|
Navicula (band)
''Navicula'' is a genus of boat-shaped diatom (single-celled photosynthetic organisms), comprising over 1,200 species, though many ''Navicula'' species likely do not belong in the genus strictly speaking. ''Navicula'' is Latin for "small ship", and also a term in English for a boat-shaped incense-holder. Oxford English Dictionary, "Navicula. 3" ''Navicula'' is a cosmopolitan genus and species are present in both freshwater and marine environments, typically attached to surfaces (i.e. benthic The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "t ...). Description ''Navicula'' species are pennate diatoms. Their valves are typically elliptical, though some species have more pinched ends than others. ''Navicula'' cells have two chloroplasts, one along each side of the valve along the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Baptiste Bory De Saint-Vincent
Jean-Baptiste Geneviève Marcellin Bory de Saint-Vincent was a French naturalist, officer and politician. He was born on 6 July 1778 in Agen (Lot-et-Garonne) and died on 22 December 1846 in Paris. Biologist and geographer, he was particularly interested in volcanology, systematics and botany. Life Youth Jean-Baptiste Bory de Saint Vincent was born at Agen on 6 July 1778. His parents were Géraud Bory de Saint-Vincent and Madeleine de Journu; his father's family were petty nobility who played important roles at the bar and in the judiciary, during and after the French Revolution. Instilled with sentiments hostile to the revolution from childhood,Biography of Jean-Baptiste Bory de Saint-Vincent on the website of the French National Assembly: http://www2.assemblee-nationale.fr/sycomore/fiche/(num_dept)/16507 he studied first at the college of Agen, then with his uncle Journu-Auber in Bordeaux in 1787. He may have attended courses in medicine and surgery from 1791 to 1793. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Navicula Species
List of plankton species in the genus ''Navicula''. Species , Algaebase AlgaeBase is a global species database of information on all groups of algae, both marine and freshwater, as well as sea-grass. History AlgaeBase began in March 1996, founded by Michael Guiry. Text was copied from this source, which is avai ... lists 1280 accepted species and more than 1900 proposed species in the plankton genus ''Navicula''. They include: A *'' Navicula abbotti'' *''Navicula abbottii'' *'' Navicula abbreviata'' *'' Navicula abdita'' *'' Navicula abducta'' *'' Navicula abelioensis'' *'' Navicula aberrans'' *'' Navicula abica'' *'' Navicula abiskoensis'' *'' Navicula aboensis'' *'' Navicula abonuensis'' *'' Navicula abraensis'' *'' Navicula abrupta'' *'' Navicula abscondita'' *'' Navicula abstrusa'' *'' Navicula abuensis'' *'' Navicula abunda'' *'' Navicula abundoides'' *'' Navicula acacia'' *'' Navicula accedens'' *'' Navicula accommoda'' *'' Navicula accurata'' *'' Navicu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navicula Tripunctata
''Navicula'' is a genus of boat-shaped diatom algae, comprising over 1,200 species. ''Navicula'' is Latin for "small ship", and also a term in English for a boat-shaped incense-holder. Diatoms — eukaryotic, primarily aquatic, single-celled photosynthetic organisms — play an important role in global ecology, producing about a quarter of all the oxygen within Earth's biosphere, often serving as foundational organisms, or keystone species in the food chain of many environments where they provide a staple for the diets of many aquatic species. Mobility ''Navicula'' diatoms have been observed to possess a motile ability to glide over one another and on hard surfaces such as microscope slides. Around the outside of the navicula's shell is a girdle of mucilage strands that can flow and thus act as a tank track. File:Navicula tripunctata 2.jpg, ''Navicula tripunctata''type species In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising several genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion metric tons of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile (800 m) deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incense
Incense is aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremony. It may also be used as a simple deodorant or insect repellent. Incense is composed of aromatic plant materials, often combined with essential oils. The forms taken by incense differ with the underlying culture, and have changed with advances in technology and increasing number of uses. Incense can generally be separated into two main types: "indirect-burning" and "direct-burning". Indirect-burning incense (or "non-combustible incense") is not capable of burning on its own, and requires a separate heat source. Direct-burning incense (or "combustible incense") is lit directly by a flame and then fanned or blown out, leaving a glowing ember that smoulders and releases a smoky fragrance. Direct-burning incense is either a paste formed around a bamboo stic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a comprehensive resource to scholars and academic researchers, as well as describing usage in its many variations throughout the world. Work began on the dictionary in 1857, but it was only in 1884 that it began to be published in unbound fascicles as work continued on the project, under the name of ''A New English Dictionary on Historical Principles; Founded Mainly on the Materials Collected by The Philological Society''. In 1895, the title ''The Oxford English Dictionary'' was first used unofficially on the covers of the series, and in 1928 the full dictionary was republished in 10 bound volumes. In 1933, the title ''The Oxford English Dictionary'' fully replaced the former name in all occurrences in its reprinting as 12 volumes with a one-v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmopolitan Distribution
In biogeography, cosmopolitan distribution is the term for the range of a taxon that extends across all or most of the world in appropriate habitats. Such a taxon, usually a species, is said to exhibit cosmopolitanism or cosmopolitism. The extreme opposite of a cosmopolitan species is an endemic one, being found only in a single geographical location. Qualification The caveat “in appropriate habitat” is used to qualify the term "cosmopolitan distribution", excluding in most instances polar regions, extreme altitudes, oceans, deserts, or small, isolated islands. For example, the housefly is highly cosmopolitan, yet is neither oceanic nor polar in its distribution. Related terms and concepts The term pandemism also is in use, but not all authors are consistent in the sense in which they use the term; some speak of pandemism mainly in referring to diseases and pandemics, and some as a term intermediate between endemism and cosmopolitanism, in effect regarding pandemism as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthic Zone
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths." Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms (e.g., bacteria and fungi) as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud. Description Oceans The benthic region of the ocean begins at the shore line (intertida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennate Diatoms
The order Pennales is a traditional subdivision of the heterokont algae known as diatoms. The order is named for the shape of the cell walls (or valves or frustules) of pennate diatoms, which are elongated in valve view. The valves may be linear or oval in shape, and usually bear bilaterally symmetrical ornamental patterns. These patterns are composed of a series of transverse lines (known as striae) that can appear as rows of dots when viewed with an optical microscope. Some pennate diatoms also exhibit a fissure along their longitudinal axis. This is known as a raphe, and is involved in gliding movements made by diatom cells; motile diatoms always possess a raphe. In terms of cell cycle, vegetative cells are diploid and undergo mitosis during normal cell division. Periodically, meiosis produces morphologically identical haploid gametes (isogametes), which fuse to produce a (sometimes binucleate) zygote that develops into an auxospore (from which full-sized vegetat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like ''Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they circulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
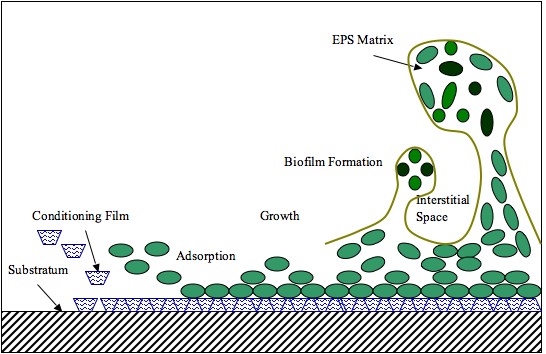
Extracellular Polymeric Substance
Extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) are natural polymers of high molecular weight secreted by microorganisms into their environment. EPSs establish the functional and structural integrity of biofilms, and are considered the fundamental component that determines the physicochemical properties of a biofilm. EPS in the matrix of biofilms provides compositional support and protection of microbial communities from the harsh environments. Components of EPS can be of different classes of polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins, Lipopolysaccharides, and minerals. Components EPSs are mostly composed of polysaccharides (exopolysaccharides) and proteins, but include other macromolecules such as DNA, lipids and humic substances. EPSs are the construction material of bacterial settlements and either remain attached to the cell's outer surface, or are secreted into its growth medium. These compounds are important in biofilm formation and cells' attachment to surfaces. EPSs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |