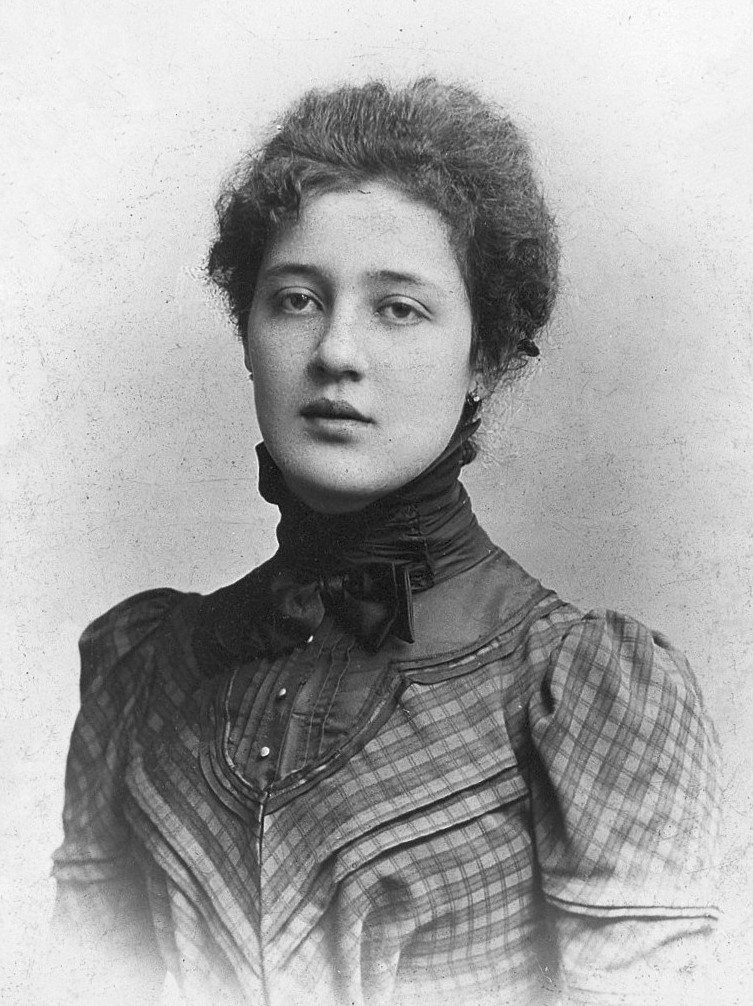|
Negative Therapeutic Reaction
The negative therapeutic reaction in psychoanalysis is the paradoxical phenomenon whereby a plausible interpretation produces, rather than improvement, a worsening of the analysand's condition. Freud's formulations Freud first named the negative therapeutic reaction in ''The Ego and the Id'' of 1923, seeing its cause, not merely in the analysand's desire to be superior to their analyst, but (more deeply) in an underlying sense of guilt: "the obstacle of an unconscious sense of guilt....they get worse during the treatment instead of getting better". The following year he offered the alternative formulation of a need for punishment instead; but in his thirties summation it was again unconscious guilt to which he attributed "the negative therapeutic reaction which is so disagreeable from the prognostic point of view". Precursors to the idea can be found in his own article Criminals from a sense of guilt, as well as in Karl Abraham's 1919 article on envy and narcissism as enemies of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoanalysis
PsychoanalysisFrom Greek: + . is a set of theories and therapeutic techniques"What is psychoanalysis? Of course, one is supposed to answer that it is many things — a theory, a research method, a therapy, a body of knowledge. In what might be considered an unfortunately abbreviated description, Freud said that anyone who recognizes transference and resistance is a psychoanalyst, even if he comes to conclusions other than his own.… I prefer to think of the analytic situation more broadly, as one in which someone seeking help tries to speak as freely as he can to someone who listens as carefully as he can with the aim of articulating what is going on between them and why. David Rapaport (1967a) once defined the analytic situation as carrying the method of interpersonal relationship to its last consequences." Gill, Merton M. 1999.Psychoanalysis, Part 1: Proposals for the Future" ''The Challenge for Psychoanalysis and Psychotherapy: Solutions for the Future''. New York: Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object Relations Theory
Object relations theory is a school of thought in psychoanalytic theory centered around theories of stages of ego development. Its concerns include the relation of the psyche to others in childhood and the exploration of relationships between external people, as well as internal images and the relations found in them. Thinkers of the school maintain that the infant's relationship with the mother primarily determines the formation of its personality in adult life. Particularly, attachment is the bedrock of the development of the self or the psychic organization that creates the sense of identity. Theory While its groundwork derives from theories of development of the ego in Freudian psychodynamics, object relations theory does not place emphasis on the role of biological drives in the formation of personality in adulthood. Thinkers of the school instead suggest that the way people relate to others and situations in their adult lives is shaped by family experiences during inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karen Horney
Karen Horney (; ; 16 September 1885 – 4 December 1952) was a German psychoanalyst who practised in the United States during her later career. Her theories questioned some traditional Freudian views. This was particularly true of her theories of sexuality and of the instinct orientation of psychoanalysis. She is credited with founding feminist psychology in response to Freud's theory of penis envy. She disagreed with Freud about inherent differences in the psychology of men and women, and she traced such differences to society and culture rather than biology. She is often classified as neo-Freudian. Early life Horney was born Karen Danielsen on 16 September 1885 in Blankenese, Germany, near Hamburg. Her father, Berndt Wackels Danielsen (1836–1910), was Norwegian but had German citizenship. He was a ship's captain in the merchant marine, and a Protestant traditionalist (his children nicknamed him "the Bible-thrower", as he did indeed throw Bibles). Her mother, Clotilde, née v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Transference
Negative transference is the psychoanalytic term for the transference of negative and hostile feelings, rather than positive ones, onto a therapist (or other emotional object). Freud's preference In his pioneering studies of transference phenomena, Freud noted the existence of both positive and negative transferences, while expressing a preference for the former, which he initially saw as a prerequisite for analytic work. Freud considered that "The hostile feelings make their appearance as a rule later than the affectionate ones and behind them"; and more frequently in same-sex than in mixed-sex analytic pairings. Otto Fenichel pointed out that whereas neurotic aggravations can follow the emergence of a negative transference, so too (paradoxically) can improvements: the patient gets better to spite the therapist for emphasising the patient's problems. Later formulations Melanie Klein in her disputes with Anna Freud laid much greater emphasis than her opponent on the constructive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanie Klein
Melanie Klein (née Reizes; 30 March 1882 – 22 September 1960) was an Austrian-British author and psychoanalyst known for her work in child analysis. She was the primary figure in the development of object relations theory. Klein suggested that pre-verbal existential anxiety in infancy catalyzed the formation of the unconscious, resulting in the unconscious splitting of the world into good and bad idealizations. In her theory, how the child resolves that split depends on the constitution of the child and the character of nurturing the child experiences; the quality of resolution can inform the presence, absence, and/or type of distresses a person experiences later in life. Life Melanie Klein was born into a Jewish family and spent most of her early life in Vienna. She was the fourth and final child of parents Moriz, a doctor, and Libussa Reizes. Educated at the Gymnasium, Klein planned to study medicine. Her family's loss of wealth caused her to change her plans. At the age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Drive
In classical Freudian psychoanalytic theory, the death drive (german: Todestrieb) is the drive toward death and destruction, often expressed through behaviors such as aggression, repetition compulsion, and self-destructiveness.Eric Berne, ''What Do You say After You Say Hello?'' (London, 1975) pp. 399–400. It was originally proposed by Sabina Spielrein in her paper "Destruction as the Cause of Coming Into Being" (''Die Destruktion als Ursache des Werdens'') in 1912, which was then taken up by Sigmund Freud in 1920 in ''Beyond the Pleasure Principle.'' This concept has been translated as "opposition between the ego or death instincts and the sexual or life instincts". In ''Pleasure Principle'', Freud used the plural "death drives" (''Todestriebe'') much more frequently than the singular. The death drive opposes Eros, the tendency toward survival, propagation, sex, and other creative, life-producing drives. The death drive is sometimes referred to as "Thanatos" in post-Freudian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acting Out
In the psychology of defense mechanisms and self-control, acting out is the performance of an action considered bad or anti-social. In general usage, the action performed is destructive to self or to others. The term is used in this way in sexual addiction treatment, psychotherapy, criminology and parenting. In contrast, the opposite attitude or behaviour of bearing and managing the impulse to perform one's impulse is called acting in. The performed action may follow impulses of an addiction (e.g. drinking, drug taking or shoplifting). It may also be a means designed (often unconsciously or semi-consciously) to garner attention (e.g. throwing a tantrum or behaving promiscuously). Acting out may inhibit the development of more constructive responses to the feelings in question. In analysis Freud considered that patients in analysis tended to act out their conflicts in preference to remembering them – repetition compulsion. The analytic task was then to help "the patient wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acting In
"Acting in" is a psychological term which has been given various meanings over the years, but which is most generally used in opposition to acting out to cover conflicts which are brought to life inside therapy, as opposed to outside. One commentator, noting the variety of usages, points out that it is often "unclear whether 'in' refers to the internalization ''into'' the personality, to the growth in ''in''sight, or to the acting with''in'' the session". Patients With respect to patients, the term 'acting in' has been used to refer to the process of a client/patient bringing an issue from outside the therapy into the analytic situation, and acting upon it there. The therapist is advised to respond to the issue immediately to prevent further and more disruptive acting in. Hanna Segal distinguished positive acting in from destructive acting in - both being aimed however at affecting the analyst's state of mind, whether to communicate or to confuse. Posture The term was used in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amour Propre
''Amour-propre'' (; ) is a French term that can be variously translated as "self-love", "self-esteem", or "vanity". In philosophy, it is a term used by Jean-Jacques Rousseau, who contrasts it with another kind of self-love which he calls ''amour de soi''. According to Rousseau, the difference between the two is that ''amour-propre'' assumes that self-esteem can only be found by gaining the approval of others, whereas ''amour de soi'' involves one's feelings for oneself alone, without any intervening concerns about how one is seen by others. According to Rousseau, ''amour de soi'' is more primitive and is compatible with wholeness and happiness, while ''amour-propre'' is a form of self-love that arose only with the appearance of society and individuals' consequent ability to compare themselves with one another. Rousseau thought that ''amour-propre'' was subject to corruption, thereby causing vice and misery. But in addition, by guiding us to seek others' approval and recognition, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freud
Sigmund Freud ( , ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating pathologies explained as originating in conflicts in the psyche, through dialogue between a patient and a psychoanalyst. Freud was born to Galician Jewish parents in the Moravian town of Freiberg, in the Austrian Empire. He qualified as a doctor of medicine in 1881 at the University of Vienna. Upon completing his habilitation in 1885, he was appointed a docent in neuropathology and became an affiliated professor in 1902. Freud lived and worked in Vienna, having set up his clinical practice there in 1886. In 1938, Freud left Austria to escape Nazi persecution. He died in exile in the United Kingdom in 1939. In founding psychoanalysis, Freud developed therapeutic techniques such as the use of free association and discovered transference, establishing its central role in the analytic proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacan
Jacques Marie Émile Lacan (, , ; 13 April 1901 – 9 September 1981) was a French psychoanalyst and psychiatrist. Described as "the most controversial psycho-analyst since Freud", Lacan gave yearly seminars in Paris from 1953 to 1981, and published papers that were later collected in the book ''Écrits''. His work made a significant impact on continental philosophy and cultural theory in areas such as post-structuralism, critical theory, feminist theory and film theory, as well as on the practice of psychoanalysis itself. Lacan took up and discussed the whole range of Freudian concepts, emphasizing the philosophical dimension of Freud's thought and applying concepts derived from structuralism in linguistics and anthropology to its development in his own work, which he would further augment by employing formulae from predicate logic and topology. Taking this new direction, and introducing controversial innovations in clinical practice, led to expulsion for Lacan and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joan Riviere
Joan Hodgson Riviere (28 June 1883 – 20 May 1962) was a British psychoanalyst, who was both an early translator of Freud into English and an influential writer on her own account. Life and career Riviere was born Joan Hodgson Verrall in Brighton, the daughter of Hugh John Verrall and his wife Ann Hodgson. Her father was a lawyer and her mother a vicar's daughter. She was educated in Brighton and then at Wycombe Abbey. At the age of seventeen, she went to Gotha, Germany, where she spent a year and became proficient in the German language. Her interests were primarily artistic and she was for a time a court dressmaker. Riviere married Evelyn Riviere in 1907 and had a child, but suffered a breakdown on the death of her father around that time. She took an interest in divorce reform and the suffragette movement. Her uncle, Arthur Woollgar Verrall organised meetings of the Society for Psychical Research where she discovered the work of Sigmund Freud and Ernest Jones, and this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |