|
Nathan F. Dixon II
Nathan Fellows Dixon (May 1, 1812 – April 11, 1881) was an attorney and bank president from Westerly, Rhode Island. The son of Nathan F. Dixon and father of Nathan F. Dixon III, he was best known for his service as a United States representative from Rhode Island from 1849 to 1851, and again from 1863 to 1871. Biography He was born in Westerly, Rhode Island on May 1, 1812, the son of Nathan F. Dixon and Elizabeth (Palmer) Dixon). He attended Plainfield Academy in Plainfield, Connecticut, and graduated from Brown University in 1833. He later pursued the study of law at Harvard Law School and Yale Law School. Dixon was admitted to the bar in 1837 and commenced practice in Westerly. He was a member of the board of directors of Westerly's Washington Bank, and succeeded his father as president when the senior Dixon died in 1842. He served as president of the bank until his death. He was a member of the Rhode Island House of Representatives from 1841 to 1849 and 1851 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
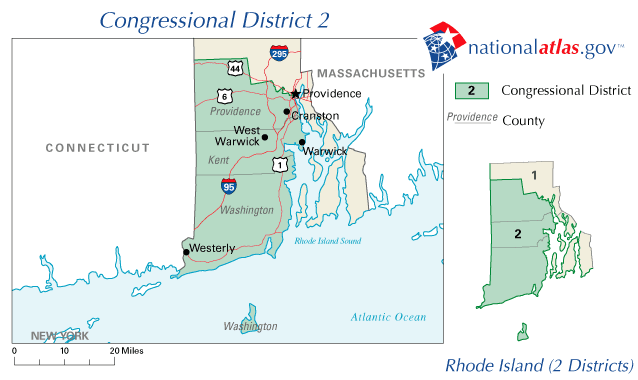
Rhode Island's 2nd Congressional District
Rhode Island's 2nd congressional district is a congressional district in southern and western Rhode Island. The district is currently represented by Democrat James Langevin, who has represented the district since January 2001. Composition The district includes: * the following communities in Providence County: ** Burrillville, Cranston, Foster, Glocester, Johnston, Providence (precincts 2809–2812, 2840–2842, 2845–2846, 2851–2897, 8100–8102) and Scituate, * all of Kent County * all of Washington County Historical district boundaries Recent results from statewide elections List of members representing the district Election history 2012 2014 2016 2018 2020 2022 See also *Rhode Island's congressional districts *List of United States congressional districts Congressional districts in the United States are electoral divisions for the purpose of electing members of the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plainfield, Connecticut
Plainfield is a town in Windham County, Connecticut, United States. The population was 14,973 at the 2020 census. The town comprises four villages: Plainfield (south, ZIP code 06374), Moosup (northeast, 06354), Wauregan (northwest, 06387), and Central Village (west, 06332). Each village has their own respective United States Post Office and fire department. The entire town is serviced by the 860 area code. History Plainfield was incorporated in 1699 as the town of Quinebaug and renamed the following year to its current name. The present name of "Plainfield" is descriptive of the original town site. Plainfield proved to be an industrial heavyweight in the 19th and early 20th centuries due largely to the ability of the Moosup and Quinebaug Rivers to provide power to the different mills throughout town. The job opportunities attracted French Canadian Americans, Irish Americans, British Americans, and people other countries during the late 19th century. Combined with the mills, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1866 National Union Convention
The National Union Convention (also known as the Loyalist Convention, the Southern Loyalist Convention, the National Loyalists' Loyal Union Convention, or the Arm-In-Arm Convention) was held on August 14, 15, and 16 1866, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Convention The convention was called in Philadelphia before of the midyear elections of 1866 in an attempt to encourage political support for US President Andrew Johnson, who was under attack by both moderate and Radical Republicans. Johnson's friends tried to rally support for his lenient pro-South Reconstruction policies. Some hoped to create a new political party, but that goal was not realized. Delegates gathered at a hastily-built temporary structure that was designed to accommodate the several thousand people expected to attend. Formally called "the Wigwam," the immense edifice was on Girard Avenue, between 19th and 20th Streets, across from Philadelphia's Girard College. About 7000 prominent politicians and activists attende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
38th United States Congress
The 38th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1863, to March 4, 1865, during the last two years of the first administration of U.S. President Abraham Lincoln. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the Eighth Census of the United States in 1860. The Senate had a Republican majority, and the House of Representatives had a Republican plurality. Major events * American Civil War, which had started in 1861, continued through this Congress and ended later in 1865 * January 8, 1863: Ground broken in Sacramento, California, on the construction of the First transcontinental railroad in the United States * November 19, 1863: Gettysburg Address * November 8, 1864: President Abraham Lincoln is reelected, defeating George McClellan. Major legislation * April ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
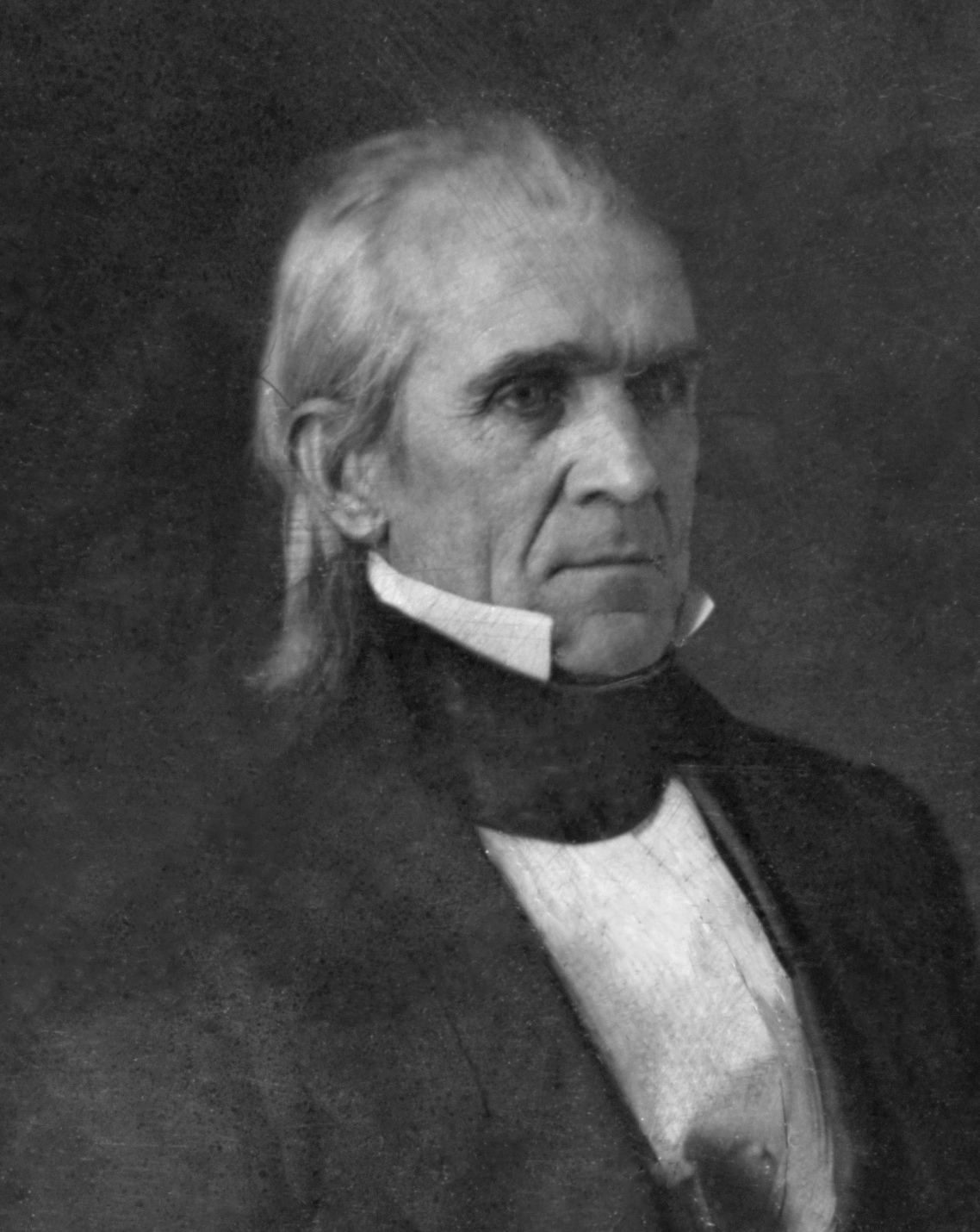
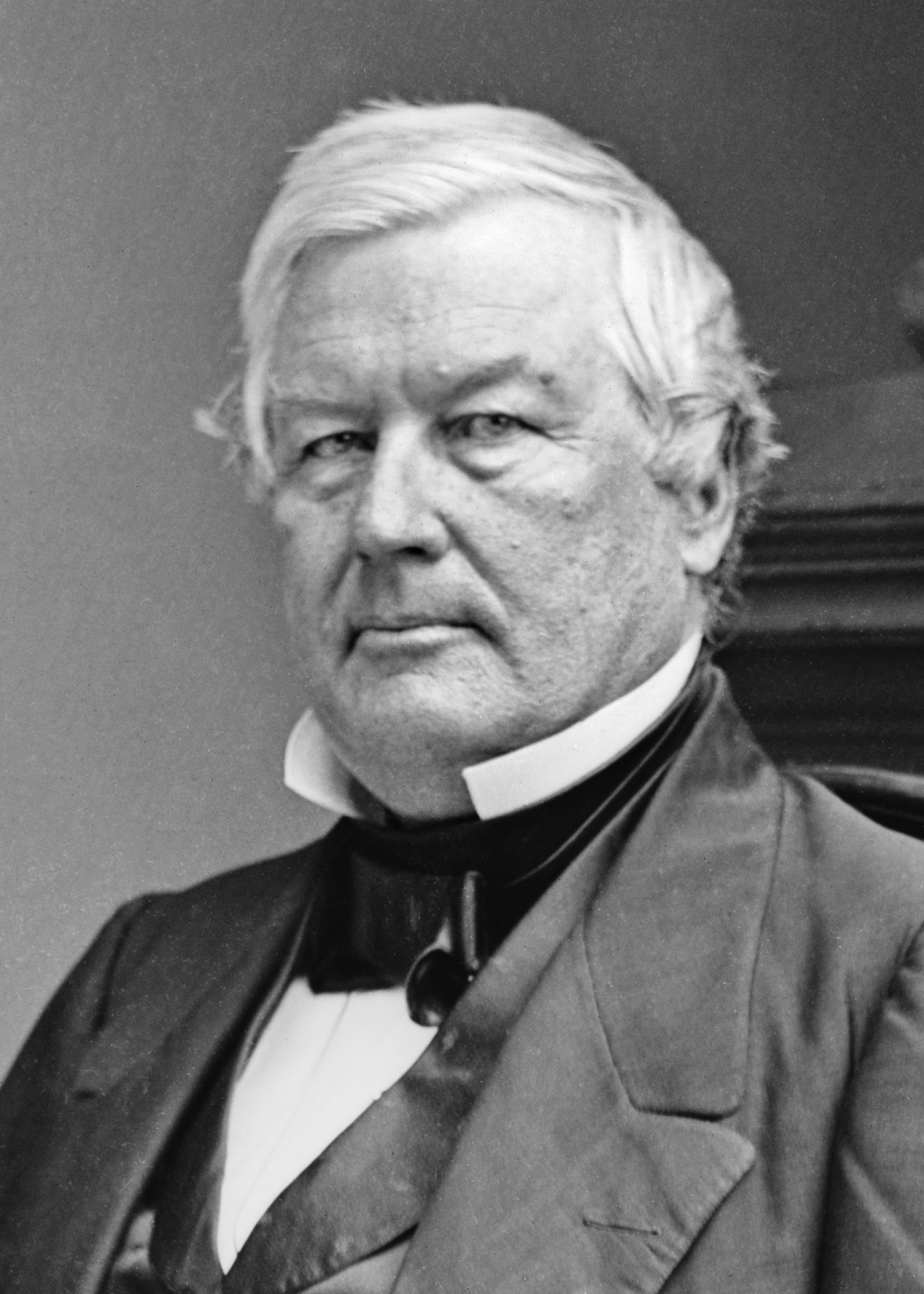
31st United States Congress
The 31st United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1849, to March 4, 1851, during the 16 months of the Zachary Taylor presidency and the first eight months of the administration of Millard Fillmore's. The apportionment of seats in this House of Representatives was based on the Sixth Census of the United States in 1840. The Senate had a Democratic majority, while there was a Democratic plurality in the House. Major events * March 4, 1849: Zachary Taylor became President of the United States * June, 1849: Relations with France broke down as the French ambassador Guillaume-Tell de La Vallée Poussin engaged in "insulting and confrontational" behavior towards President Taylor, shortly after this a row erupted with France over reparations which France owed the United States. The President of F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Frelinghuysen
Theodore Frelinghuysen (March 28, 1787April 12, 1862) was an American politician who represented New Jersey in the United States Senate. He was the Whig vice presidential nominee in the election of 1844, running on a ticket with Henry Clay. Born in Somerset County, New Jersey, Frelinghuysen established a legal practice in Newark, New Jersey after graduating from the College of New Jersey. He was the son of Senator Frederick Frelinghuysen and the adoptive father of Secretary of State Frederick Theodore Frelinghuysen. He served as the New Jersey Attorney General from 1817 to 1829 and as a United States Senator from 1829 to 1835. In the Senate, Frelinghuysen strongly opposed President Andrew Jackson's policy of Indian removal. After leaving the Senate, he served as the Mayor of Newark, New Jersey, Mayor of Newark from 1837 to 1838. Frelinghuysen was selected as Clay's running mate at the 1844 Whig National Convention. In the 1844 election, the Whig ticket was narrowly defeated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Clay
Henry Clay Sr. (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American attorney and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the U.S. Senate and House of Representatives. He was the seventh House speaker as well as the ninth secretary of state, also receiving electoral votes for president in the 1824, 1832, and 1844 presidential elections. He helped found both the National Republican Party and the Whig Party. For his role in defusing sectional crises, he earned the appellation of the "Great Compromiser" and was part of the "Great Triumvirate" of Congressmen, alongside fellow Whig Daniel Webster and John C. Calhoun. Clay was born in Hanover County, Virginia, in 1777, beginning his legal career in Lexington, Kentucky, in 1797. As a member of the Democratic-Republican Party, Clay won election to the Kentucky state legislature in 1803 and to the U.S. House of Representatives in 1810. He was chosen as Speaker of the House in early 1811 and, along with President James Madison, led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1844 United States Presidential Election
The 1844 United States presidential election was the 15th quadrennial United States presidential election, presidential election, held from Friday, November 1 to Wednesday, December 4, 1844. History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democrat James K. Polk defeated Whig Party (United States), Whig Henry Clay in a close contest turning on the controversial issues of slavery in the United States, slavery and the Texas annexation, annexation of the Republic of Texas. This is the only election where both major party nominees served as Speaker of the House at one point. President John Tyler's pursuit of Texas annexation divided both major parties. Annexation would geographically expand American slavery. It also risked Mexican–American War, war with Mexico while the United States engaged in sensitive possession and boundary negotiations with the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, Great Britain, which controlled Canada, over Oregon Country, Oregon. Texas annexation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorr Rebellion
The Dorr Rebellion (1841–1842) (also referred to as Dorr's Rebellion, Dorr's War or Dorr War) was an attempt by disenfranchised residents to force broader democracy in the U.S. state of Rhode Island, where a small rural elite was in control of government. It was led by Thomas Wilson Dorr, who mobilized the disenfranchised to demand changes to the state's electoral rules. The state was still using its 1663 colonial charter as a constitution; it required that voters own land as qualification to vote. The rebellion established a parallel government alongside the existing chartered government and wrote a new constitution for Rhode Island. Although the rebellion was crushed militarily, it forced the rewriting of the state constitution to expand eligibility to vote. Precursors and causes Under Rhode Island's colonial charter, originally received in 1663, only male landowners could vote. At the time, most of the citizens of the colonies were farmers and held land, and this qualific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Ward King
Samuel Ward King (May 23, 1786 – January 20, 1851) was the 15th Governor of Rhode Island from 1839 to 1843. King was born in Johnston, Providence County, Rhode Island, to William Borden King and Welthian Walton. He attended Brown University but did not graduate. He became a medical doctor and worked as a surgeon during the War of 1812. In 1820 King was elected town clerk of Johnston. He became a Whig when the party was founded, and was a presidential elector in 1832. In 1838 he was elected to the Rhode Island Senate. He first became governor in 1839 when the legislature failed to grant a majority of votes to the three leading contenders. He was elected to three other terms. During his administration as governor of Rhode Island he took a strong stand against the expanded voting franchise that led to the Dorr Rebellion in 1841 – 1842. President John Tyler John Tyler (March 29, 1790 – January 18, 1862) was the tenth president of the United States The pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admission To The Bar In The United States
Admission to the bar in the United States is the granting of permission by a particular court system to a lawyer to practice law in the jurisdiction and before those courts. Each U.S. state and similar jurisdiction (e.g. territories under federal control) has its own court system and sets its own rules for bar admission, which can lead to different admission standards among states. In most cases, a person is "admitted" or "called" to the bar of the highest court in the jurisdiction and is thereby authorized to practice law in the jurisdiction. Federal courts, although often overlapping in admission standards with states, set their own requirements for practice in each of those courts. Typically, lawyers seeking admission to the bar of one of the U.S. states must earn a Juris Doctor degree from a law school approved by the jurisdiction, pass a bar exam administered by the regulating authority of that jurisdiction, pass a professional responsibility examination, and undergo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yale Law School
Yale Law School (Yale Law or YLS) is the law school of Yale University, a Private university, private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. It was established in 1824 and has been ranked as the best law school in the United States by ''U.S. News & World Report'' every year between 1990 and 2022, when Yale made a decision to voluntarily pull out of the rankings, citing issues with the rankings' methodology. One of the most selective academic institutions in the world, the 2020–21 acceptance rate was 4%, the lowest of any law school in the United States. Its Yield (college admissions), yield rate of 87% is also consistently the highest of any law school in the United States. Yale Law alumni include many List of Yale Law School alumni, prominent figures in law and politics, including President of the United States, United States presidents Gerald Ford and Bill Clinton and former United States Secretary of State, U.S. secretary of state and presidential nominee, Hillary Cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)




