|
Nerita Fulgurans
''Nerita fulgurans'' is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Neritidae. Distribution Usually found on hard structures in estuarine conditions protected from significant wave action. Found along the Atlantic coast of Florida, as far North as the St. Augustine inlet, to the south it has been identified on the island Barbados. Description ''Nerita fulgurans'' is dark in colour with various shades of yellow and black on the shell. The maximum recorded shell length is 37 mm.Welch J. J. (2010). "The "Island Rule" and Deep-Sea Gastropods: Re-Examining the Evidence". '' PLoS ONE'' 5(1): e8776. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008776. Circulatory system: The osmotic pressure of the hemolymph of ''Nerita fulgurans'' is 1060 mOsm. Habitat Minimum recorded depth is 0 m. Maximum recorded depth is 0 m. The snail occupies the high rocky intertodal zone and prefers brackish habitats such as mangrove forests and seagrass beds A seagrass meadow o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Friedrich Gmelin
, fields = , workplaces = University of GöttingenUniversity of Tübingen , alma_mater = University of Tübingen , doctoral_advisor = Philipp Friedrich GmelinFerdinand Christoph Oetinger , academic_advisors = , doctoral_students = Georg Friedrich HildebrandtFriedrich StromeyerCarl Friedrich KielmeyerWilhelm August LampadiusVasily Severgin , notable_students = , known_for = Textbooks on chemistry, pharmaceutical science, mineralogy, and botany , author_abbrev_bot = J.F.Gmel. , author_abbrev_zoo = Gmelin , influences = Carl Linnaeus , influenced = , relatives = Leopold Gmelin (son) , awards = Johann Friedrich Gmelin (8 August 1748 – 1 November 1804) was a German naturalist, botanist, entomologist, herpetologist, and malacologist. Education Johann Friedrich Gmelin was born as the eldest son of Philipp Friedrich Gmelin in 1748 in Tübingen. He studied medicine under his father at University of Tübingen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturalis Biodiversity Center - ZMA
Naturalis Biodiversity Center ( nl, Nederlands Centrum voor Biodiversiteit Naturalis) is a national museum of natural history and a research center on biodiversity in Leiden, Netherlands. It was named the European Museum of the Year 2021. Although its current name and organization are relatively recent, the history of Naturalis can be traced back to the early 1800s. Its collection includes approximately 42 million specimens, making it one of the largest natural history collections in the world. History The beginnings of Naturalis go back to the creation of the Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie (abbreviated RMNH, National Museum of Natural History) by Dutch King William I on August 9, 1820. In 1878, the geological and mineralogical collections of the museum were split off into a separate museum, remaining distinct until the merger of the Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie with the Rijksmuseum van Geologie en Mineralogie (abbreviated RGM) in 1984, to form the Nationaal Natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
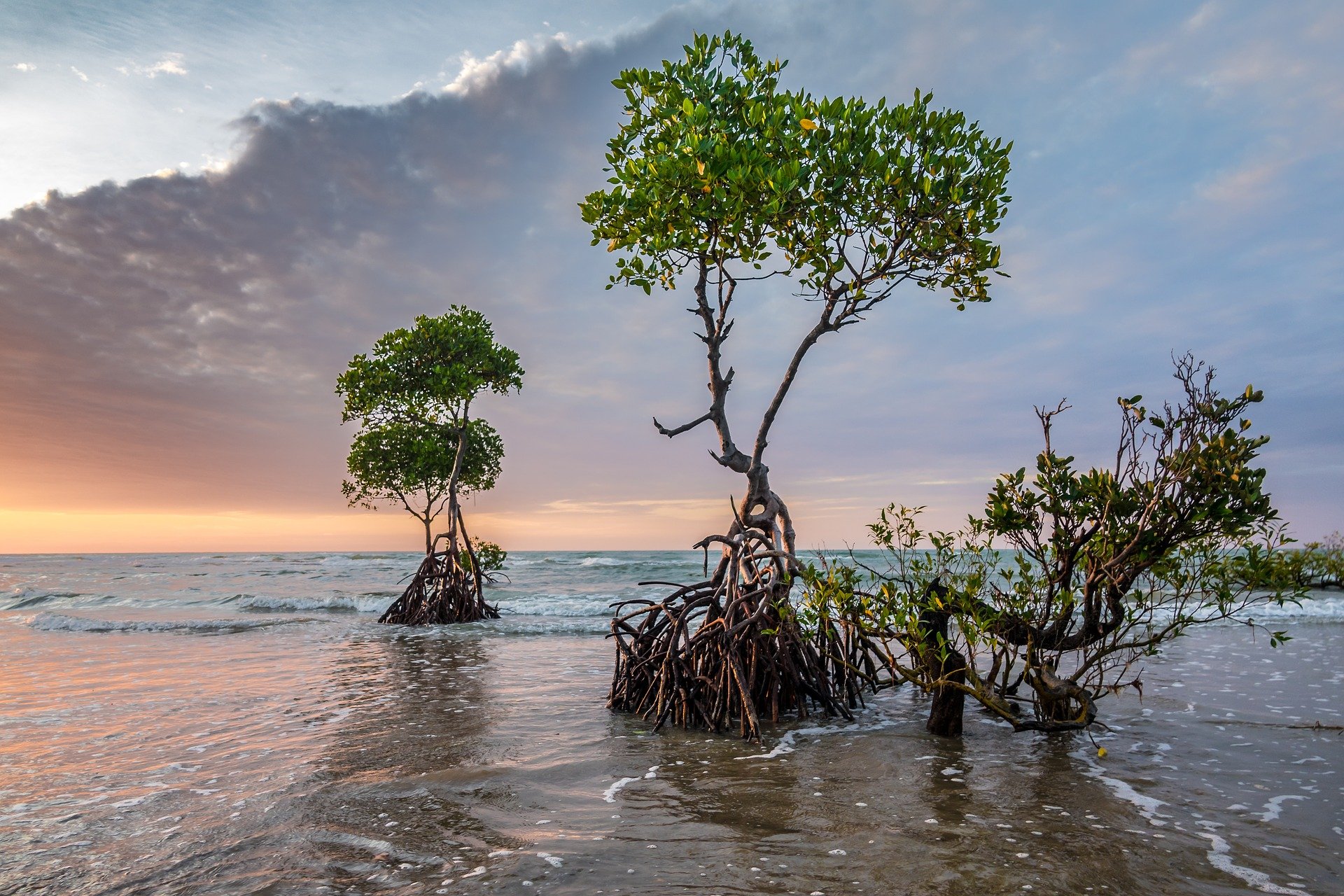
Seagrass Meadow
A seagrass meadow or seagrass bed is an underwater ecosystem formed by seagrasses. Seagrasses are marine (saltwater) plants found in shallow coastal waters and in the brackish waters of estuaries. Seagrasses are flowering plants with stems and long green, grass-like leaves. They produce seeds and pollen and have roots and rhizomes which anchor them in seafloor sand. Seagrasses form dense underwater meadows which are among the most productive ecosystems in the world. They provide habitats and food for a diversity of marine life comparable to that of coral reefs. This includes invertebrates like shrimp and crabs, cod and flatfish, marine mammals and birds. They provide refuges for endangered species such as seahorses, turtles, and dugongs. They function as nursery habitats for shrimps, scallops and many commercial fish species. Seagrass meadows provide coastal storm protection by the way their leaves absorb energy from waves as they hit the coast. They keep coastal waters healthy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mangrove Forest
Mangrove forests, also called mangrove swamps, mangrove thickets or mangals, are productive wetlands that occur in coastal intertidal zones. Mangrove forests grow mainly at tropical and subtropical latitudes because mangroves cannot withstand freezing temperatures. There are about 80 different species of mangroves, all of which grow in areas with low-oxygen soil, where slow-moving waters allow fine sediments to accumulate.What is a mangrove forest? National Ocean Service, NOAA. Updated: 25 March 2021. Retrieved: 4 October 2021. Many mangrove forests can be recognised by their dense tangle of prop roots that make the trees appear to be standing on stilts above the water. This tangle of roots allows the trees to handle the daily rise and fall of tides, which means that most mangroves get flooded at least twice per day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOsm
Osmotic concentration, formerly known as osmolarity, is the measure of solute concentration, defined as the number of osmoles (Osm) of solute per litre (L) of solution (osmol/L or Osm/L). The osmolarity of a solution is usually expressed as Osm/L (pronounced "osmolar"), in the same way that the molarity of a solution is expressed as "M" (pronounced "molar"). Whereas molarity measures the number of moles of solute per unit volume of solution, osmolarity measures the number of ''osmoles of solute particles'' per unit volume of solution. This value allows the measurement of the osmotic pressure of a solution and the determination of how the solvent will diffuse across a semipermeable membrane (osmosis) separating two solutions of different osmotic concentration. Unit The unit of osmotic concentration is the osmole. This is a non- SI unit of measurement that defines the number of moles of solute that contribute to the osmotic pressure of a solution. A milliosmole (mOsm) is 1/1,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemolymph
Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, analogous to the blood in vertebrates, that circulates in the interior of the arthropod (invertebrate) body, remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which hemolymph cells called hemocytes are suspended. In addition to hemocytes, the plasma also contains many chemicals. It is the major tissue type of the open circulatory system characteristic of arthropods (e.g. arachnids, crustaceans and insects). In addition, some non-arthropods such as molluscs possess a hemolymphatic circulatory system. Oxygen-transport systems were long thought unnecessary in insects, but ancestral and functional hemocyanin has been found in the hemolymph. Insect "blood" generally does not carry hemoglobin, although hemoglobin may be present in the tracheal system instead and play some role in respiration. Method of transport In the grasshopper, the closed portion of the system consists of tubular hearts and an aort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmotic Pressure
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane. It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in a pure solvent by osmosis. Potential osmotic pressure is the maximum osmotic pressure that could develop in a solution if it were separated from its pure solvent by a semipermeable membrane. Osmosis occurs when two solutions containing different concentrations of solute are separated by a selectively permeable membrane. Solvent molecules pass preferentially through the membrane from the low-concentration solution to the solution with higher solute concentration. The transfer of solvent molecules will continue until equilibrium is attained. Theory and measurement Jacobus van 't Hoff found a quantitative relationship between osmotic pressure and solute concentration, expressed in the following equation: :\Pi = icRT where \Pi is osmotic p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
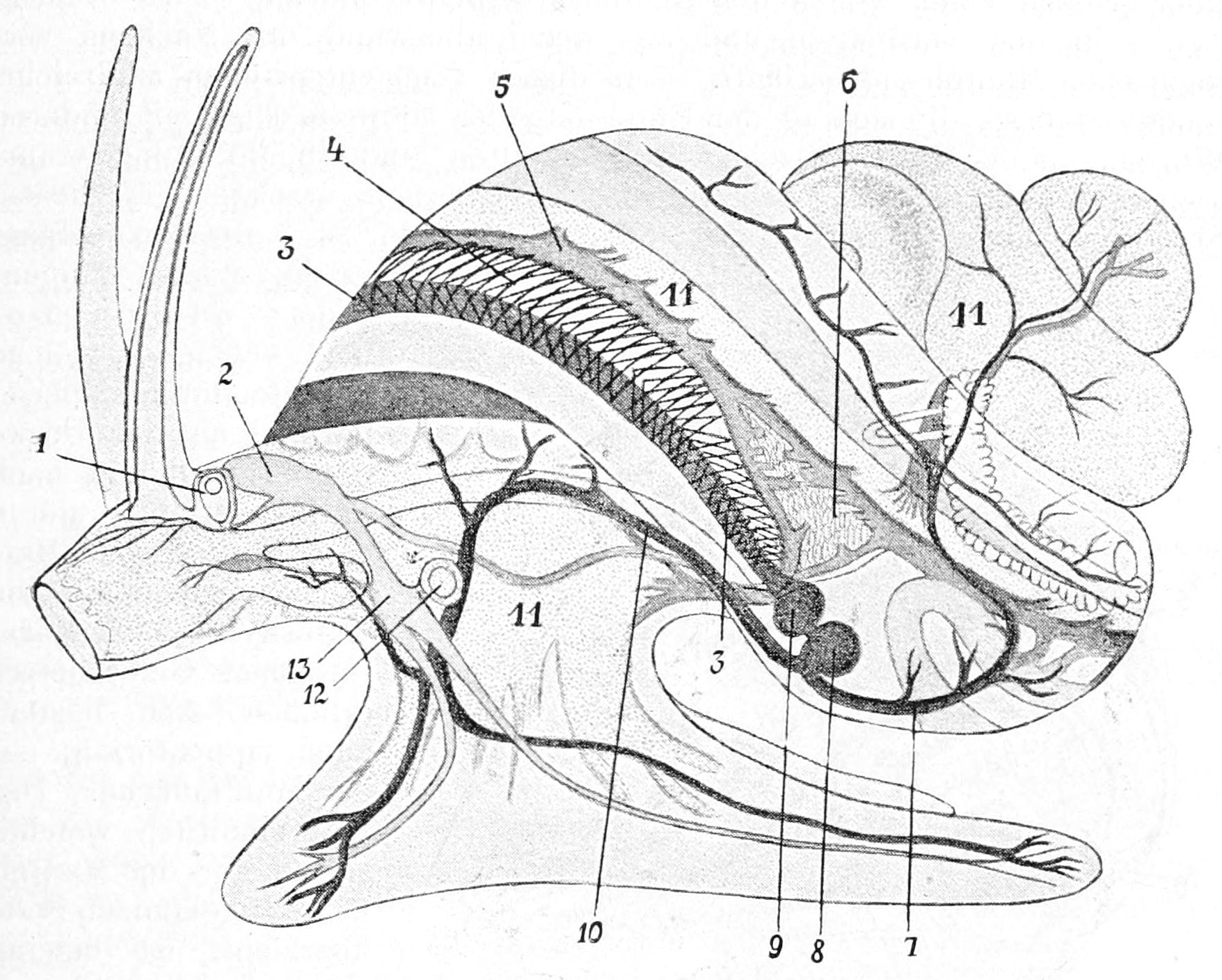
Circulatory System Of Gastropods
As in other molluscs, the circulatory system of gastropods is open, with the fluid, or haemolymph, flowing through sinuses and bathing the tissues directly. The haemolymph typically contains haemocyanin, and is blue in colour. Circulation The heart is muscular and located in the anterior part of the visceral mass. In the great majority of species, it has two chambers; an auricle, which receives haemolymph from the gill or lung, and a ventricle, which pumps it into the aorta. However, some primitive gastropods possess two gills, each supplying its own auricle, so that their heart has three chambers. The aorta is relatively short, and soon divides into two main vessels, one supplying the visceral mass, and the other supplying the head and foot. In some groups, these two vessels arise directly from the heart, so that the animal may be said to have two aortas. These two vessels in turn divide into many finer vessels throughout the body, and deliver haemolymph to open arterial sinuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropod Shell
The gastropod shell is part of the body of a Gastropoda, gastropod or snail, a kind of mollusc. The shell is an exoskeleton, which protects from predators, mechanical damage, and dehydration, but also serves for muscle attachment and calcium storage. Some gastropods appear shell-less (slugs) but may have a remnant within the mantle, or in some cases the shell is reduced such that the body cannot be retracted within it (semi-slug). Some snails also possess an operculum that seals the opening of the shell, known as the Aperture (mollusc), aperture, which provides further protection. The study of mollusc shells is known as conchology. The biological study of gastropods, and other molluscs in general, is malacology. Shell morphology terms vary by species group. Shell layers The gastropod shell has three major layers secreted by the Mantle (mollusc), mantle. The calcareous central layer, tracum, is typically made of calcium carbonate precipitated into an organic matrix known as c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate). Its capital and largest city is Bridgetown. Inhabited by Island Caribs, Kalinago people since the 13th century, and prior to that by other Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Amerindians, Spanish navigators took possession of Barbados in the late 15th century, claiming it for the Crown of Castile. It first appeared on a Spanish map in 1511. The Portuguese Empire claimed the island between 1532 and 1536, but abandoned it in 1620 with their only remnants being an introduction of wild boars for a good supply of meat whenever the island was visited. An Kingdom of England, English ship, the ''Olive Blossom'', arrived in Barbados on 14 May 1625; its men took possession of the island in the name of James VI and I, King James I. In 1627, the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Friedrich Röding
Peter Friedrich Röding (17 June 1767 – 8 June 1846) was a German malacologist who lived in Hamburg. Very little is known about this naturalist. Many of Röding's descriptions (often simply a German rendition of the Latin binomial name) are of species which were first named by earlier authors such as Johann Hieronymus Chemnitz, Friedrich Wilhelm Martini and Martin Lister. Röding's references to pre-existing descriptions and figures make these names also valid, since they are unequivocally recognizable, and were (after Röding) subsequently adopted by many later authors. Museum Boltenianum He was the principal author of a 1798 catalogue of an important mollusc collection. The catalogue was entitled ''Museum Boltenianum sive catalogus cimeliorum e tribus regnis naturæ quæ olim collegerat Joa. Fried Bolten, M. D. p. d. per XL. annos proto physicus Hamburgensis. Pars secunda continens conchylia sive testacea univalvia, bivalvia & multivalvia'' and was published in Hamburg. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |