|
Neochoristodera
Neochoristodera is a lineage of specialised crocodile-like fully aquatic choristodere reptiles. Noted for their long jaws and large size, these animals were predominant across the Northern Hemisphere, occurring in freshwater and coastal environments across the Cretaceous and early Cenozoic. Systematics Neochoristoderes form a monophyletic group, however there is no consensus about the relationships of the genera, which have been recovered as a polytomy in recent studies. Neochoristodera contains the named genera ''Champsosaurus'', '' Ikechosaurus'', '' Kosmodraco'', '' Liaoxisaurus'', '' Mengshanosaurus'', ''Simoedosaurus'' and '' Tchoiria''. Various taxa of uncertain affinities within this group are known, including a partial femur of a choristodere, possibly of a neochoristodere from the Cedar Mountain Formation of the United States and an indeterminate partial skeleton from the Kuwajima Formation of Japan. Evolution Neochoristoderes first appear in the Early Cretaceous of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyphalosauridae
Choristodera (from the Greek χωριστός ''chōristos'' + δέρη ''dérē'', 'separated neck') is an extinct order of semiaquatic diapsid reptiles that ranged from the Middle Jurassic, or possibly Triassic, to the late Miocene (168 to 11.6 million years ago). Choristoderes are morphologically diverse, with the best known members being the crocodile-like neochoristoderes such as ''Champsosaurus''. Other choristoderans had lizard-like or long necked morphologies. Choristoderes appear to have been confined to the Northern Hemisphere, having been found in North America, Asia, and Europe, and possibly also North Africa. Choristoderes are generally thought to be derived neodiapsids that are close relatives or members of Sauria. History of Discovery Choristodera was erected in 1876, originally as a suborder of Rhynchocephalia by Edward Drinker Cope to contain ''Champsosaurus,'' which was described from Late Cretaceous strata of Montana by Cope in the same paper. A year l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monjurosuchidae
Choristodera (from the Greek χωριστός ''chōristos'' + δέρη ''dérē'', 'separated neck') is an extinct order of semiaquatic diapsid reptiles that ranged from the Middle Jurassic, or possibly Triassic, to the late Miocene (168 to 11.6 million years ago). Choristoderes are morphologically diverse, with the best known members being the crocodile-like neochoristoderes such as ''Champsosaurus''. Other choristoderans had lizard-like or long necked morphologies. Choristoderes appear to have been confined to the Northern Hemisphere, having been found in North America, Asia, and Europe, and possibly also North Africa. Choristoderes are generally thought to be derived neodiapsids that are close relatives or members of Sauria. History of Discovery Choristodera was erected in 1876, originally as a suborder of Rhynchocephalia by Edward Drinker Cope to contain ''Champsosaurus,'' which was described from Late Cretaceous strata of Montana by Cope in the same paper. A year l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choristodere
Choristodera (from the Greek χωριστός ''chōristos'' + δέρη ''dérē'', 'separated neck') is an extinct order of semiaquatic diapsid reptiles that ranged from the Middle Jurassic, or possibly Triassic, to the late Miocene (168 to 11.6 million years ago). Choristoderes are morphologically diverse, with the best known members being the crocodile-like neochoristoderes such as ''Champsosaurus''. Other choristoderans had lizard-like or long necked morphologies. Choristoderes appear to have been confined to the Northern Hemisphere, having been found in North America, Asia, and Europe, and possibly also North Africa. Choristoderes are generally thought to be derived neodiapsids that are close relatives or members of Sauria. History of Discovery Choristodera was erected in 1876, originally as a suborder of Rhynchocephalia by Edward Drinker Cope to contain ''Champsosaurus,'' which was described from Late Cretaceous strata of Montana by Cope in the same paper. A year l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
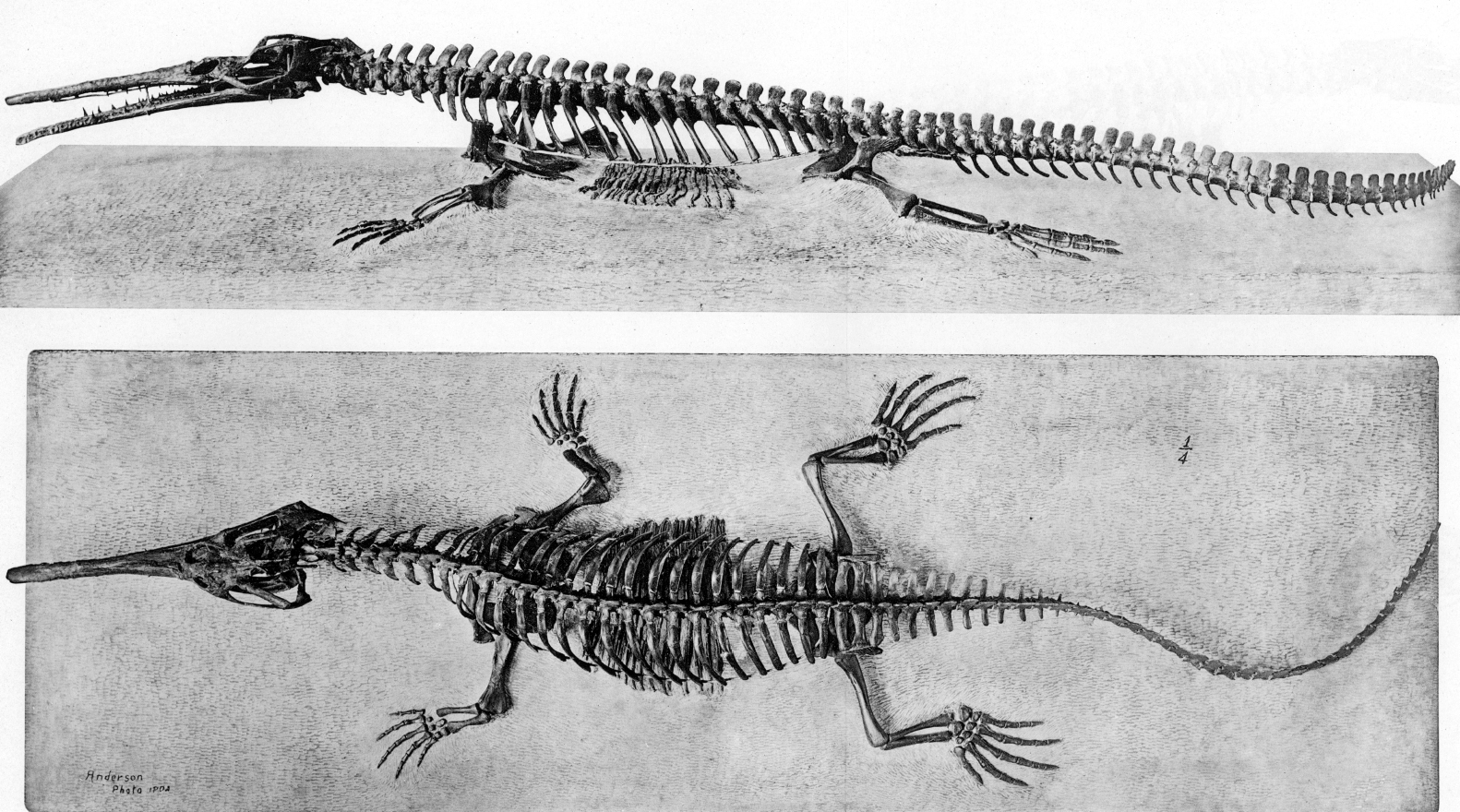
Champsosaurus
''Champsosaurus'' is an extinct genus of crocodile-like choristodere reptile, known from the Late Cretaceous and early Paleogene periods of North America and Europe (Campanian-Paleocene). The name ''Champsosaurus'' is thought to come from , () said in an Ancient Greek source to be an Egyptian word for "crocodiles", and , () Greek for "lizard". The morphology of ''Champsosaurus'' resembles that of gharials, with a long, elongated snout. It was native to freshwater environments where it likely preyed on fish, similar to living gharials. History of research ''Champsosaurus'' was the first member of the Choristodera to be described. ''Champsosaurus'' was named by Edward Drinker Cope in 1876, from isolated vertebrae found in Late Cretaceous strata of the Judith River Formation on the banks of the Judith River in Fergus County, Montana. Cope designated ''C. annectens'' as the type species rather than the first named ''C. profundus'' due to the larger number of vertebrae he attributed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmodraco
''Kosmodraco'' is a genus of large bodied choristodere from the Paleocene of North America. Originally described as a species of ''Simoedosaurus'', it was found to represent a distinct genus in 2022. Multiple fossil skulls show a relatively short and robust snout and a skull that is considerably wider behind the eyes. Two species are currently recognized, ''K. dakotensis'' and ''K. magnicornis''. History and naming The first specimen now known to belong to ''Kosmodraco'' was discovered in 1964 and 1968 in the Polecat Bench Formation (Wyoming). These two skulls, alongside others from Montana's Bear Creek, were reported on briefly by Sigogneau-Russell and Donald in 1978, who regarded them as evidence for the presence of the Eurasian genus ''Simoedosaurus'' in North America. However, at the time, these four specimens, although thought to be diagonstic at a genus level, were still unprepared and not assigned to a species. They were subsequently stored in the collection of the Princ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meng-Yin Formation
The Meng-Yin or Mengyin Formation () is a geological formation in Shandong, China, whose strata date back to the Berriasian and Valanginian stages of the Early Cretaceous.Mengyin Formation at .orgWilson & Upchurch, 2009 Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel et al., 2004, "Dinosaur distribution (Late Jurassic, Asia).", pp.550–552 The type material for the titanosauriform dinosaur '' |
Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by an asteroid impact and possibly volcanism, marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of living species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. In the Paleocene, the continents of the Northern Hemisphere were still connected v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', " chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuwajima Formation
The Kuwajima Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in Japan. Its precise age is uncertain due to a lack of identifying fossils, and it was previously considered likely Valanginian to Hauterivian in age. However, it is now considered to probably be Barremian in age. Dinosaurs and other vertebrates has been recovered from the Kaseki-kabe "Fossil-bluff" locality in the uppermost part of the formation. The multituberculate mammals ''Hakusanobaatar matsuoi'' and '' Tedoribaatar reini'' are known from the Kuwajima Formation. A member of Tritylodontidae, '' Montirictus kuwajimaensis'', has also been recovered from the unit.Hiroshige Matsuoka, Nao Kusuhashi and Ian J. Corfe (2016). "A new Early Cretaceous tritylodontid (Synapsida, Cynodontia, Mammaliamorpha) from the Kuwajima Formation (Tetori Group) of central Japan". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. Online edition: Vertebrate Paleobiota Fish Amphibians Choristoderes Squamates Dinosaurs Mammaliam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mengshanosaurus
''Mengshanosaurus'' is an extinct genus of choristodere from the Early Cretaceous The Early Cretaceous (geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous ( chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma. Geology Pr ... Meng-Yin Formation of China. The type and only known species is ''M. minimus,'' known from a juvenile skull, around 3.5 cm long. It was found to be the basalmost neochoristodere. References {{Eureptilia, S. Choristodera Prehistoric reptile genera Fossil taxa described in 2021 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikechosaurus
''Ikechosaurus'' is an extinct genus of choristodere reptile which existed in China and Mongolia during the Early Cretaceous. It contains the species ''Ikechosaurus sunailinae'' and ''Ikechosaurus gaoi''. It belongs to the crocodilian-like clade Neochoristodera Neochoristodera is a lineage of specialised crocodile-like fully aquatic choristodere reptiles. Noted for their long jaws and large size, these animals were predominant across the Northern Hemisphere, occurring in freshwater and coastal environ ... and was initially assigned to the Champsosauridae by Sigogneau-Russell (1981). Compared to other neochoristoderes, ''Ikechosaurus'' has a rather simple dentition, lacking the speciations seen in latter species. It also has parasphenoid palatal teeth, a feature not seen in any other choristodere. References Choristodera Cretaceous reptiles of Asia Cretaceous choristoderes Prehistoric reptile genera Fossil taxa described in 1981 {{Cretaceous-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Plate, North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as a part of North America geographically. North America covers an area of about , about 16.5% of Earth's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface. North America is the third-largest continent by area, following Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. In 2013, its population was estimated at nearly 579 million people in List of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In Americas (terminology)#Human ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_NMNS.jpg)





.jpg)