Railway Station
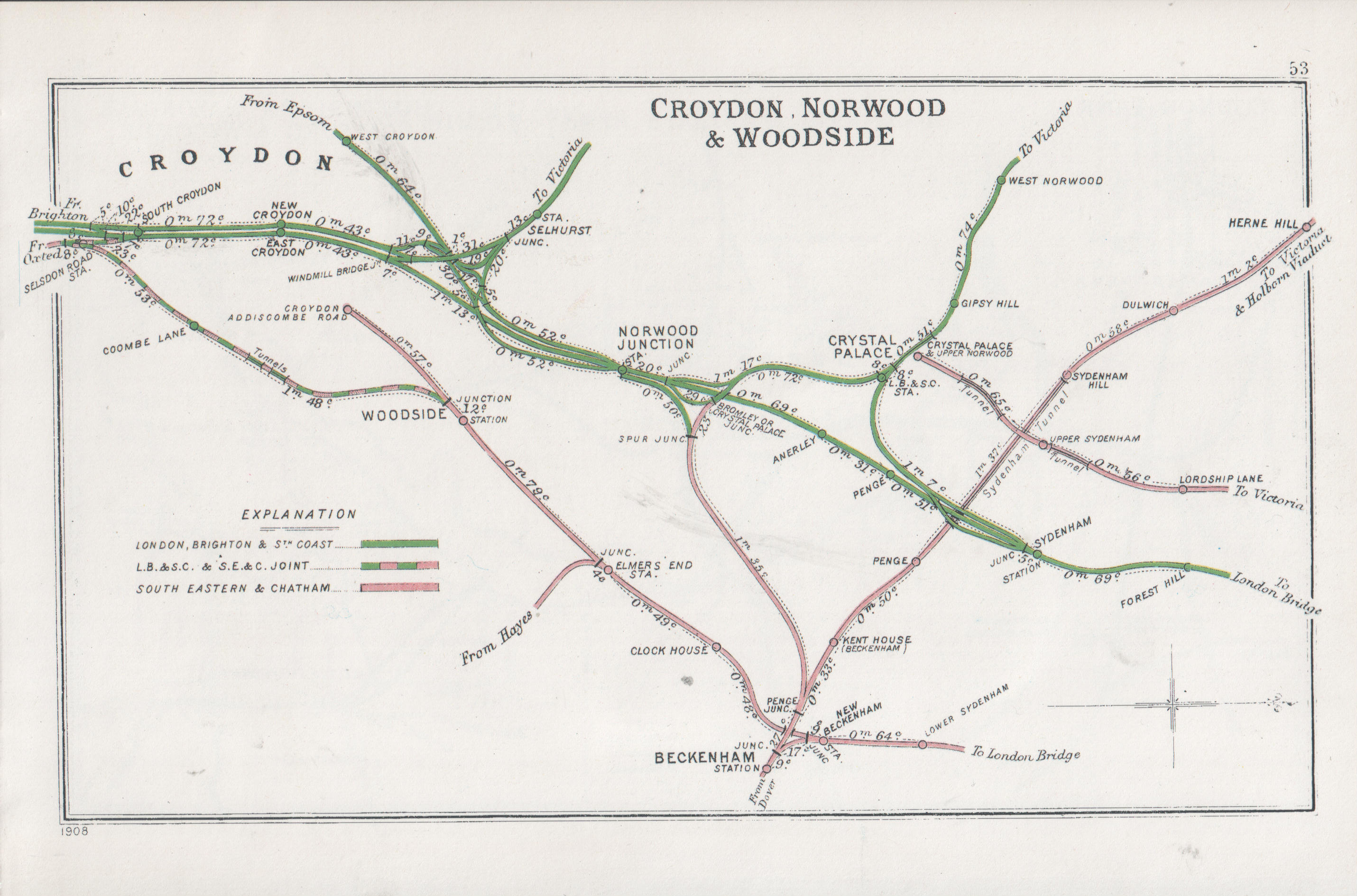
New Beckenham railway station serves Beckenham in the London Borough of Bromley in south-east London, in Travelcard Zone 4. It is measured from . The station and all trains serving it are operated by Southeastern. History Early years (1857–1922) The Mid-Kent line was built by the Mid-Kent and North Kent Junction Railway (MK&NKJR), and was opened as far as Beckenham Junction on 1 January 1857 (although at that time it was not technically a junction, for the West End of London and Crystal Palace Railway's line did not open until 3 May 1858). From its opening the line was worked by the South Eastern Railway (SER). Seven years later, the MK&NKJR built an extension from a new junction station at New Beckenham to Croydon (Addiscombe Road), which again was operated by the SER. This first short-lived station was located immediately south of the junction and may have had platforms on the 1857 and 1864 lines. Two years later, in October 1866, the current station built just nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeastern (train Operating Company)
SE Trains Limited, trading as Southeastern, is a train operator, owned by DfT OLR Holdings for the Department for Transport, that took over operating the South Eastern franchise in South East England from privately owned London & South Eastern Railway (which also traded as Southeastern) on 17 October 2021. History In September 2021, the Department for Transport announced it would be terminating the South Eastern franchise operated by Govia Govia is a transport company based in the United Kingdom. It was formed in November 1996 as a joint venture between Go-Ahead Group (65%) and Keolis (35%) to bid for rail franchises during the privatisation of British Rail. History Establi ...-owned Southeastern (train operating company 2006–2021), Southeastern after revenue declaration discrepancies involving £25million of public money were discovered. SE Trains, as an operator of last resort, took over the franchise on 17 October 2021, for a three-year period until October 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Cross Railway Station
New Cross railway station serves New Cross in south-east London, England. It is down the line from and is in London fare zone 2. The platforms are lettered rather than numbered to avoid confusion with those at by staff who worked at both stations before privatisation of the stations in 1997. Platform D is used exclusively by London Overground services. Ticket barriers control access to all platforms. History In the early Victorian railway boom two companies constructed lines through the area. The London and Croydon Railway (L&CR) built a station on the New Cross Road close to Hatcham in 1839. On 14 October 1844 a large fire that broke out in a paint shop destroyed carriage and engine sheds and workshops adjacent to the station. The fire was witnessed by Louis Philippe I, King of France who was travelling from the station to Dover. On 30 July 1849 the South Eastern Railway (SER) opened a station at North Kent Junction when the North Kent line opened linking Strood with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromley South Railway Station
Bromley South railway station is on the Chatham Main Line in England, serving the town centre and high street of Bromley, south-east London. It is down the line from and is situated between and . The station and most trains that serve the station are operated by Southeastern, with some services also operated by Thameslink. It is in Travelcard Zone 5. Services Services at Bromley South are operated by Southeastern and Thameslink using , , , and EMUs. The typical off-peak service in trains per hour is: * 4 tph to (3 of these run non-stop and 1 calls at only) * 2 tph to via * 2 tph to London Blackfriars via * 2 tph to * 2 tph to via * 1 tph to * 1 tph to via * 1 tph to via Chatham * 1 tph to via A number of additional services call at the station during the peak hours. These include additional stopping services to London Victoria via Herne Hill, direct Southeastern trains to London Blackfriars as well as additional trains between London and Ashford via Maidsto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewisham Station
Lewisham is a National Rail and Docklands Light Railway station in Lewisham, south-east London which first opened in 1849. On the National Rail network it is measured from and is operated by Southeastern (train operating company), Southeastern.SoutheasternStation facilities: Lewisham Station layout There are four platforms for main-line trains: 3 and 4 on the North Kent Line, and 1 and 2 on the Mid-Kent line which is also used as a loop off the South Eastern Main Line. The current station which dates from 1857 is constructed of yellow stock brick with stone dressing and has an unusual survival of a wooden clapboard building at the back. The facade has a pleasing symmetry of three windows, three entrance doors, and three windows. Original doors sash windows skirting tiling and banisters are present inside. The original corniced ceiling of the main hall is currently concealed by a lowered fake ceiling. Platform 3 has kept its original canopy with its elaborate cast iron brack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network SouthEast
Network SouthEast (NSE) was one of the three passenger sectors of British Rail created in 1982. NSE mainly operated commuter rail trains within Greater London and inter-urban services in densely populated South East England, although the network went as far west as Exeter. Before 1986, the sector was originally known as ''London & South Eastern''. During the privatisation of British Rail, it was gradually divided into a number of franchises. History Before the sectorisation of British Rail (BR) in 1982 the system was split into largely autonomous regional operations: those operating around London were the London Midland Region, Southern Region, Western Region and Eastern Region. Sectorisation of BR changed this setup by instead organising by the traffic type: commuter services in the south-east of England, long-distance intercity services, local services in the UK regions, parcels and freight. The aim was to introduce greater budgetary efficiency and managerial accounta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InterCity (British Rail)
InterCity (or, in the earliest days, the hyphenated Inter-City) was introduced by British Rail in 1966 as a brand-name for its long-haul express passenger services (see British Rail brand names for a full history). In 1986 the British Railways Board divided its operations into a number of sectors ( sectorisation). The sector responsible for long-distance express trains assumed the brand-name InterCity, although many routes that were previously operated as InterCity services were assigned to other sectors (e.g. London to King's Lynn services were transferred to the commuter sector Network SouthEast). InterCity brand Etymology InterCity derives from the prepositional of the with ''City'' giving rise to meaning ''between cities''. The Inter-City train British Rail first used the term ''Inter-City'' in 1950 as the name of a train running between London Paddington and Wolverhampton Low Level. This was part of an overall policy of introducing new train names in the post Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladywell Railway Station
Ladywell railway station is in Ladywell, in the London Borough of Lewisham in south east London, in Travelcard Zone 3. It is measured from . The station and all trains serving it are operated by Southeastern. The Grade II station opened in 1857 and is in Ladywell Fields, adjacent to University Hospital, Lewisham. History Early years (1857-1922) The Mid-Kent line was built by the Mid-Kent and North Kent Junction Railway (MK&NKJR) and was opened on 1 January 1857 as far as Beckenham Junction (although it was not technically a junction as the West End of London and Crystal Palace Railway's line did not open until 3 May 1858). From opening the line was worked by the South Eastern Railway (SER). Seven years later the MK&NKJR built an extension from a new junction station at New Beckenham to Croydon (Addiscombe Road) which again was operated by the SER. In September 1866 a spur was opened from the north end of Ladywell station to the recently opened main line (which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British railway companies, and was privatised in stages between 1994 and 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. The period of nationalisation saw sweeping changes in the railway. A process of dieselisation and electrification took place, and by 1968 steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction, except for the Vale of Rheidol Railway (a narrow-gauge tourist line). Passengers replaced freight as the main source of business, and one-third of the network was closed by the Beeching cuts of the 1960s in an effort to reduce rail subsidies. On privatis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Rail
A third rail, also known as a live rail, electric rail or conductor rail, is a method of providing electric power to a railway locomotive or train, through a semi-continuous rigid conductor placed alongside or between the rails of a railway track. It is used typically in a mass transit or rapid transit system, which has alignments in its own corridors, fully or almost fully segregated from the outside environment. Third rail systems are usually supplied from direct current electricity. Modern tram systems, street-running, avoid the risk of electrocution by the exposed electric rail by implementing a segmented ground-level power supply, where each segment is electrified only while covered by a vehicle which is using its power. The third-rail system of electrification is not related to the third rail used in dual gauge railways. Description Third-rail systems are a means of providing electric traction power to trains using an additional rail (called a "conductor rail") fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Electrification In Great Britain
Railway electrification in Great Britain began in the late 19th century. A range of voltages has been used, employing both overhead lines and conductor rails. The two most common systems are using overhead lines, and the third rail system used in Southeast England and on Merseyrail. As of March 2020, (38%) of the British Rail transport in Great Britain, rail network was Railway electrification system, electrified. According to Network Rail, as at 2003, 64% of the electrified network used the 25kVAC overhead system, and 36% used the 660/750VDC third-rail system.Network Rail, 2003 Technical Plan, Chapter 11 "Network Capability", page 7 "Electrification". "Approximately 40% of the rail network is currently equipped with electrification." From page 1, total network is 30764 km, 7587 km of 25 kV AC, 4285 km of 650/750 V DC and 28 km of 1500 V DC. Excludes CTRL, LUL, Old Danby test track, bulk of Tyne and Wear Metro, etc. NB it does not state what method of counting length of netw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railways Act 1921
The Railways Act 1921 (c. 55), also known as the Grouping Act, was an Act of Parliament enacted by the British government and intended to stem the losses being made by many of the country's 120 railway companies, by "grouping" them into four large companies dubbed the " Big Four". This was intended to move the railways away from internal competition, and retain some of the benefits which the country had derived from a government-controlled railway during and after the Great War of 1914–1918. The provisions of the Act took effect from the start of 1923. History The British railway system had been built up by more than a hundred railway companies, large and small, and often, particularly locally, in competition with each other. The parallel railways of the East Midlands and the rivalry between the South Eastern Railway and the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway at Hastings were two examples of such local competition. During the First World War the railways were under st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
