|
National Council Of Ayllus And Markas Of Qollasuyu
The National Council of Ayllus and Markas of Qullasuyu ( qu, Qullasuyu Ayllukunap Markakunap Mamallaqta Kunaqnin; es, Consejo Nacional de Ayllus y Markas del Qullasuyu; CONAMAQ) is a confederation of traditional governing bodies of Quechua-, Aymara- and Uru-speaking highland indigenous communities in the departments of La Paz, Oruro, Potosí, Cochabamba, Chuquisaca and Tarija, Bolivia. Specifically, it represents the following 16 suyus: Jacha Carangas, Jatun Quillacas, Asamajaquis, Charcas Qara Qara, Council of Ayllus of Potosí, Qara Qara Suyu, Sora, Kallawaya, Leco, Larecaja, Colla, Chui, Paca Jake, Ayllus of Cochabamba, Kapaj Omasuyus and Yapacaní. CONAMAQ was founded on March 22, 1997, with the purpose of restoring the self-governance of "original nations" including "collective rights to land and natural resources, re-definition of administrative units and self-determination exercised through indigenous autonomies and direct representation in state institutions." CONAMAQ is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg , flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center , flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square patchwork with the (top left to bottom right) diagonals forming colored stripes (green, blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, white, green, blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, from top right to bottom left) , other_symbol = , other_symbol_type = Dual flag: , image_coat = Escudo de Bolivia.svg , national_anthem = " National Anthem of Bolivia" , image_map = BOL orthographic.svg , map_width = 220px , alt_map = , image_map2 = , alt_map2 = , map_caption = , capital = La Paz Sucre , largest_city = , official_languages = Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Paz
La Paz (), officially known as Nuestra Señora de La Paz (Spanish pronunciation: ), is the seat of government of the Plurinational State of Bolivia. With an estimated 816,044 residents as of 2020, La Paz is the third-most populous city in Bolivia. Its metropolitan area, which is formed by La Paz, El Alto, Achocalla, Viacha, and Mecapaca makes up the second most populous urban area in Bolivia, with a population of 2.0 million, after Santa Cruz de la Sierra with a population of 2.3 million. It is also the capital of the La Paz Department. The city, in west-central Bolivia southeast of Lake Titicaca, is set in a canyon created by the Choqueyapu River. It is in a bowl-like depression, part of the Amazon basin, surrounded by the high mountains of the Altiplano. Overlooking the city is the towering, triple-peaked Illimani. Its peaks are always snow-covered and can be seen from many parts of the city. At an elevation of roughly above sea level, La Paz is the highest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergio Hinojosa Singuri
Sergio may refer to: * Sergio (given name), for people with the given name Sergio * Sergio (carbonado), the largest rough diamond ever found * ''Sergio'' (album), a 1994 album by Sergio Blass * ''Sergio'' (2009 film), a documentary film * ''Sergio'' (2020 film), a biographical drama film * Sergio, the mascot for the Old Orchard Beach Surge Old or OLD may refer to: Places *Old, Baranya, Hungary *Old, Northamptonshire, England * Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD) *OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, Ma ... baseball team See also * Hurricane Sergio (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechua Language
Quechua (, ; ), usually called ("people's language") in Quechuan languages, is an indigenous language family spoken by the Quechua peoples, primarily living in the Peruvian Andes. Derived from a common ancestral language, it is the most widely spoken pre-Columbian language family of the Americas, with an estimated 8–10 million speakers as of 2004.Adelaar 2004, pp. 167–168, 255. Approximately 25% (7.7 million) of Peruvians speak a Quechuan language. It is perhaps most widely known for being the main language family of the Inca Empire. The Spanish encouraged its use until the Peruvian struggle for independence of the 1780s. As a result, Quechua variants are still widely spoken today, being the co-official language of many regions and the second most spoken language family in Peru. History Quechua had already expanded across wide ranges of the central Andes long before the expansion of the Inca Empire. The Inca were one among many peoples in present-day Peru who already spok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aymara Language
Aymara (; also ) is an Aymaran language spoken by the Aymara people of the Bolivian Andes. It is one of only a handful of Native American languages with over one million speakers.The other native American languages with more than one million speakers are Nahuatl, Quechua languages, and Guaraní. Aymara, along with Spanish and Quechua, is an official language in Bolivia and Peru. It is also spoken, to a much lesser extent, by some communities in northern Chile, where it is a recognized minority language. Some linguists have claimed that Aymara is related to its more widely spoken neighbor, Quechua. That claim, however, is disputed. Although there are indeed similarities, like the nearly identical phonologies, the majority position among linguists today is that the similarities are better explained as areal features rising from prolonged cohabitation, rather than natural genealogical changes that would stem from a common protolanguage. Aymara is an agglutinating an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uru Language
The Uru language, more specifically known as Iru-Itu, and Uchumataqu, is an extinct language formerly spoken by the Uru people. In 2004, it had 2 remaining native speakers out of an ethnic group of 140 people in the La Paz Department, Bolivia near Lake Titicaca, the rest having shifted to Aymara and Spanish. The language is close enough to the Chipaya language to sometimes be considered a dialect of that language. Uru is also called Ochosuma (Uchuzuma), a historical name for the Uru ethnic group. Olson (1964) mentions a variety of Uru, Uru of Ch'imu, spoken on the Isla del Sol in Lake Titicaca. It is not clear if this was a dialect of Iru Itu or a separate Uru language. Identifying Uchumataqu Since one of the Urus' names for their language was "Pukina", Uchumataqu has previously been mistakenly identified with Puquina. While the personal and possessive pronouns of the unrelated Puquina bear limited similarities to those of Arawakan languages, Uru differs drastically from Ara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
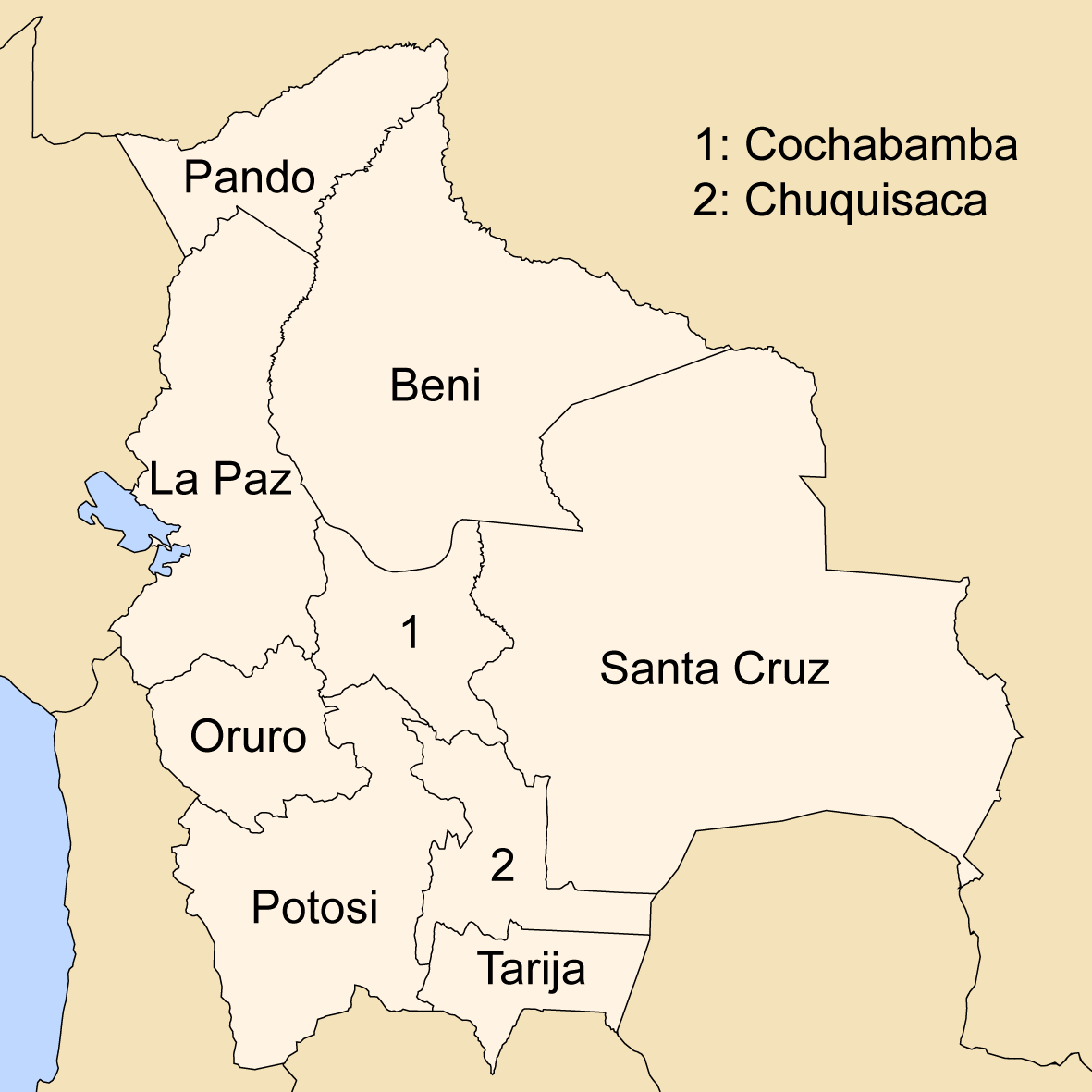
Departments Of Bolivia
Bolivia is a unitary state consisting of nine departments ( es, departamentos). Departments are the primary subdivisions of Bolivia, and possess certain rights under the Constitution of Bolivia. Each department is represented in the Plurinational Legislative Assembly—a bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. Each department is represented by four Senators, while Deputies are awarded to each department in proportion to their total population. Out of the nine departments, La Paz was originally the most populous, with 2,706,351 inhabitants as of 2012 but the far eastern department of Santa Cruz has since surpassed it by 2020; Santa Cruz also claims the title as the largest, encompassing . Pando is the least populated, with a population of 110,436. The smallest in area is Tarija, encompassing . Departments Former Departments By population Notes See also * ISO 3166-2:BO, the ISO codes for the departments of Bolivia. * Bolivian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Coordination For Change
The National Coordinator for Change ( es, Coordinadora Nacional por el Cambio; CONALCAM) is a Bolivian political coordination of social movements aligned with the governing Movement for Socialism-Political Instrument for the Sovereignty of the Peoples (MAS-IPSP). It was founded on 22 January 2007, during the Constituent Assembly of 2006-2007. " ''Constituyente Soberana'' (website), January 23, 2007Moira Zuazo, ¿Los movimientos sociales en el poder? El gobierno del MAS en Bolivia " ''Nueva Sociedad'' 227, May-June 2010. CONALCAM mobilizes its member organizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pact Of Unity
The Pact of Unity ( es, Pacto de Unidad) is an evolving national alliance of Bolivian grassroots organizations in support of indigenous and agrarian rights, land reform, the rewriting of the 1967 constitution through a Constituent Assembly, and a left-indigenous transformation of the Bolivian state. Since 2005, the Pact has been a close ally of Bolivian President Evo Morales, and it forms the nucleus of the National Coordination for Change, a pro-government alliance. The composition of the Pact of Unity has varied over time, but since 2006 it has generally consisted of five nationwide organizations: * Unique Confederation of Rural Laborers of Bolivia (CSUTCB) * National Confederation of Peasant Indigenous Native Women of Bolivia - Bartolina Sisa * Syndicalist Confederation of Intercultural Communities of Bolivia (CSCIB) * Confederation of Indigenous Peoples of Bolivia (CIDOB) * National Council of Ayllus and Markas of Qullasuyu (CONAMAQ) In 2011, CONAMAQ and CIDOB withdrew from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isiboro Sécure National Park And Indigenous Territory
Isiboro Sécure National Park and Indigenous Territory (''Territorio Indígena y Parque Nacional Isiboro Secure,'' TIPNIS) is a protected area and Native Community Land in Bolivia situated between the north of the Cochabamba Department and the south of the Beni Department ( Chapare, Moxos, and Marbán provinces). It protects part of the Bolivian Yungas ecoregion. The indigenous people living within the park belong to the Tsimané, Yuracaré, and Mojeño-Trinitario peoples. The southern portion of the park has been colonized by agricultural settlers, primarily coca farmers, since the 1970s. The Bolivian government estimates that 10% of the park has been deforested by their presence. Establishment The park was made into a National Park by Supreme Decree 7401 on November 22, 1965 and recognized as an indigenous territory (formally as Native Community Land) through Supreme Decree 22610 on September 24, 1990, following pressure by local native peoples and the March for Territ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayllu
The ''ayllu'', a family clan, is the traditional form of a community in the Andes, especially among Quechuas and Aymaras. They are an indigenous local government model across the Andes region of South America, particularly in Bolivia and Peru. Ayllus functioned prior to Inca conquest, during the Inca and Spanish colonial period, and continue to exist to the present day – such as the Andean community Ocra. Membership gave individual families more variation and security on the land that they farmed. Ayllus had defined territories and were essentially extended family or kin groups, but could include non-related members. Their primary function was to solve subsistence issues, and issues of how to get along in family, and the larger community. Ayllus descended from stars in the Inca cosmogony, and just like stars had unique celestial locations, each ayllu had a terrestrial location defined by the paqarina, the mythical point of emergence of the lineage huaca. Current practice '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apu Mallku
Apu Mallku is an Aymara title meaning "supreme leader" or "king" conferred on a Mallku or "prince". The Apu Mallku's mandate is to oversee the vast network of Ayllus, an ancient Andean system of governing councils that predates even the Inca empire. It appears that the mandate of the Apu Mallku was initially restricted to the Collasuyu (the traditional Aymara lands of Bolivia, parts of Peru and northern Chile) but it could now be interpreted (since a resolution in 2000) to extend to the bounds of the much larger former Inca realm of the Tawantinsuyu which stretched throughout the Andes incorporating the modern states of Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Chile and Argentina. The self-appellation for the people of this combined territory is ''Qullana''. It would seem through the ayllus system there is a large degree of coordination between both the Aymara and the Quechua nations. Apu Mallku was the title bestowed upon Evo Morales on 21 January 2006 at Tiwanaku, the day before his official ina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)