|
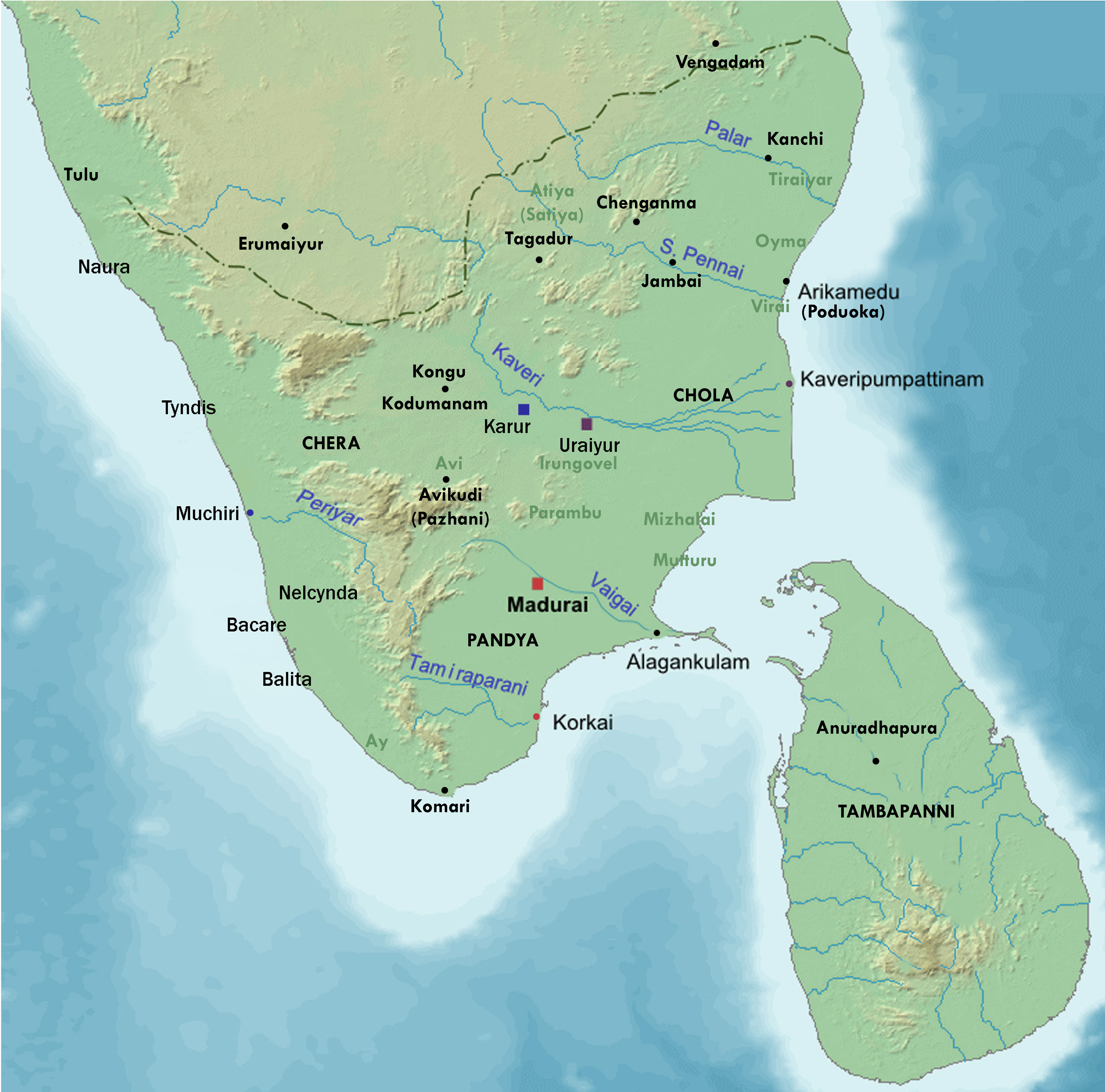
Nedunj Cheliyan I
Nedunjcheliyan I ( c. 270 BCE) (Tamil: நெடுஞ்செழியன்) was a Pandya king.He was also known as Arya Padai kadantha Nedunjezhiya Pandiyan Archaeological evidence His name is present in the Mangulam inscriptions of 3rd century BCE. The inscriptions mentions that workers of ''Nedunchezhiyan I'', a Pandyan king of Sangam period, (c. 270 BCE) made stone beds for Jain monks. In popular culture Nedunjeliyan I was also the Pandya king of the epic ''Silappatikaram'' authored by the Sangam poet Ilango Adigal who later died of a broken heart along with his queen consort Kopperundevi. He is portrayed by O. A. K. Thevar in the film Poompuhar (1964). See also * List of Sangam poets Sangam refers to the assembly of the highly learned people of the ancient Tamil land, with the primary aim of advancing the literature. There were historically three Sangams. With the details of the first two Sangams remaining obscure, all the ... Notes References * P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saivism
Shaivism (; sa, शैवसम्प्रदायः, Śaivasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Supreme Being. One of the largest Hindu denominations, it incorporates many sub-traditions ranging from devotional dualistic theism such as Shaiva Siddhanta to yoga-orientated monistic non-theism such as Kashmiri Shaivism.Ganesh Tagare (2002), The Pratyabhijñā Philosophy, Motilal Banarsidass, , pages 16–19 It considers both the Vedas and the Agama texts as important sources of theology.Mariasusai Dhavamony (1999), Hindu Spirituality, Gregorian University and Biblical Press, , pages 31–34 with footnotesMark Dyczkowski (1989), The Canon of the Śaivāgama, Motilal Banarsidass, , pages 43–44 Shaivism developed as an amalgam of pre-Vedic religions and traditions derived from the southern Tamil Shaiva Siddhanta traditions and philosophies, which were assimilated in the non-Vedic Shiva-tradition. In the process of Sanskritisation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Language
Tamil (; ' , ) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore, and the Indian territory of Puducherry. Tamil is also spoken by significant minorities in the four other South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by the Tamil diaspora found in many countries, including Malaysia, Myanmar, South Africa, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia and Mauritius. Tamil is also natively spoken by Sri Lankan Moors. One of 22 scheduled languages in the Constitution of India, Tamil was the first to be classified as a classical language of India. Tamil is one of the longest-surviving classical languages of India.. "Tamil is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India" (p. 7). A. K. Ramanujan described it as "the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mangulam
Mangulam or Mankulam is a village in Madurai district, Tamil Nadu, India. It is located from Madurai. The inscriptions discovered in the region are the earliest Tamil-Brahmi inscriptions. Information A hill in the region which is known as Mangulam hill or Kalugumalai (eagle hill) or Ovamalai, is where Tamil Jain monks lived in the caves during when their religion flourished in the ancient Tamil country. They converted the caves into their ''Palli'' (monastery) and lived here from 3 BCE to the 9th century CE. Mangulam inscriptions were discovered by Robert Sewell in the caves of the hill in 1882. This was the earliest finding of such kind of inscriptions. In 1906, Indian epigraphist V. Venkayya tried to read the inscriptions and found that it similar to the Brahmi script in Ashokan edicts, he thought that the inscriptions were in Pali language. In 1919, epigraphist H. Krishna Sastri identified few Tamil words in the inscriptions. In 1924, K. V. Subrahmanya Aiyar disco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal ''dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and '' aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), '' satya'' (truth), '' asteya'' (not stealing), ''brahmacharya'' (chastity), and '' aparigraha'' (non-possessiveness). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silappatikaram
''Cilappatikāram'' ( ta, சிலப்பதிகாரம் ml, ചിലപ്പതികാരം,IPA: ʧiləppət̪ikɑːrəm, ''lit.'' "the Tale of an Anklet"), also referred to as ''Silappathikaram'' or ''Silappatikaram'', is the earliest Tamil epic. It is a poem of 5,730 lines in almost entirely ''akaval'' (''aciriyam'') meter. The epic is a tragic love story of an ordinary couple, Kannaki and her husband Kovalan. The ''Silappathikaram'' has more ancient roots in the Tamil bardic tradition, as Kannaki and other characters of the story are mentioned or alluded to in the Sangam literature such as in the ''Naṟṟiṇai'' and later texts such as the ''Kovalam Katai''. It is attributed to a prince-turned-monk Iḷaṅkõ Aṭikaḷ, and was probably composed in the 5th or 6th century CE. The ''Silappatikaram'' is set in a flourishing seaport city of the early Chola kingdom. Kannaki and Kovalan are a newly married couple, in love, and living in bliss. Over time, Kova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sangam Literature
The Sangam literature (Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், ''caṅka ilakkiyam'';) historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' (Tamil: சான்றோர் செய்யுள், ''Cāṉṟōr ceyyuḷ'') connotes the ancient Tamil literature and is the earliest known literature of South India. The Tamil tradition and legends link it to three literary gatherings around Madurai and Kapāṭapuram ( Pandyan capitals): the first over 4,440 years, the second over 3,700 years, and the third over 1,850 years before the start of the common era. Scholars consider this Tamil tradition-based chronology as ahistorical and mythical. Most scholars suggest the historical Sangam literature era spanned from c. 300 BCE to 300 CE, while others variously place this early classical Tamil literature period a bit later and more narrowly but all before 300 CE. According to Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature and history scholar, the most acceptable range for the Sangam l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilango Adigal
Ilango Adigal ()() was a Jainism, Jain monk and a poet, sometimes identified as a Chera dynasty, Chera prince. He is traditionally credited as the author of ''Cilappatikaram'', one of the Five Great Epics of Ancient Tamil literature. He is one of the greatest poets from Chera dynasty, Cheranadu (now Kerala). In a ''patikam'' (prologue) to the epic poem, he identifies himself as the brother of a famous Chera dynasty, Chera king Ceṅkuṭṭuvan (Senguttuvan). This Chera king, as stated by Elizabeth Rosen, ruled over his kingdom in late 2nd or early 3rd century CE. However, this is doubtful because a Sangam poem in ''Patiṟṟuppattu'' – the fifth ten – provides a biography of Ceṅkuṭṭuvan, his family and rule, but never mentions that he had a brother who became an ascetic or wrote one of the most cherished epics. This has led scholars to conclude that the legendary author Ilango Adikal myth was likely inserted later into the epic. In a 1968 note, Kamil Zvelebil suggeste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broken Heart
Broken heart (also known as a heartbreak or heartache) is a metaphor for the intense emotional stress or pain one feels at experiencing great and deep longing. The concept is cross-cultural, often cited with reference to unreciprocated or lost love. Failed romantic love can be extremely painful; people with a broken heart may succumb to depression, anxiety and, in more extreme cases, post-traumatic stress disorder. Physiology The intense pain of a broken heart is believed to be part of the survival instinct. The " social-attachment system" uses the " pain system" to encourage humans to maintain their close social relationships by causing pain when those relationships are lost. Psychologists Geoff MacDonald of the University of Queensland and Mark Leary of Wake Forest University proposed in 2005 the evolution of common mechanisms for both physical and emotional pain responses and argue that such expressions are "more than just a metaphor". The concept is believed to be univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poompuhar (film)
''Poompuhar'' is a 1964 Indian Tamil-language epic film directed by P. Neelakantan and written by M. Karunanidhi. It is the second film based on the epic ''Cilappatikaram'' after ''Kannagi'' (1942). The film stars S. S. Rajendran, C. R. Vijayakumari, Rajasree and K. B. Sundarambal. It was released on 18 September 1964. Plot Kovalan, the son of a wealthy merchant in the city of Kaveripattinam, marries Kannagi, the daughter of another merchant. They live together happily in Kaveripattinam, until Kovalan met the courtesan Madhavi and fell in love with her. In his infatuation, he leaves his wife and gradually spends all his wealth on Madhavi. Eventually penniless, Kovalan realises his mistake, and returns to Kannagi after a year. Their only asset is a precious pair of anklets called Silambu, which Kannagi gave to him willingly. With these as their capital, they go to the city of Madurai, where Kovalan hopes to recoup his fortunes by trade. Madurai is ruled by the Pandya king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |