|
Near-Earth Object Confirmation Page
The Near-Earth Object Confirmation Page (NEOCP) is a web service listing recently-submitted observations of objects that may be near-Earth objects (NEOs). It is a service of the Minor Planet Center (MPC), which is the official international archive for astrometric observations of minor planets. The NEOCP was established by the MPC on the World Wide Web in March 1996. Astrometric observations of new NEO candidates are submitted by observers either through email or cURL, after which they are placed in the NEOCP for a period of time until they are confirmed to be a new object, confirmed to be an already-known object, or not confirmed with sufficient follow-up observations. If the object is confirmed as a new NEO, it is given a provisional designation and its observations will be immediately published in a ''Minor Planet Electronic Circular'' (MPEC). If the object is a recovery of an already-designated NEO on a new opposition, it will also be immediately published in an MPEC. Otherwise, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-Earth Object
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body whose orbit brings it into proximity with Earth. By convention, a Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical units (AU). If a NEO's orbit crosses the Earth's orbit, and the object is larger than across, it is considered a potentially hazardous object (PHO). Most known PHOs and NEOs are asteroids, but a small fraction are comets. There are over 30,503 known near-Earth asteroids (NEAs) and over a hundred known short-period near-Earth comets (NECs). A number of solar-orbiting meteoroids were large enough to be tracked in space before striking the Earth. It is now widely accepted that collisions in the past have had a significant role in shaping the geological and biological history of the Earth. Asteroids as small as in diameter can cause significant damage to the local environment and human populations. Larger asteroids penetrate the atmosphere to the surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observation Arc
In observational astronomy, the observation arc (or arc length) of a Solar System body is the time period between its earliest and latest observations, used for tracing the body's path. It is usually given in days or years. The term is mostly used in the discovery and tracking of asteroids and comets. Arc length has the greatest influence on the accuracy of an orbit. The number and spacing of intermediate observations has a lesser effect. Short arcs A very short arc leaves a high uncertainty parameter. The object might be in one of many different orbits, at many distances from Earth. In some cases, the initial arc was too short to determine if the object was in orbit around the Earth, or orbiting out in the asteroid belt. With a 1-day observation arc, was thought to be a trans-Neptunian dwarf planet, but is now known to be a 1 km main-belt asteroid. With an observation arc of 3 days, was thought to be a Mars-crossing asteroid that could be a threat to Earth, but was later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
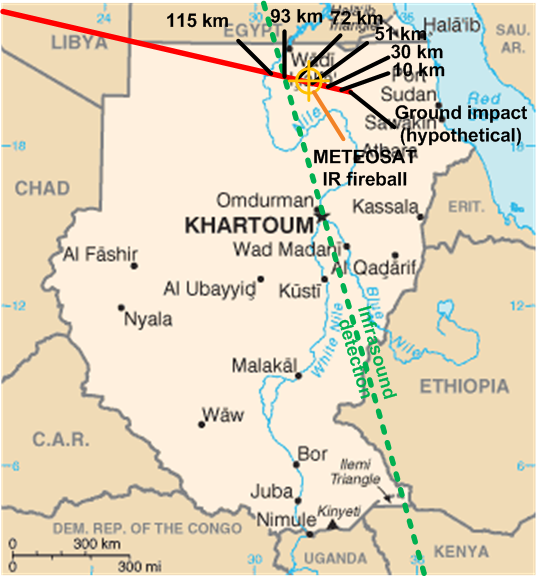
Asteroid Impact Prediction
Asteroid impact prediction is the prediction of the dates and times of asteroids impacting Earth, along with the locations and severities of the impacts. The process of impact prediction follows three major steps: # Discovery of an asteroid and initial assessment of its orbit which is generally based on a short observation arc of less than 2 weeks. # Follow up observations to improve the orbit determination # Calculating if, when and where the orbit may intersect with Earth at some point in the future. In addition, although not strictly part of the prediction process, once an impact has been predicted, an appropriate response needs to be made. Most asteroids are discovered by a camera on a telescope with a wide field of view. Image differencing software compares a recent image with earlier ones of the same part of the sky, detecting objects that have moved, brightened, or appeared. Those systems usually obtain a few observations per night, which can be linked up into a very pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-Earth Object
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body whose orbit brings it into proximity with Earth. By convention, a Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical units (AU). If a NEO's orbit crosses the Earth's orbit, and the object is larger than across, it is considered a potentially hazardous object (PHO). Most known PHOs and NEOs are asteroids, but a small fraction are comets. There are over 30,503 known near-Earth asteroids (NEAs) and over a hundred known short-period near-Earth comets (NECs). A number of solar-orbiting meteoroids were large enough to be tracked in space before striking the Earth. It is now widely accepted that collisions in the past have had a significant role in shaping the geological and biological history of the Earth. Asteroids as small as in diameter can cause significant damage to the local environment and human populations. Larger asteroids penetrate the atmosphere to the surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEOCP Hazard Assessment
The Near-Earth Object Confirmation Page (NEOCP) is a web service listing recently-submitted observations of objects that may be near-Earth objects (NEOs). It is a service of the Minor Planet Center (MPC), which is the official international archive for astrometric observations of minor planets. The NEOCP was established by the MPC on the World Wide Web in March 1996. Astrometric observations of new NEO candidates are submitted by observers either through email or cURL, after which they are placed in the NEOCP for a period of time until they are confirmed to be a new object, confirmed to be an already-known object, or not confirmed with sufficient follow-up observations. If the object is confirmed as a new NEO, it is given a provisional designation and its observations will be immediately published in a '' Minor Planet Electronic Circular'' (MPEC). If the object is a recovery of an already-designated NEO on a new opposition, it will also be immediately published in an MPEC. Otherwise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lost Minor Planet
A minor planet is "lost" when today's observers cannot find it, because its location is too uncertain to target observations. This happens if the orbital elements of a minor planet are not known accurately enough, typically because the observation arc for the object is too short, or too few observations were made before the object became unobservable (e.g. too faint due to increasing distance, or too close to the Sun to view at night). By some definitions thousands, if not tens of thousands, of mostly small observed minor planets are lost. Some lost minor planets discovered in decades past cannot be found because the available observational data is insufficient for reliable orbit determination. With limited information astronomers cannot know where to look for the object at future dates. Lost objects are sometimes recovered when serendipitously re-observed by a later astronomical survey. If the orbital elements of the newly found object are sufficiently close to those of the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isolated Tracklet File
Isolation is the near or complete lack of social contact by an individual. Isolation or isolated may also refer to: Sociology and psychology * Isolation (health care), various measures taken to prevent contagious diseases from being spread **Isolation ward, a separate ward used to isolate patients with infectious diseases *Isolation (psychology), a defense mechanism in psychoanalytic theory * Emotional isolation, a feeling of isolation despite a functioning social network * Isolation effect, a psychological effect of distinctive items more easily remembered Mathematics * Real-root isolation In mathematics, and, more specifically in numerical analysis and computer algebra, real-root isolation of a polynomial consist of producing disjoint intervals of the real line, which contain each one (and only one) real root of the polynomial, and ... * Isolation lemma, a technique used to reduce the number of solutions to a computational problem. Natural sciences *Electrical or galvanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |