|
Neurally Controlled Animat
A neurally controlled animat is the conjunction of #a cultured neuronal network #a virtual or physical robotic body, the Animat, "living" in a virtual computer generated environment or in a physical arena, connected to this array Patterns of neural activity are used to control the virtual body, and the computer is used as a sensory device to provide electrical feedback to the neural network about the Animat's movement in the virtual environment. The current aim of the Animat research is to study the neuronal activity and plasticity when learning and processing information in order to find a mathematical model for the neural network, and to determine how information is processed and encoded in the rat cortex. It leads towards interesting questions about consciousness Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultured Neuronal Networks
A cultured neuronal network is a cell culture of neurons that is used as a model to study the central nervous system, especially the brain. Often, cultured neuronal networks are connected to an input/output device such as a multi-electrode array (MEA), thus allowing two-way communication between the researcher and the network. This model has proved to be an invaluable tool to scientists studying the underlying principles behind neuronal learning, memory, plasticity, connectivity, and information processing. Cultured neurons are often connected via computer to a real or simulated robotic component, creating a hybrot or animat, respectively. Researchers can then thoroughly study learning and plasticity in a realistic context, where the neuronal networks are able to interact with their environment and receive at least some artificial sensory feedback. One example of this can be seen in the Multielectrode Array Art (MEART) system developed by the Potter Research Group at the Georg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animat
Animat are artificial animals and is a contraction of animal and materials. The term includes physical robots and virtual simulations. The animat model includes features of a simple animal capable of interacting with its environment. It is, therefore, designed to simulate the ability to associate certain signals from the environment within a learning phase that indicate a potential for cognitive structure. Animat research, a subset of Artificial Life studies, has become rather popular since Rodney Brooks' seminal paper "Intelligence without representation". Development Animats is derived from the third-person indicative present of the Latin verb ''animō''), which means to "animate, give or bring life". The term was coined by S.W. Wilson in 1985,in "Knowledge growth in an artificial animal", published in the first ''Proceedings'' ''of an International Conference on Genetic Algorithms and Their Applications''. Wilson's conceptualization built on the works of W.G. Walter, particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Reality
Virtual reality (VR) is a simulated experience that employs pose tracking and 3D near-eye displays to give the user an immersive feel of a virtual world. Applications of virtual reality include entertainment (particularly video games), education (such as medical or military training) and business (such as virtual meetings). Other distinct types of VR-style technology include augmented reality and mixed reality, sometimes referred to as extended reality or XR, although definitions are currently changing due to the nascence of the industry. Currently, standard virtual reality systems use either virtual reality headsets or multi-projected environments to generate realistic images, sounds and other sensations that simulate a user's physical presence in a virtual environment. A person using virtual reality equipment is able to look around the artificial world, move around in it, and interact with virtual features or items. The effect is commonly created by VR headsets consisting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
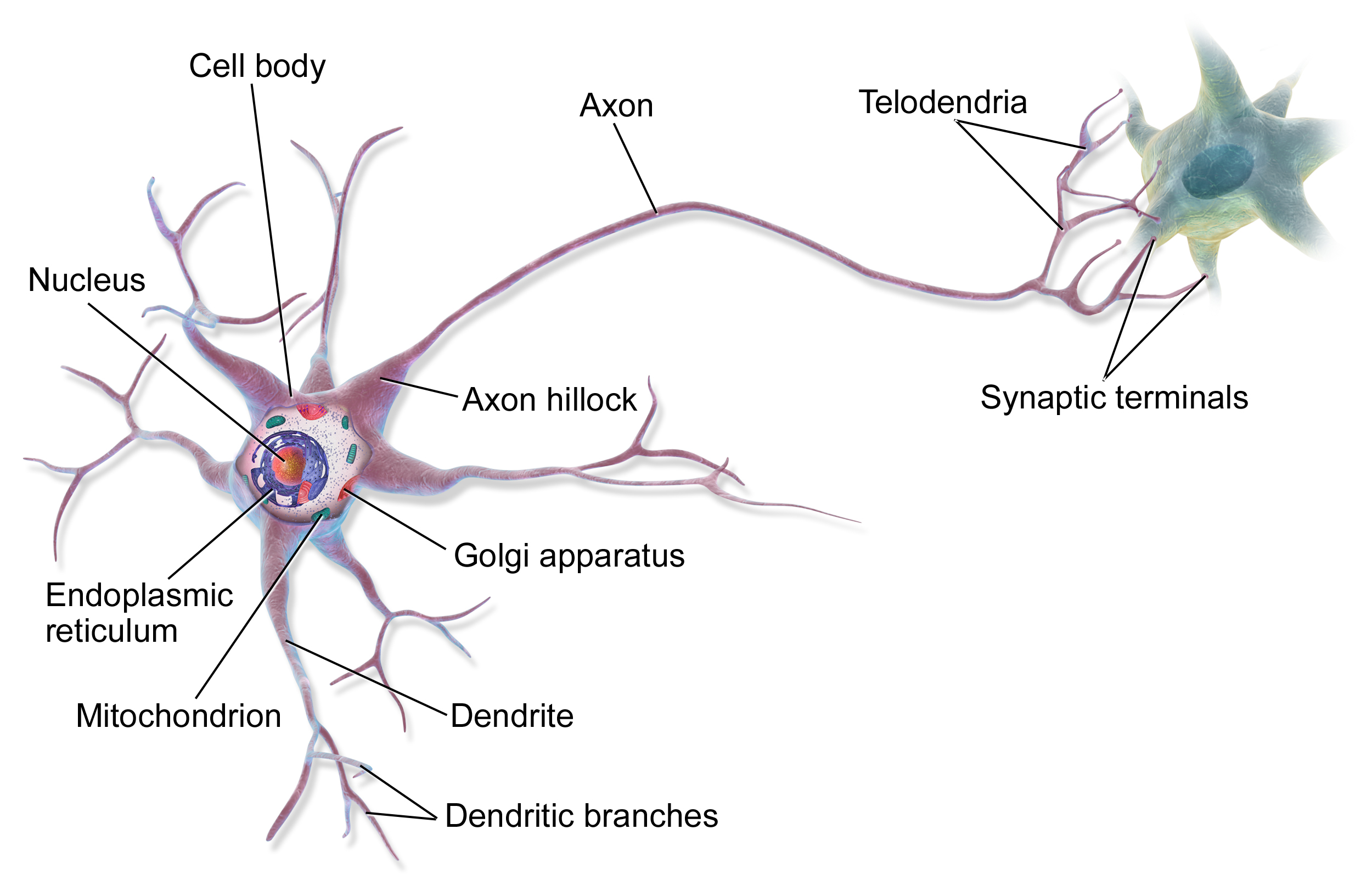
Neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body (soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon and dend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used in the natural sciences (such as physics, biology, earth science, chemistry) and engineering disciplines (such as computer science, electrical engineering), as well as in non-physical systems such as the social sciences (such as economics, psychology, sociology, political science). The use of mathematical models to solve problems in business or military operations is a large part of the field of operations research. Mathematical models are also used in music, linguistics, and philosophy (for example, intensively in analytic philosophy). A model may help to explain a system and to study the effects of different components, and to make predictions about behavior. Elements of a mathematical model Mathematical models can take many forms, including dynamical systems, statisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scientists. Opinions differ about what exactly needs to be studied or even considered consciousness. In some explanations, it is synonymous with the mind, and at other times, an aspect of mind. In the past, it was one's "inner life", the world of introspection, of private thought, imagination and volition. Today, it often includes any kind of cognition, experience, feeling or perception. It may be awareness, awareness of awareness, or self-awareness either continuously changing or not. The disparate range of research, notions and speculations raises a curiosity about whether the right questions are being asked. Examples of the range of descriptions, definitions or explanations are: simple wakefulness, one's sense of selfhood or sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Circuits
A neural circuit is a population of neurons interconnected by synapses to carry out a specific function when activated. Neural circuits interconnect to one another to form large scale brain networks. Biological neural networks have inspired the design of artificial neural networks, but artificial neural networks are usually not strict copies of their biological counterparts. Early study Early treatments of neural networks can be found in Herbert Spencer's ''Principles of Psychology'', 3rd edition (1872), Theodor Meynert's ''Psychiatry'' (1884), William James' ''Principles of Psychology'' (1890), and Sigmund Freud's Project for a Scientific Psychology (composed 1895). The first rule of neuronal learning was described by Hebb in 1949, in the Hebbian theory. Thus, Hebbian pairing of pre-synaptic and post-synaptic activity can substantially alter the dynamic characteristics of the synaptic connection and therefore either facilitate or inhibit signal transmission. In 1959, the neur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |