|
Narkinae
Members of the family Narkidae are commonly known as sleeper rays. They are restricted to the temperate and tropical Indo-West Pacific from South Africa to Japan to Indonesia, and are exclusively marine and are absent from freshwater habitats. They occur from the intertidal zone to the continental shelf and the upper continental slope to a depth of 350 meters, favoring soft-bottomed habitats. Description Adult sleeper rays range in size from 8 to 46 cm in length and have flattened oval, circular, or pear-shaped pectoral fin discs. They have naked skin, without dermal denticles or thorns. The snout is moderately elongate and broadly rounded, with the rostral cartilage reduced to a slender medial rod. This distinguishes the narkids from the family Narcinidae, which have somewhat longer snouts supported by broad rostral cartilages. The mouth is straight, very narrow, and not highly protrusible, with strong labial folds and a weak groove around the periphery. The nostrils are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onefin Electric Ray
The onefin electric ray or Cape numbfish (''Narke capensis'') is a common but little-known species of electric ray in the family Narkidae, native to South Africa and Namibia. It is a benthic fish found in shallow coastal bays over sandy or muddy bottoms. This small species reaches in length, and has a nearly circular pectoral fin disc and a short, muscular tail that supports a large caudal fin. It can be identified by its single dorsal fin, which is located over the large pelvic fins. Its dorsal coloration is yellowish to dusky brown. Like other members of its family, the onefin electric ray can defend itself with a strong electric shock produced from a pair of kidney-shaped electric organs beside its head. It feeds mainly on polychaete worms, and likely gives birth to live young. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) presently lacks enough information to assess the conservation status of this species. It is often caught incidentally by bottom trawl fisheri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocelli
A simple eye (sometimes called a pigment pit) refers to a form of eye or an optical arrangement composed of a single lens and without an elaborate retina such as occurs in most vertebrates. In this sense "simple eye" is distinct from a multi-lensed "compound eye", and is not necessarily at all simple in the usual sense of the word. The structure of an animal's eye is determined by the environment in which it lives, and the behavioural tasks it must fulfill to survive. Arthropods differ widely in the habitats in which they live, as well as their visual requirements for finding food or conspecifics, and avoiding predators. Consequently, an enormous variety of eye types are found in arthropods. They possess a wide variety of novel solutions to overcome visual problems or limitations. Use of the term ''simple eye'' is flexible, and must be interpreted in proper context; for example, the eyes of humans and of other large animals such as most cephalopods, are ''camera eyes'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phillip C
Philip, also Phillip, is a male given name, derived from the Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominent Philips who popularized the name include kings of Macedonia and one of the apostles of early Christianity. ''Philip'' has many alternative spellings. One derivation often used as a surname is Phillips. It was also found during ancient Greek times with two Ps as Philippides and Philippos. It has many diminutive (or even hypocoristic) forms including Phil, Philly, Lip, Pip, Pep or Peps. There are also feminine forms such as Philippine and Philippa. Antiquity Kings of Macedon * Philip I of Macedon * Philip II of Macedon, father of Alexander the Great * Philip III of Macedon, half-brother of Alexander the Great * Philip IV of Macedon * Philip V of Macedon New Testament * Philip the Apostle * Philip the Evangelist Others * Philippus of Croton (c. 6th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonard Compagno
Leonard Joseph Victor Compagno is an international authority on shark taxonomy and the author of many scientific papers and books on the subject, best known of which is his 1984 catalogue of shark species produced for the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations. Compagno was mentioned in the credits of the 1975 film ''Jaws'' along with the National Geographic Society. Career *Ph.D, Stanford University, 1979 *Adjunct professor, San Francisco State University, 1979 to 1985 *Curator of Fishes in the Division of Life Sciences and Head of the Shark Research Centre (SRC), Iziko Museums, Cape Town *Director, Shark Research Institute(SRI) Selected bibliography *Compagno, L.J.V., 1979. ''Carcharhinoid sharks: morphology, systematics and phylogeny''. Unpublished Ph. D. Thesis, Stanford University, 932 p. Available from University Microfilms International, Ann Arbor, Michigan. *Leonard Compagno, 1984a. FAO The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrolux (fish)
The ornate sleeper-ray (''Electrolux addisoni'') is a species of electric ray in the family Narkidae, and the only member of the genus ''Electrolux''. It lives on reefs feeding on polychaete worms and small crustaceans, it has only been seen by divers to feed during the daytime. It is endemic to the coast of South Africa. It was first recorded in 1984 but was not described until 2007. It was ranked as the number one newly described species of 2007 by the International Institute for Species Exploration. In an episode of ''Extinct or Alive'', an ornate-sleeper ray is caught on footage feeding. Description ''Electrolux addisoni'' is easily distinguished from other narkids by its striking colour pattern consisting of a dark brown dorsal surface of the disc with numerous small pale yellow spots and a series of concentric stripes. It can also be distinguished by its large spiracular papillae. It and '' Heteronarce'' are the only genera in the family Narkidae that have two dorsal fins. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crassinarke Dormitor
The sleeper torpedo (''Crassinarke dormitor'') is a species of electric ray in the family Narkidae. It is the only species in its genus. It occurs in relatively shallow water off the coasts of southern Japan, China and Taiwan Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort .... It may be the same species as the Japanese sleeper ray (''Narke japonica'') References * sleeper torpedo Fish of Japan Marine fauna of East Asia sleeper torpedo Strongly electric fish {{Chondrichthyes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazunori Takagi
Kazunori (written: 一慶, 一典, 一則, 一謙, 一徳, 一矩, 一紀, 和典, 和則, 和徳, 和行, 和範 or 和憲) is a masculine Japanese given name. Notable people with the name include: *, Japanese samurai *, Japanese footballer *, Japanese anime screenwriter and artist *, Japanese footballer *, Japanese sumo wrestler *, Japanese high jumper *, Japanese judoka *, Japanese politician *, Japanese actor *, Japanese baseball player *, Japanese politician *, Japanese video game designer *, Japanese actor *, Japanese mixed martial artist and judoka *, Japanese footballer {{given name Japanese masculine given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crassinarke
The sleeper torpedo (''Crassinarke dormitor'') is a species of electric ray in the family Narkidae. It is the only species in its genus. It occurs in relatively shallow water off the coasts of southern Japan, China and Taiwan Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort .... It may be the same species as the Japanese sleeper ray (''Narke japonica'') References * sleeper torpedo Fish of Japan Marine fauna of East Asia sleeper torpedo Strongly electric fish {{Chondrichthyes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)french: link=no, Organisation des Nations unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture; it, Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per l'Alimentazione e l'Agricoltura is an international organization that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, ', translates to "let there be bread". It was founded on 16 October 1945. The FAO is composed of 195 members (including 194 countries and the European Union). Their headquarters is in Rome, Italy, and the FAO maintains regional and field offices around the world, operating in over 130 countries. It helps governments and development agencies coordinate their activities to improve and develop agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and land and water resources. It also conducts research, provides technical assistance to projects, operates educational and training programs, and collects data on agricultural output, produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egg (biology)
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the animal hatches. Most arthropods such as insects, vertebrates (excluding live-bearing mammals), and mollusks lay eggs, although some, such as scorpions, do not. Reptile eggs, bird eggs, and monotreme eggs are laid out of water and are surrounded by a protective shell, either flexible or inflexible. Eggs laid on land or in nests are usually kept within a warm and favorable temperature range while the embryo grows. When the embryo is adequately developed it hatches, i.e., breaks out of the egg's shell. Some embryos have a temporary egg tooth they use to crack, pip, or break the eggshell or covering. The largest recorded egg is from a whale shark and was in size. Whale shark eggs typically hatch within the mother. At and up to , the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovoviviparous
Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a term used as a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-laying oviparous and live-bearing viviparous reproduction. Ovoviviparous animals possess embryos that develop inside eggs that remain in the mother's body until they are ready to hatch. The young of some ovoviviparous amphibians, such as ''Limnonectes larvaepartus'', are born as larvae, and undergo further metamorphosis outside the body of the mother. Members of genera ''Nectophrynoides'' and ''Eleutherodactylus'' bear froglets, not only the hatching, but all the most conspicuous metamorphosis, being completed inside the body of the mother before birth. Among insects that depend on opportunistic exploitation of transient food sources, such as many Sarcophagidae and other carrion flies, and species such as many Calliphoridae, that rely on fresh dung, and parasitoids such as tachinid flies that depend on entering the host as soon as possible, the emb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
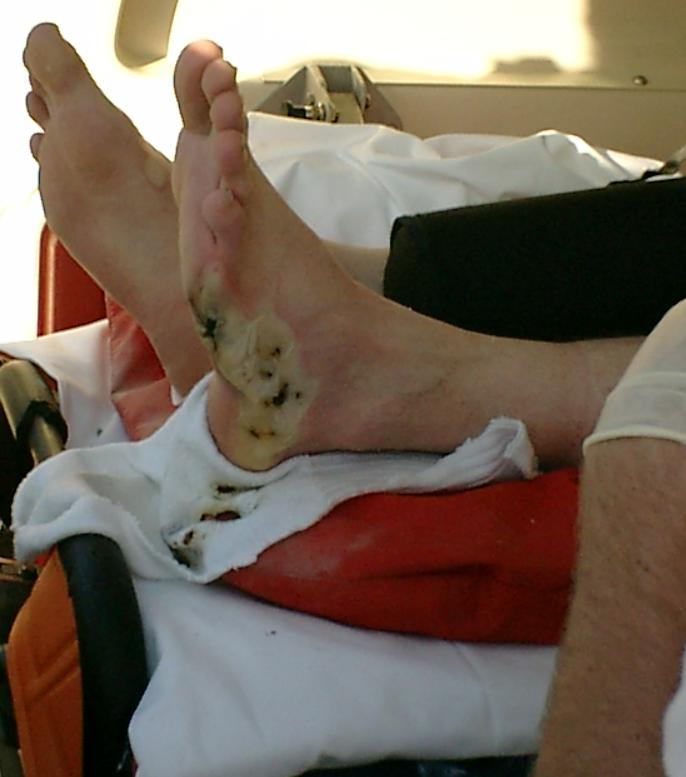
Electric Shock
Electrical injury is a physiological reaction caused by electric current passing through the body. The injury depends on the density of the current, tissue resistance and duration of contact. Very small currents may be imperceptible or produce a light tingling sensation. A shock caused by low and otherwise harmless current could startle an individual and cause injury due to jerking away or falling. Stronger currents may cause some degree of discomfort or pain, while more intense currents may induce involuntary muscle contractions, preventing the person from breaking free of the source of electricity. Still larger currents result in tissue damage and may trigger ventricular fibrillation or cardiac arrest. Consequences of injury from electricity may include amputations, bone fractures and orthopedic and musculoskeletal injuries. If death results from an electric shock the cause of death is generally referred to as electrocution. Electric injury occurs upon contact of a body part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |