|
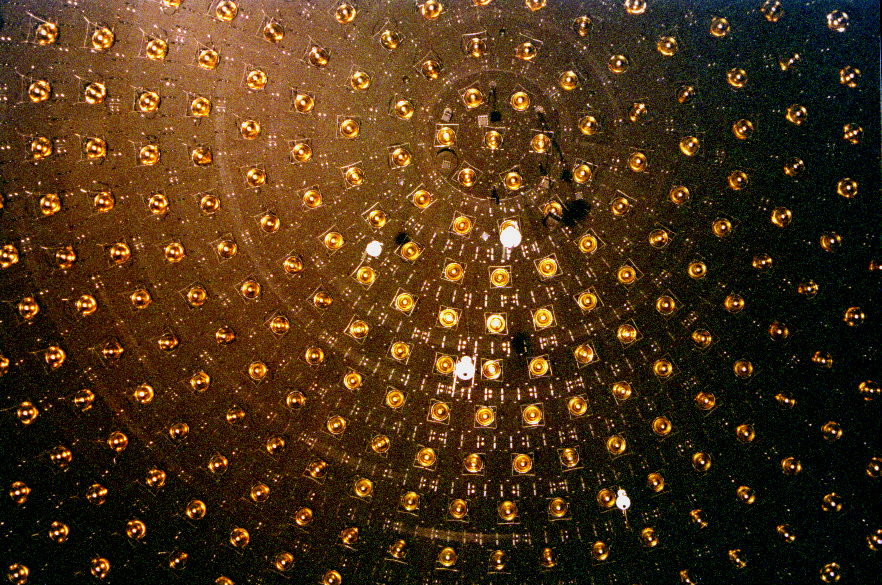
Neutrino Observatory
A neutrino detector is a physics apparatus which is designed to study neutrinos. Because neutrinos only weakly interact with other particles of matter, neutrino detectors must be very large to detect a significant number of neutrinos. Neutrino detectors are often built underground, to isolate the detector from cosmic rays and other background radiation. The field of neutrino astronomy is still very much in its infancy – the only confirmed extraterrestrial sources are the Sun and the supernova 1987A in the nearby Large Magellanic Cloud. Another likely source (three standard deviations) is the blazar TXS 0506+056 about 3.7 billion light years away. Neutrino observatories will "give astronomers fresh eyes with which to study the universe". Various detection methods have been used. Super Kamiokande is a large volume of water surrounded by phototubes that watch for the Cherenkov radiation emitted when an incoming neutrino creates an electron or muon in the water. The Sudbur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MiniBooNE
MiniBooNE is a Cherenkov detector experiment at Fermilab designed to observe neutrino oscillations (BooNE is an acronym for the Booster Neutrino Experiment). A neutrino beam consisting primarily of muon neutrinos is directed at a detector filled with 800 tons of mineral oil (ultrarefined methylene compounds) and lined with 1,280 photomultiplier tubes. An excess of electron neutrino events in the detector would support the neutrino oscillation interpretation of the LSND (Liquid Scintillator Neutrino Detector) result. MiniBooNE started collecting data in 2002 and was still running in 2017. In May 2018, physicists of the MiniBooNE experiment reported a possible signal indicating the existence of sterile neutrinos. History and motivation Experimental observation of solar neutrinos and atmospheric neutrinos provided evidence for neutrino oscillations, implying that neutrinos have masses. Data from the LSND experiment at Los Alamos National Laboratory are controversial since th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium
Gallium is a chemical element with the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875, Gallium is in group 13 of the periodic table and is similar to the other metals of the group (aluminium, indium, and thallium). Elemental gallium is a soft, silvery metal in standard temperature and pressure. In its liquid state, it becomes silvery white. If too much force is applied, the gallium may fracture conchoidally. Since its discovery in 1875, gallium has widely been used to make alloys with low melting points. It is also used in semiconductors, as a dopant in semiconductor substrates. The melting point of gallium is used as a temperature reference point. Gallium alloys are used in thermometers as a non-toxic and environmentally friendly alternative to mercury, and can withstand higher temperatures than mercury. An even lower melting point of , well below the freezing point of water, is claimed for the alloy galinstan (62–� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale form. These models offer a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, and large-scale structure. The overall uniformity of the Universe, known as the flatness problem, is explained through cosmic inflation: a sudden and very rapid expansion of space during the earliest moments. However, physics currently lacks a widely accepted theory of quantum gravity that can successfully model the earliest conditions of the Big Bang. Crucially, these models are compatible with the Hubble–Lemaître law—the observation that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KM3NeT
The Cubic Kilometre Neutrino Telescope, or KM3NeT, is a future European research infrastructure that will be located at the bottom of the Mediterranean Sea. It will host the next-generation neutrino astronomy, neutrino telescope in the form of a water Cherenkov detector with an instrumented volume of several cubic kilometres distributed over three locations in the Mediterranean: KM3NeT-Fr (off Toulon, France), KM3NeT-It (off Portopalo di Capo Passero, Sicily, Italy) and KM3NeT-Gr (off Pylos, Peloponnese, Greece). The KM3NeT project continues work done under the ANTARES (telescope), ANTARES (telescope built off coast of France), Neutrino Mediterranean Observatory, NEMO (planned telescope off coast of Italy) and NESTOR Project, NESTOR (planned telescope off coast of Greece) neutrino telescope projects. KM3NeT will search for neutrinos from distant astrophysical sources like supernova remnants, gamma-ray bursts, supernovae or colliding stars and will be a powerful tool in the searc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IceCube
The IceCube Neutrino Observatory (or simply IceCube) is a neutrino observatory constructed at the Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station in Antarctica. The project is a recognized CERN experiment (RE10). Its thousands of sensors are located under the Antarctic ice, distributed over a cubic kilometre. Similar to its predecessor, the Antarctic Muon And Neutrino Detector Array (AMANDA), IceCube consists of spherical optical sensors called Digital Optical Modules (DOMs), each with a photomultiplier tube (PMT) and a single-board data acquisition computer which sends digital data to the counting house on the surface above the array. IceCube was completed on 18 December 2010. DOMs are deployed on strings of 60 modules each at depths between 1,450 and 2,450 meters into holes melted in the ice using a hot water drill. IceCube is designed to look for point sources of neutrinos in the teraelectronvolt (TeV) range to explore the highest-energy astrophysical processes. In November 2013 it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANTARES (telescope)
ANTARES is the name of a neutrino detector residing 2.5 km under the Mediterranean Sea off the coast of Toulon, France. It is designed to be used as a directional neutrino telescope to locate and observe neutrino flux from cosmic origins in the direction of the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth, a complement to the South Pole neutrino detector IceCube that detects neutrinos from both hemispheres. The name comes from Astronomy with a Neutrino Telescope and Abyss environmental RESearch project; the acronym is also the name of the prominent star Antares. The experiment is a recognized CERN experiment (RE6). Other neutrino telescopes designed for use in the nearby area include the Greek NESTOR telescope and the Italian NEMO telescope, which are both in early design stages. The data taking of ANTARES was finished in February 2022, after 16 years of continuous operation. Design The array contains a set of twelve separate vertical strings of photomultiplier tubes. Each one has 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoacoustics
Thermoacoustics is the interaction between temperature, density and pressure variations of acoustic waves. Thermoacoustic heat engines can readily be driven using solar energy or waste heat Waste heat is heat that is produced by a machine, or other process that uses energy, as a byproduct of doing work. All such processes give off some waste heat as a fundamental result of the laws of thermodynamics. Waste heat has lower utility ... and they can be controlled using proportional control. They can use heat available at low temperatures which makes it ideal for heat recovery and low power applications. The components included in thermoacoustic engines are usually very simple compared to conventional Engine, engines. The device can easily be controlled and maintained. Thermoacoustic effects can be observed when partly molten glass tubes connected to glass vessels. Sometimes spontaneously a loud and monotone sound is produced. A similar effect is observed if one side of a stainle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avalanche Photodiode
An avalanche photodiode (APD) is a highly sensitive semiconductor photodiode detector that exploits the photoelectric effect to convert light into electricity. From a functional standpoint, they can be regarded as the semiconductor analog of photomultiplier tubes. The avalanche photodiode (APD) was invented by Japanese engineer Jun-ichi Nishizawa in 1952. However, study of avalanche breakdown, microplasma defects in silicon and germanium and the investigation of optical detection using p-n junctions predate this patent. Typical applications for APDs are laser rangefinders, long-range fiber-optic telecommunication, and quantum sensing for control algorithms. New applications include positron emission tomography and particle physics. It was discovered in 2020 that adding graphene layer can prevent degradation over time to keep avalanche photodiode''like new'' which is important in shrinking their size and costs for many diverse applications & bringing devices out of vacuum tubes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOνA
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramatic appearance of a nova vary, depending on the circumstances of the two progenitor stars. All observed novae involve white dwarfs in close binary systems. The main sub-classes of novae are classical novae, recurrent novae (RNe), and dwarf novae. They are all considered to be cataclysmic variable stars. Classical nova eruptions are the most common type. They are likely created in a close binary star system consisting of a white dwarf and either a main sequence, subgiant, or red giant star. When the orbital period falls in the range of several days to one day, the white dwarf is close enough to its companion star to start drawing accreted matter onto the surface of the white dwarf, which creates a dense but shallow atmosphere. This atmospher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudocumene
1,2,4-Trimethylbenzene, also known as pseudocumene, is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH(CH). Classified as an aromatic hydrocarbon, it is a flammable colorless liquid with a strong odor. It is nearly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. It occurs naturally in coal tar and petroleum (about 3%). It is one of the three isomers of trimethylbenzene. Production Industrially, it is isolated from the C aromatic hydrocarbon fraction during petroleum distillation. Approximately 40% of this fraction is 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene. It is also generated by methylation of toluene and xylenes and the disproportionation of xylene over aluminosilicate catalysts.Karl Griesbaum, Arno Behr, Dieter Biedenkapp, Heinz-Werner Voges, Dorothea Garbe, Christian Paetz, Gerd Collin, Dieter Mayer, Hartmut Höke "Hydrocarbons" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002 Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Uses Pseudocumene is a precursor to mellitic anhydride, from which high performance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borexino
Borexino is a particle physics Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) an ... experiment to study low energy (sub-MeV) solar neutrinos. The detector is the world's most radio-pure liquid Scintillation counter, scintillator calorimeter. It is placed within a stainless steel sphere which holds the photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) used as signal detectors and is shielded by a water tank to protect it against external radiation and tag incoming Cosmic ray, cosmic muons that manage to penetrate the overburden of the mountain above. The primary aim of the experiment is to make a precise measurement of the individual neutrino fluxes from the Sun and compare them to the Standard solar model predictions. This will allow scientists to test and to further understand the functioning of the Sun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scintillator
A scintillator is a material that exhibits scintillation, the property of luminescence, when excited by ionizing radiation. Luminescent materials, when struck by an incoming particle, absorb its energy and scintillate (i.e. re-emit the absorbed energy in the form of light). Sometimes, the excited state is metastable, so the relaxation back down from the excited state to lower states is delayed (necessitating anywhere from a few nanoseconds to hours depending on the material). The process then corresponds to one of two phenomena: delayed fluorescence or phosphorescence. The correspondence depends on the type of transition and hence the wavelength of the emitted optical photon. Principle of operation A scintillation detector or scintillation counter is obtained when a scintillator is coupled to an electronic light sensor such as a photomultiplier tube (PMT), photodiode, or silicon photomultiplier. PMTs absorb the light emitted by the scintillator and re-emit it in the form of ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |