|
Need For Affiliation
The need for affiliation (N-Affil) is a term that was popularized by David McClelland and describes a person's need to feel a sense of involvement and "belonging" within a social group; McClelland's thinking was strongly influenced by the pioneering work of Henry Murray who first identified underlying psychological human needs and motivational processes (1938). It was Murray who set out a classification of needs, including achievement, power and affiliation—and placed these in the context of an integrated motivational model. People with a high need for affiliation require warm interpersonal relationships and approval from those with whom they have regular contact. Having a strong bond with others make a person feel as if they are a part of something important that creates a powerful impact. People who place high emphasis on affiliation tend to be supportive team members, but may be less effective in leadership positions. A person who takes part in a group, whether it be a movemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David McClelland
David Clarence McClelland (May 20, 1917 – March 27, 1998) was an American psychologist, noted for his work on motivation Need Theory. He published a number of works between the 1950s and the 1990s and developed new scoring systems for the Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) and its descendants.Biography - David C. McClelland retrieved June 24, 2008 McClelland is credited with developing Achievement Motivation Theory, commonly referred to as "need for achievement" or ''n''-achievement theory. A '''' survey published in 2002, ranked McClelland as the 15th most cited psychologist of the 20th century. Life and career |
Pager
A pager (also known as a beeper or bleeper) is a wireless telecommunications device that receives and displays alphanumeric or voice messages. One-way pagers can only receive messages, while response pagers and two-way pagers can also acknowledge, reply to and originate messages using an internal transmitter. Pagers operate as part of a paging system which includes one or more fixed transmitters (or in the case of response pagers and two-way pagers, one or more base stations), as well as a number of pagers carried by mobile users. These systems can range from a restaurant system with a single low power transmitter, to a nationwide system with thousands of high-power base stations. Pagers were developed in the 1950s and 1960s, and became widely used by the 1980s. In the 21st century, the widespread availability of cellphones and smartphones has greatly diminished the pager industry. Nevertheless, pagers continue to be used by some emergency services and public safety personn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motivational Theories
Motivation is the reason for which humans and other animals initiate, continue, or terminate a behavior at a given time. Motivational states are commonly understood as forces acting within the agent that create a disposition to engage in goal-directed behavior. It is often held that different mental states compete with each other and that only the strongest state determines behavior. This means that we can be motivated to do something without actually doing it. The paradigmatic mental state providing motivation is desire. But various other states, such as beliefs about what one ought to do or intentions, may also provide motivation. Motivation is derived from the word 'motive', which denotes a person's needs, desires, wants, or urges. It is the process of motivating individuals to take action in order to achieve a goal. The psychological elements fueling people's behavior in the context of job goals might include a desire for money. Various competing theories have been proposed con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpersonal Relationships
The concept of interpersonal relationship involves social associations, connections, or affiliations between two or more people. Interpersonal relationships vary in their degree of intimacy or self-disclosure, but also in their duration, in their reciprocity and in their power distribution, to name only a few dimensions. The context can vary from family or kinship relations, friendship, marriage, relations with associates, work, clubs, neighborhoods, and places of worship. Relationships may be regulated by law, custom, or mutual agreement, and form the basis of social groups and of society as a whole. Interpersonal relationships are created by people's interactions with one another in social situations. This association of interpersonal relations being based on social situation has inference since in some degree love, solidarity, support, regular business interactions, or some other type of social connection or commitment. Interpersonal relationships thrive through equitable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Identity
Cultural identity is a part of a person's identity, or their self-conception and self-perception, and is related to nationality, ethnicity, religion, social class, generation, locality or any kind of social group that has its own distinct culture. In this way, cultural identity is both characteristic of the individual but also of the culturally identical group of members sharing the same cultural identity or upbringing. Cultural identity is a fluid process that is changed by different social, cultural, and historical experiences. Some people undergo more cultural identity changes as opposed to others, those who change less often have a clear cultural identity. This means that they have a dynamic yet stable integration of their culture. There are three pieces that make up a persons cultural identity, these are cultural knowledge, category label, and social connections. Cultural knowledge is when a person connects to their identity through understanding their culture's core ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
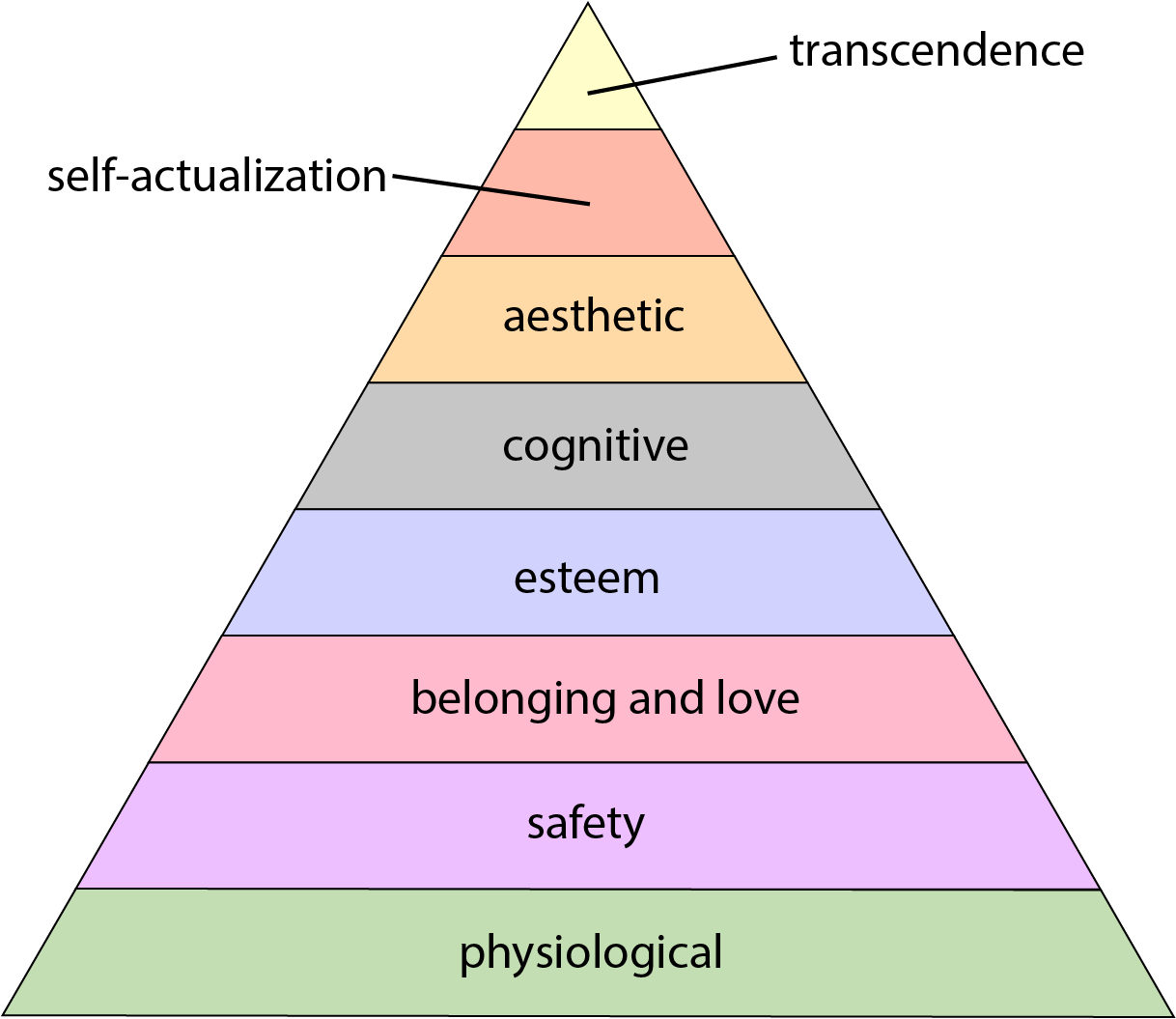
Maslow's Hierarchy Of Needs
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is an idea in psychology proposed by American psychologist Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper "A Theory of Human Motivation" in the journal ''Psychological Review''. Maslow subsequently extended the idea to include his observations of humans' innate curiosity. His theories parallel many other theories of human developmental psychology, some of which focus on describing the stages of growth in humans. The theory is a classification system intended to reflect the universal needs of society as its base, then proceeding to more acquired emotions. The hierarchy of needs is split between deficiency needs and growth needs, with two key themes involved within the theory being individualism and the prioritization of needs. While the theory is usually shown as a pyramid in illustrations, Maslow himself never created a pyramid to represent the hierarchy of needs. The hierarchy of needs is a psychological idea and also an assessment tool, particularly in educatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murray's System Of Needs
In 1938, Henry Murray developed a system of needs A need is dissatisfaction at a point of time and in a given context. Needs are distinguished from wants. In the case of a need, a deficiency causes a clear adverse outcome: a dysfunction or death. In other words, a need is something required for ... as part of his theory of personality, which he named ''personology''. He argued that everyone had a set of universal basic needs, with individual differences on these needs leading to the uniqueness of personality through varying dispositional tendencies for each need; in other words, specific needs are more important to some than to others. In his theory, Murray argues that needs and presses (another component of the theory) acted together to create an internal state of disequilibrium; the individual is then driven to engage in some sort of behavior to reduce the tension. Murray believed that the study of personality should look at the entire person over the course of their lifespan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Need For Achievement
Need for achievement (N-Ach) is an individual's desire for significant accomplishment, mastering of skills, control, or high standards. The term was first used by Henry Murray and associated with a range of actions. These include: "intense, prolonged and repeated efforts to accomplish something difficult. To work with singleness of purpose towards a high and distant goal. To have the determination to win". The concept of N-Ach was subsequently popularized by the psychologist David McClelland.D. C. McClelland. (1961). The Achieving Society. Free Press, New York __TOC__ Overview This personality trait is characterized by an enduring and consistent concern with setting and meeting high standards of achievement. This need is influenced by internal drive for action (intrinsic motivation), and the pressure exerted by the expectations of others (extrinsic motivation). Measured with the thematic apperception test (TAT), need for achievement motivates an individual to succeed in competiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Need Theory
Need theory, also known as Three needs theory, Umuc.edu. Retrieved July 16, 2014. proposed by , is a motivational model that attempts to explain how the s for , affiliation, and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affection
Affection or fondness is a " disposition or state of mind or body" that is often associated with a feeling or type of love. It has given rise to a number of branches of philosophy and psychology concerning emotion, disease, influence, and state of being. "Affection" is popularly used to denote a feeling or type of love, amounting to more than goodwill or friendship. Writers on ethics generally use the word to refer to distinct states of feeling, both lasting and spasmodic. Some contrast it with '' passion'' as being free from the distinctively sensual element. Even a very simple demonstration of affection can have a broad variety of emotional reactions, from embarrassment, to disgust, pleasure, and annoyance. It also has a different physical effect on the giver and the receiver. Restricted definition More specifically, the word has been restricted to emotional states, the object of which is a living thing such as a human or animal. Affection is compared with passion, from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fear
Fear is an intensely unpleasant emotion in response to perceiving or recognizing a danger or threat. Fear causes physiological changes that may produce behavioral reactions such as mounting an aggressive response or fleeing the threat. Fear in human beings may occur in response to a certain stimulus occurring in the present, or in anticipation or expectation of a future threat perceived as a risk to oneself. The fear response arises from the perception of danger leading to confrontation with or escape from/avoiding the threat (also known as the fight-or-flight response), which in extreme cases of fear ( horror and terror) can be a freeze response or paralysis. In humans and other animals, fear is modulated by the process of cognition and learning. Thus, fear is judged as rational or appropriate and irrational or inappropriate. An irrational fear is called a phobia. Fear is closely related to the emotion anxiety, which occurs as the result of threats that are percei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Need
A need is dissatisfaction at a point of time and in a given context. Needs are distinguished from wants. In the case of a need, a deficiency causes a clear adverse outcome: a dysfunction or death. In other words, a need is something required for a safe, stable and healthy life (e.g. air, water, food, land, shelter) while a want is a desire, wish or aspiration. When needs or wants are backed by purchasing power, they have the potential to become economic demands. Basic needs such as air, water, food and protection from environmental dangers are necessary for an organism to live. In addition to basic needs, humans also have needs of a social or societal nature such as the human need to socialise or belong to a family unit or group. Needs can be objective and physical, such as the need for food, or psychical and subjective, such as the need for self-esteem. The concept of "unmet need" arises in relation to needs in a social context which are not being fulfilled. Needs and wants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

