|
Nechako Country
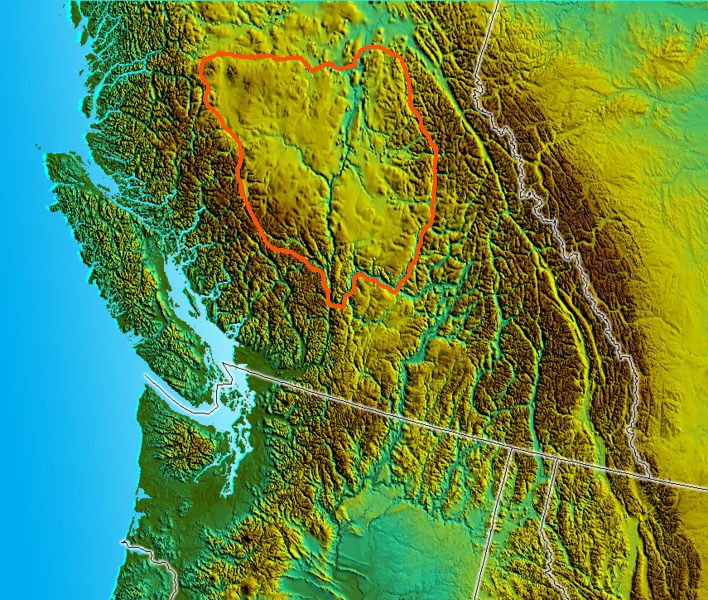
The Nechako Country, also referred to as the Nechako District or simply "the Nechako" is one of the historical geographic regions of the Canadian province of British Columbia, located southwest of the city of Prince George and south of Hwy 16 on the inland side of the Hazelton Mountains (an inland subrange of the Coast Mountains), and comprising the basin of the Nechako River and its tributaries. "Nechako" is an anglicization of ''netʃa koh'', its name in the indigenous Carrier language which means "big river". The area is sparsely populated, mostly by members of the Carrier people, and is noted for its many large lakes, including Ootsa Lake Reservoir, which is the source of water for the Kemano Powerhouse on a neighbouring coastal inlet, which is the power supply for the aluminum smelter at Kitimat. To the north of the Nechako Country are the Omineca Country and Bulkley Valley, while to its south is the Chilcotin Country and to the southeast the Cariboo Country. See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Province
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada (which upon Confederation was divided into Ontario and Quebec)—united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area. The major difference between a Canadian province and a territory is that provinces receive their power and authority from the ''Constitution Act, 1867'' (formerly called the ''British North America Act, 1867''), whereas territorial governments are creatures of statute with powers delegated to them by the Parliament of Canada. The powers flowing from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kemano Powerhouse
Kemano was a settlement situated 75 km (47 mi) southeast of Kitimat in the province of British Columbia in Canada. It was built to service a hydroelectric power station, built to provide energy for Alcan to smelt aluminum from its ore. The Kemano Generating Station is built 427 m (1,400 ft) inside the base of Mt Dubose in a blasted cavern. It produces 896 MW of power from its eight generators, each of which has a capacity of 112MW. History The plant comprises a 16 km (9.9 mi) long tunnel, the width of a two-lane highway, drilled and blasted through the coastal mountains to carry water to the penstocks of the Kemano powerhouse. The water plunges 800 m (2,600 ft) to drive the generators. The two 300 kV power transmission lines travel 82 km (51 mi) from Kemano to KitimatThe Tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nechako Plateau
The Nechako Plateau is the northernmost subdivision of the Interior Plateau, one of the main geographic regions of the Canadian province of British Columbia. It spans the basin of the Nechako River and its tributaries the Stuart River and Endako Rivers, and is bounded on the south by the West Road River (Blackwater River), south of which is the Chilcotin Plateau and on the north by the Nation River and the valleys of Babine and Takla Lakes, beyond which are the Omineca Mountains (N) and Skeena Mountains (NW). To the west, it abuts the various ranges of the Hazelton Mountains while on its east it is bounded by the pass between Prince George, British Columbia and the Parsnip Arm of Williston Lake, beyond which is the McGregor Plateau, which skirts the Northern Rockies. Some classification systems include the plateau area on the east bank of the Fraser River beyond the city of Prince George; this area neighbours the northernmost reaches of the Quesnel Highland and Cariboo Mountains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
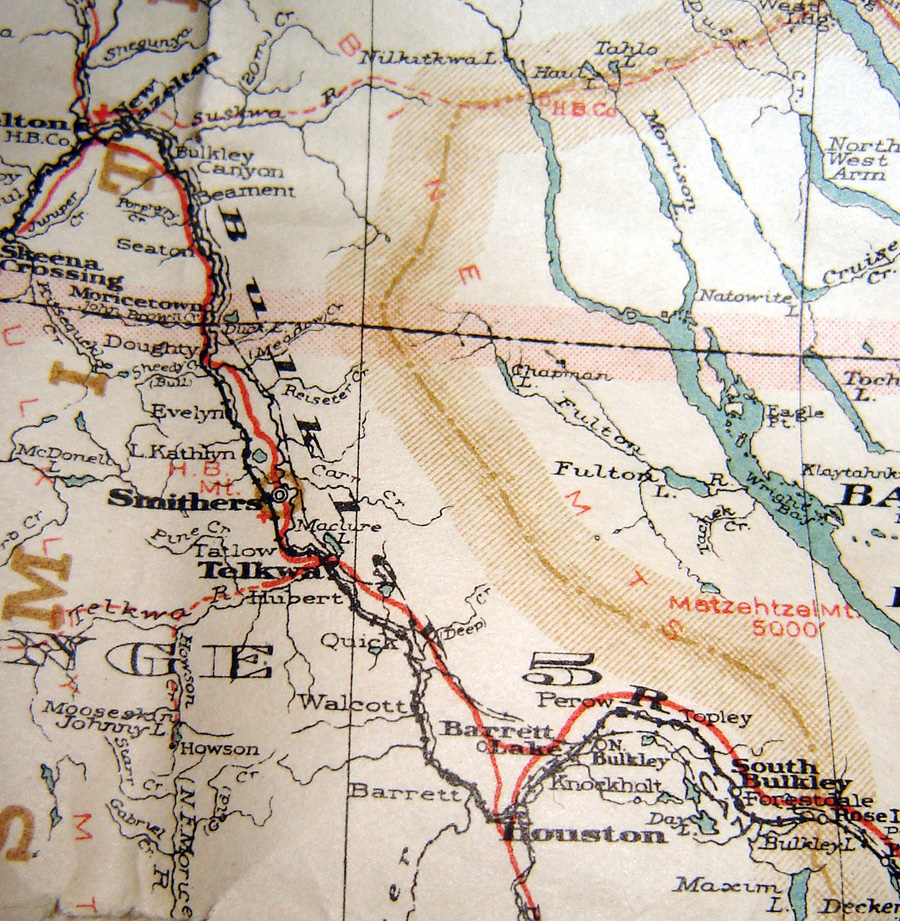
Lejac
Lejac is a locality on the Canadian National Railway line in the Nechako Country region of British Columbia, located on the south shore of Fraser Lake between the communities of Fraser Lake (W) and Fort Fraser (E). Name origin Lejac derives its name from the now-closed Lejac Residential School, which had been named for one of the co-founders of the residential school at Fort St. James. Though not on Indian reserve itself, Lejac is a community of the Nadleh Whut'en First Nation of the Dakelh (Carrier) people, whose main community, Nadleh Village, is adjacent to the original site of the fort, which is located in Beaumont Provincial Park. Nadleh was also referred to as Fort Fraser, though today's non-native community of that name was based around the CNR stop of that name, and is on the opposite side of the Nechako River, which is connected to the outflow from Fraser Lake by the short Nautley River, whose name comes from the Nadleh Whuten people. Fort Fraser was the site of the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cariboo
The Cariboo is an intermontane region of British Columbia, Canada, centered on a plateau stretching from Fraser Canyon to the Cariboo Mountains. The name is a reference to the caribou that were once abundant in the region. The Cariboo was the first region of the interior north of the lower Fraser River and its canyon to be settled by non-indigenous people, and played an important part in the early history of the colony and province. The boundaries of the Cariboo proper in its historical sense are debatable, but its original meaning was the region north of the forks of the Quesnel River and the low mountainous basins between the mouth of that river on the Fraser at the city of Quesnel and the northward end of the Cariboo Mountains, an area that is mostly in the Quesnel Highland and focused on several now-famous gold-bearing creeks near the head of the Willow River. The richest of them all, Williams Creek, is the location of Barkerville, which was the capital of the Cariboo Gol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilcotin District
The Chilcotin () region of British Columbia is usually known simply as "the Chilcotin", and also in speech commonly as "the Chilcotin Country" or simply Chilcotin. It is a plateau and mountain region in British Columbia on the inland lee of the Coast Mountains on the west side of the Fraser River. Chilcotin is also the name of the river draining that region. In the language of the Chilcotin people their name and the name of the river means "people of the red ochre river" (its tributary the Chilko River means "red ochre river") The Chilcotin district is often viewed as an extension of the Cariboo region, east of that river, although it has a distinct identity from the Cariboo District. It is, nonetheless, part of the Cariboo Regional District which is a municipal-level body governing some aspects of infrastructure and land-used planning. The vast majority of the population are First Nations people, members of the Tsilhqot'in and Dakelh peoples, while others are settlers and ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulkley Valley
The Bulkley Valley is in the northwest Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. Geography The Bulkley, a stream running through Houston, British Columbia, joins the larger Morice River about to the west. At the confluence, they become not the Morice, but unusually, take the name of the smaller Bulkley. The Bulkley River flows northwestward through the valley that is bounded on the west by the Hudson Bay Mountain range and on the east by the Babine Mountains. The northern boundary of the valley is usually considered the Bulkey's confluence with the Skeena River at Hazelton, although it is sometimes placed further south near Witset. The valley's southern edge is at Bulkley Lake, part way between Houston and Burns Lake. History First Nations The Wet'suwet'en people called the valley home for thousands of years. In the Delgamuukw decision of 1997, the Supreme Court of Canada affirmed that the Wet'suwet'en and neighbouring Gitxsan had Aboriginal title in the area. Surveys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omineca Country
The Omineca Country, also called the Omineca District or the Omineca, is a historical geographic region of the Northern Interior of British Columbia, roughly defined by the basin of the Omineca River but including areas to the south which allowed access to the region during the Omineca Gold Rush of the 1860s. The term Omineca District also refers to the Omineca Mining District which referred to the same area but was a government administrative division. Today the name loosely refers to the region northwest of Prince George and north of Hwy 16 (the Yellowhead Highway) and occurs in the names of such entities as electoral districts, e.g. Prince George-Omineca. See also *Cariboo *Chilcotin District * Lost Creek *Peace River Block * Slate Creek *Stikine Country The Stikine Country , also referred to as the Stikine District or simply "the Stikine", is one of the historical geographic regions of the Canadian province of British Columbia, located inland from the central Alaska Panh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitimat, British Columbia
Kitimat is a district municipality in the North Coast region of British Columbia, Canada. It is a member municipality of the Regional District of Kitimat–Stikine regional government. The Kitimat Valley is part of the most populous urban district in northwest British Columbia, which includes Terrace to the north along the Skeena River Valley. The city was planned and built by the Aluminum Company of Canada (Alcan) during the 1950s. Its post office was approved on June 6, 1952. Kitimat's municipal area is . It is located on tidewater in one of the few wide, flat valleys on the coast of British Columbia. The 2016 census recorded 8,131 citizens. The District of Kitimat Development Services situates the port of Kitimat as an integral part of the Northwest Corridor connecting North America to the Pacific Ocean and the Pacific Rim. History "Kitimat" in the Tsimshian language refers to the Haisla First Nation as the "People of the Snow". Before 1950 the Kitimat township was a small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ootsa Lake Reservoir
The Nechako Reservoir, sometimes called the Ootsa Lake Reservoir, is a hydroelectric reservoir in British Columbia, Canada that was formed by the Kenney Dam making a diversion of the Nechako River through a 16-km intake tunnel in the Kitimat Ranges of the Coast Mountains to the 890 MW Kemano Generating Station at sea level at Kemano to service the then-new Alcan aluminum smelter at Kitimat. When it was constructed on the Nechako River in 1952, it resulted in the relocation of over 75 families. It was one of the biggest reservoirs built in Canada until the completion of the Columbia Treaty Dams and the W.A.C. Bennett Dam that created Lake Williston. The water level may swing 10 feet between 2790 and 2800 feet. The damming "linked the rivers and lakes of Ootsa, Intata, Whitesail, Chelaslie, Tetachuck, Tahtsa and Natalkuz into the reservoir with a surface area of over 90,000 hectares." "The water of these lakes and rivers was diverted westward to the Pacific Ocean, instead of eastward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, forests, lakes, mountains, inland deserts and grassy plains, and borders the province of Alberta to the east and the Yukon and Northwest Territories to the north. With an estimated population of 5.3million as of 2022, it is Canada's third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria and its largest city is Vancouver. Vancouver is the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada; the 2021 census recorded 2.6million people in Metro Vancouver. The first known human inhabitants of the area settled in British Columbia at least 10,000 years ago. Such groups include the Coast Salish, Tsilhqotʼin, and Haida peoples, among many others. One of the earliest British settlements in the area was Fort Victoria, established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakelh
The Dakelh (pronounced ) or Carrier are the indigenous people of a large portion of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. The "Carrier" name was derived from an English translation of ''Aghele'', the name from the neighbouring Sekani (Tsek'ehne) ("people of the rocks or mountains", Lht'at'en / Lht'at'enne, ᒡᗧᗥᐣ) for Dakelh people. Sekani people played an important role in the early period of contact between the fur traders and Dakelh people because some Sekani people could speak both Dakelh and Cree and served as interpreters between the fur traders and Dakelh people. They call themselves "Dakelh / Dakelh-ne" (ᑕᗸᒡ, people who “travel upon water”, lit. "people who travel by boat early in the morning", a Synaeresis of uda ukelh and ne), and add the suffixes -xwoten, “people of” or -t’en, “people” to village names or locations to refer to specific groups (e.g., Tl’azt’en, Wet’suwet’en). the Wetʼsuwetʼen (Whutsot'en, ᗘᙢᗥᐣ, "Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |