|
Natal Chart
A horoscope (or other commonly used names for the horoscope in English include natal chart, astrological chart, astro-chart, celestial map, sky-map, star-chart, cosmogram, vitasphere, radical chart, radix, chart wheel or simply chart) is an astrological chart or diagram representing the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, astrological aspects and sensitive angles at the time of an event, such as the moment of a person's birth. The word horoscope is derived from the Greek words ''ōra'' and ''scopos'' meaning "time" and "observer" (''horoskopos'', pl. ''horoskopoi'', or "marker(s) of the hour"). It is used as a method of divination regarding events relating to the point in time it represents, and it forms the basis of the horoscopic traditions of astrology. Horoscope columns are often featured in print and online newspapers. In common usage, horoscope often refers to an astrologer's interpretation, usually based on a system of solar Sun sign astrology; based strictly on the pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrological Chart - New Millennium
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamic world, and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Astrology
Jyotisha or Jyotishya (from Sanskrit ', from ' “light, heavenly body" and ''ish'' - from Isvara or God) is the traditional Hindu system of astrology, also known as Hindu astrology, Indian astrology and more recently Vedic astrology. It is one of the six auxiliary disciplines in Hinduism, that is connected with the study of the Vedas. The ''Vedanga Jyotisha'' is one of the earliest texts about astronomy within the Vedas. Some scholars believe that the horoscopic astrology practiced in the Indian subcontinent came from Hellenistic influences, however, this is a point of intense debate and other scholars believe that Jyotisha developed independently although it may have interacted with Greek astrology. Following a judgement of the Andhra Pradesh High Court in 2001 which favoured astrology, some Indian universities now offer advanced degrees in Hindu astrology. The scientific consensus is that astrology is a pseudoscience. Etymology Jyotisha, states Monier-Williams, is rooted in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrological Aspect
In astrology, an aspect is an angle that planets make to each other in the Horoscope; as well as to the Ascendant, Midheaven, Descendant, Lower Midheaven, and other points of astrological interest. As viewed from Earth, aspects are measured by the angular distance in degrees and minutes of ecliptic longitude between two points. According to astrological tradition, they indicate the timing of transitions and developmental changes in the lives of people and affairs relative to the Earth. For example, if an astrologer creates a Horoscope that shows the apparent positions of the celestial bodies at the time of a person's birth (Natal Chart), and the angular distance between Mars and Venus is 92° ecliptic longitude, the chart is said to have the aspect "Venus Square Mars" with an orb of 2° (i.e., it is 2° away from being an exact Square; a Square being a 90° aspect). The more exact an aspect, the stronger or more dominant it is said to be in shaping character or manifesting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Parts
In astrology, the Arabian/Arabic parts or lots are constructed points based on mathematical calculations of three horoscopic entities such as planets or angles. The distance between two of the points is added to the position of the third (very often the ascendant) to derive the location of the lot. History The lots are a very ancient astrological technique which can be traced back to pre-Hellenistic sources. Their origin is obscure; they could originally be Babylonian, Ancient Egyptian, Magian, Persian or Hermetic, but by the time of Dorotheus of Sidon in the first century A.D. (and probably earlier) they had become an established tenet of Hellenistic astrological practice. One of the best informational sources for the lots is the ''Introduction'' to astrology by fourth-century astrologer Paulus Alexandrinus and the ''Commentary'' on this work by sixth-century philosopher Olympiodorus the Younger. Paulus used a dozen or so major lots for almost every aspect of his analysis. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
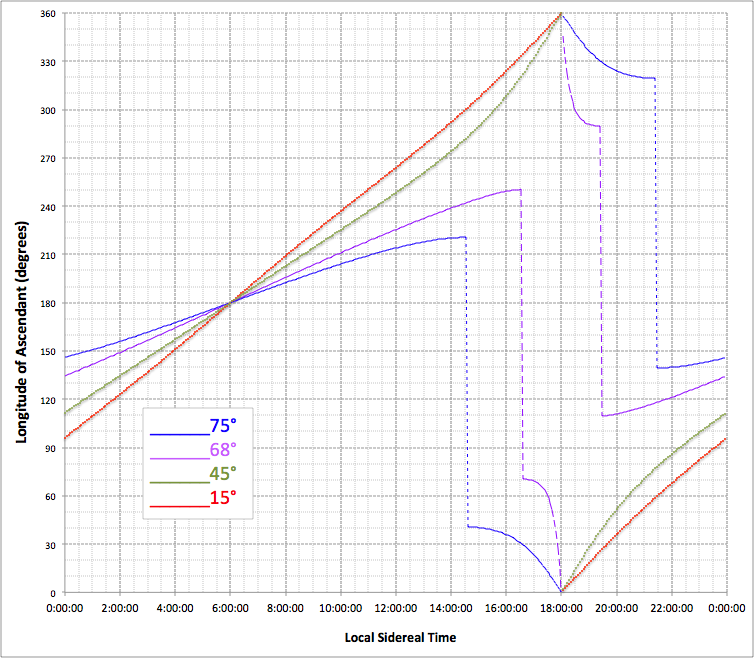
Ascendant
The ascendant (Asc, Asc or As) is the astrological sign on the eastern horizon when the person was born. According to certain astrological theories, celestial phenomena reflect or influence human activity on the principle of "as above, so below." Thus some astrologers consider that the ascendant signifies a person's physical appearance, and awakening consciousness. Because the ascendant is specific to a particular time and place, to astrologers it signifies the individual environment and conditioning that a person receives during their upbringing, and also the circumstances of their childhood. For this reason, astrologers consider that the ascendant is also concerned with how a person has learned to present themself to the world, especially in public and in impersonal situations. History Although Babylonian astronomers observed the actual rising times of the signs, there is no specific mention of the ascendant in the texts that have survived on clay tablets. By the 3rd centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midheaven
A horoscope (or other commonly used names for the horoscope in English include natal chart, astrological chart, astro-chart, celestial map, sky-map, star-chart, cosmogram, vitasphere, radical chart, radix, chart wheel or simply chart) is an astrological chart or diagram representing the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, astrological aspects and sensitive angles at the time of an event, such as the moment of a person's birth. The word horoscope is derived from the Greek words ''ōra'' and ''scopos'' meaning "time" and "observer" (''horoskopos'', pl. ''horoskopoi'', or "marker(s) of the hour"). It is used as a method of divination regarding events relating to the point in time it represents, and it forms the basis of the horoscopic traditions of astrology. Horoscope columns are often featured in print and online newspapers. In common usage, horoscope often refers to an astrologer's interpretation, usually based on a system of solar Sun sign astrology; based strictly on the pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House (astrology)
Most Horoscopic astrology, horoscopic traditions of astrology systems divide the horoscope into a number (usually twelve) of houses whose positions depend on time and location rather than on date. In Jyotiṣa, Hindu astrological tradition these are known as Bhāvas. The houses of the horoscope represent different fields of experience wherein the energies of the signs and planets operateArroyo (1989), p. 111.—described in terms of physical surroundings as well as personal life experiences. Description Every house system is also affiliated with a zodiac sign can be dependent on the Earth's rotation, rotational movement of Earth on its axis, but there is a wide range of approaches to calculating house divisions and different opinions among astrologers over which house system is most accurate. To calculate the houses, it is necessary to know the exact time, date, and location. In natal astrology, some astrologers will use a birth time set for noon or sunrise if the actual tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Node
A lunar node is either of the two orbital nodes of the Moon, that is, the two points at which the orbit of the Moon intersects the ecliptic. The ''ascending'' (or ''north'') node is where the Moon moves into the northern ecliptic hemisphere, while the ''descending'' (or ''south'') node is where the Moon enters the southern ecliptic hemisphere. Eclipses A lunar eclipse can occur only when the full Moon is near either lunar node (within 11° 38' ecliptic longitude), while a solar eclipse can occur only when the new Moon is near either lunar node (within 17° 25'). Both solar eclipses of July 2000 (on the 1st and 31st days) occurred around the time when the Moon was at its ascending node. Ascending-node eclipses recur after one draconic year on average, which is about 0.94901 Gregorian year, as do descending-node eclipses. Precession Because the orbital plane of the Moon precesses in space, the lunar nodes also precess around the ecliptic, completing one revolution (called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliocentric Astrology
Heliocentric astrology is a method of astrology based on birth charts cast using the heliocentric model of the Solar System, with the Sun at the center. Description Most forms of astrology are geocentric. The geocentric horoscope is drawn with the Earth at the center, and the planets are placed around the cartwheel in the positions that they would appear in the sky as seen by a person who is looking at them from the center of the Earth. The Greek language word "helios" means the Sun. Heliocentric astrology draws birth charts with the Sun at the center, and the planets are placed around the cartwheel in the positions that they would appear if someone looked at them from the center of the Sun. Geocentric astrology relies heavily on the ascendant, midheaven, houses, the Moon, planetary aspects (astrological aspects) and placements of birth planets in the houses and signs. But heliocentric astrology does not have houses (due to not having a location on the surface of the sun to comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forer Effect
The Barnum effect, also called the Forer effect or, less commonly, the Barnum–Forer effect, is a common psychological phenomenon whereby individuals give high accuracy ratings to descriptions of their personality that supposedly are tailored specifically to them, yet which are in fact vague and general enough to apply to a wide range of people. This effect can provide a partial explanation for the widespread acceptance of some paranormal beliefs and practices, such as astrology, fortune telling, aura reading, and some types of personality tests. These characterizations are often used by practitioners as a con-technique to convince victims that they are endowed with a paranormal gift. Because the assessment statements are so vague, people ascribe their own interpretation, thus the statement becomes "personal" to them. Also, individuals are more likely to accept negative assessments of themselves if they perceive the person presenting the assessment as a high-status professiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various times through the centuries. The encyclopaedia is maintained by about 100 full-time editors and more than 4,000 contributors. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopaedia. Printed for 244 years, the ''Britannica'' was the longest running in-print encyclopaedia in the English language. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in the Scottish capital of Edinburgh, as three volumes. The encyclopaedia grew in size: the second edition was 10 volumes, and by its fourth edition (1801–1810) it had expanded to 20 volumes. Its rising stature as a scholarly work helped recruit eminent con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |