|
Naming Conventions For Destroyers Of The Royal Navy
In the Royal Navy there have been a variety of naming conventions for destroyers. Origins Destroyers were originally developed as a defence against torpedo boats, and the first torpedo boat destroyer (TBD) in the Royal Navy was of 1893. From 1906, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" began to appear in the shortened form "destroyer" when referring to destroyer flotillas. There is no official British Admiralty, Admiralty order pertaining to the change and the abbreviated term "TBD" is present in the Navy List up to 1919, even though destroyer was the term used in most official orders from 1917. Up to 1913, names were allocated under no fixed system, leading to a heterogeneous array, although two groups were named systematically; after rivers and tribes (later the River-class destroyer, E and Tribal-class destroyer (1905), F classes, respectively). In 1913, with burgeoning numbers of TBDs, the Admiralty took the confusing situation in hand; ''Havock'' and her similar "27 Knot (unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Destroyer Classes Of The Royal Navy
{{Royal Navy ship types This is a list of destroyer classes of the Royal Navy of the United Kingdom, organised chronologically by entry into service. Torpedo boat destroyers In 1913, the surviving members of the large heterogeneous array of older 27-knot and 30-knot torpedo boat destroyer types (all six of the original 26-knot ships had been disposed of by the end of 1912) were organised into the A, B, C and D classes according to their design speed and the number of funnels they possessed. All were of a "turtle-back" design and, excepting a few "builder's specials", powered by steam engine, reciprocating engines. It should be stressed that these A to D class designations did not exist before 1913, and only applied to those "turtle-backed" destroyers surviving to that time. * "26-knotter" types ** Daring-class destroyer (1893), ''Daring'' class: 2 ships, 1893–1894 ** Havock-class destroyer, ''Havock'' class: 2 ships, 1893 ** Ferret-class destroyer, ''Ferret'' class: 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Emergency Programme Destroyers
The War Emergency Programme destroyers were destroyers built for the British Royal Navy during World War I and World War II. World War I emergency programmes The 323 destroyers ordered during the First World War belonged to several different classes and were the subject of 14 separate War Programmes between 1914 and 1918. 40 of these were cancelled at the end of the war. The total excludes destroyers building in UK for other navies which were purchased for the Royal Navy following the outbreak of war. World War II emergency programme The 112 destroyers built during the Second World War were based on the hull and machinery of the earlier J-, K- and N-class destroyers of the 1930s. Each of the fourteen flotillas produced consisted of eight destroyers. Due to supply problems and the persistent failure by the Royal Navy to develop a suitable dual-purpose weapon for destroyers, they were fitted with whatever armament was available. Advances in radar and weaponry were incorporated a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
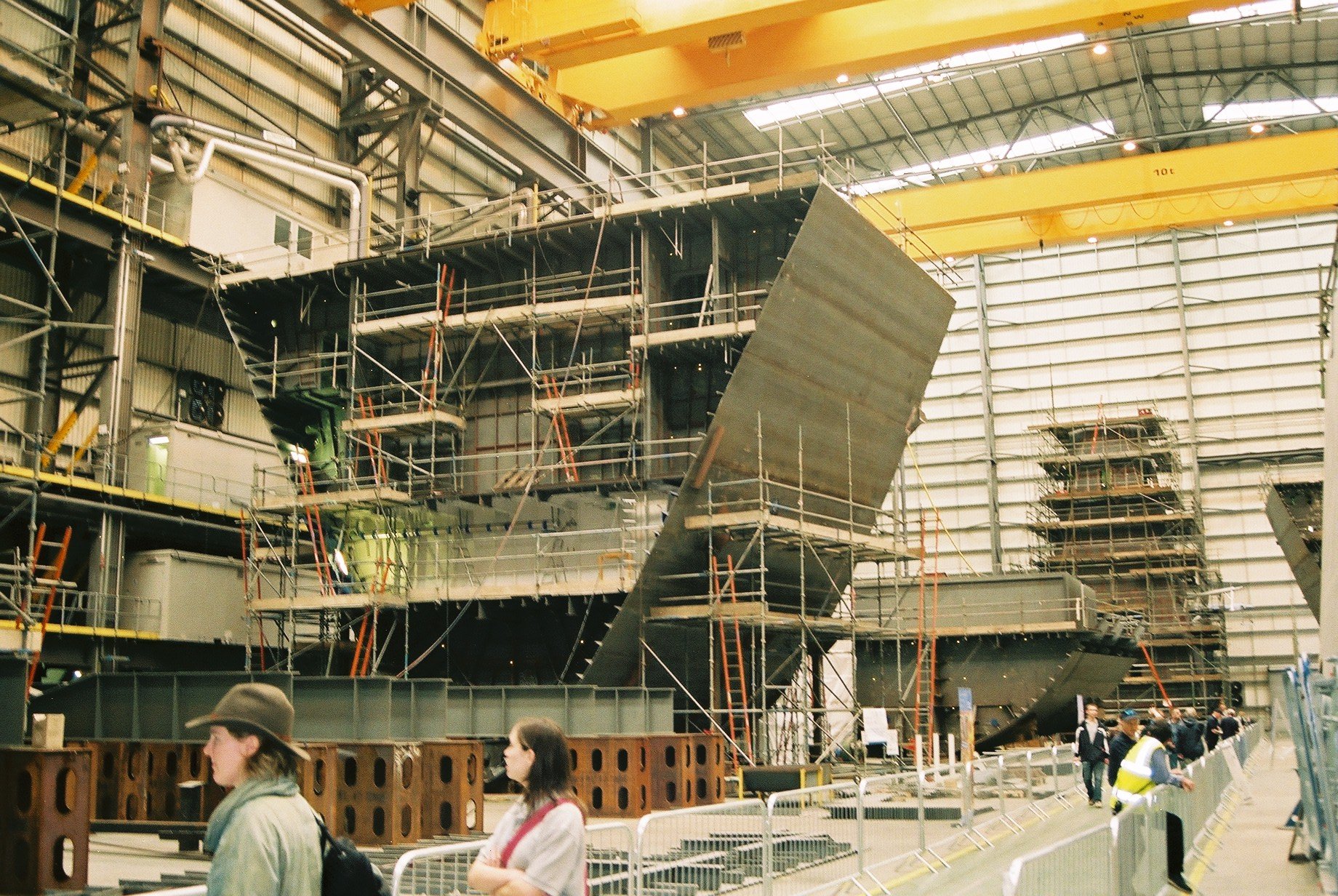
Type 45 Destroyer
The Type 45 destroyer, also known as the D or ''Daring'' class, is a class of six guided-missile destroyers built for the United Kingdom's Royal Navy in the early 21st century. The class is primarily designed for anti-aircraft and anti-missile warfare and is built around the PAAMS (Sea Viper) air-defence system using the SAMPSON Active electronically scanned array (AESA) and the S1850M long-range radars. The first three destroyers were assembled by BAE Systems Surface Fleet Solutions from partially prefabricated "blocks" built at different shipyards; the remaining three were built by BAE Systems Maritime – Naval Ships. The first ship in the ''Daring'' class, HMS ''Daring'', was launched on 1 February 2006 and commissioned on 23 July 2009. The Type 45 destroyers were built to replace the Type 42 (''Sheffield''-class) destroyers that had served during the Falklands War, with the last Type 42 being decommissioned in 2013. The National Audit Office reported that, during an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type System Of The Royal Navy
The Type system is a classification system used by the British Royal Navy to classify surface escorts by function. The system evolved in the early 1950s, when the Royal Navy was experimenting with building single-purpose escort vessels with specific roles in light of experience gained in World War II. The original (July 1950) numbering scheme was: Type 1X were Anti-Submarine (ASW) frigates (when the numbers ran out in the 1960s, ASW frigates continued as the Type 2X series). Type 3X were General-Purpose (GP) frigates (Chosen 2015) Type 4X were Anti-Aircraft (AAW) frigates (this later evolved into the "Destroyer" Type series). Type 6X were Aircraft-Direction (ADW) frigates. Type 8X were multi-role ships. An Admiralty Fleet Order defined these ships as "destroyers" if they could achieve "fleet speed" or as "sloops" if they could not. Types 11-30, anti-submarine frigates * Type 11 : Diesel powered anti-submarine frigate based on hull of Type 41 / 61. Not built. * Type 12 ''Whitby'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daring-class Destroyer (1949)
The ''Daring'' class was a class of eleven destroyers built for the Royal Navy (RN) and Royal Australian Navy (RAN). Constructed after World War II, and entering service during the 1950s, eight ships were constructed for the RN, and three ships for the RAN. Two of the RN destroyers were subsequently sold to and served in the Peruvian Navy (MGP). A further eight ships were planned for the RN but were cancelled before construction commenced, while a fourth RAN vessel was begun but was cancelled before launch and broken up on the slipway. The ''Daring''-class ships were both the largest and most heavily armed ships serving in Commonwealth navies to be classified as destroyers. They were intended to fill some of the duties of cruisers, which post WW2 were considered both expensive and obsolete by naval planners, and were briefly officially considered a hybrid type (Darings) before being rated as destroyers. They were also the last destroyers of the RN and RAN to possess guns as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ch-class Destroyer
The C class was a class of 32 destroyers of the Royal Navy that were launched from 1943 to 1945. The class was built in four flotillas of 8 vessels, the "Ca", "Ch", "Co" and "Cr" groups or sub-classes, ordered as the 11th, 12th, 13th and 14th Emergency Flotillas respectively. The sub-class names are derived from the initial 2 letters of the member ships' names, although the "Ca" class were originally ordered with a heterogeneous mix of traditional destroyer names. A fifth flotilla, the "Ce" or 15th Emergency Flotilla, was planned but were cancelled in favour of the s after only the first two ships had been ordered. The pennant numbers were all altered from "R" superior to "D" superior at the close of World War II; this involved some renumbering to avoid duplications. Design They were built as part of the War Emergency Programme, based on the hull and machinery of the pre-war J class, incorporating whatever advances in armament and naval radar were available at the time. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Canadian Navy
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN; french: Marine royale canadienne, ''MRC'') is the naval force of Canada. The RCN is one of three environmental commands within the Canadian Armed Forces. As of 2021, the RCN operates 12 frigates, four attack submarines, 12 coastal defence vessels, eight patrol class training vessels, two offshore patrol vessels, and several auxiliary vessels. The RCN consists of 8,570 Regular Force and 4,111 Primary Reserve sailors, supported by 3,800 civilians. Vice-Admiral Angus Topshee is the current commander of the Royal Canadian Navy and chief of the Naval Staff. Founded in 1910 as the Naval Service of Canada (French: ''Service naval du Canada'') and given royal sanction on 29 August 1911, the RCN was amalgamated with the Royal Canadian Air Force and the Canadian Army to form the unified Canadian Armed Forces in 1968, after which it was known as Maritime Command (French: ''Commandement maritime'') until 2011. In 2011, its historical title of "Royal Cana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C And D-class Destroyer
The C and D class was a group of 14 destroyers built for the Royal Navy in the early 1930s. As in previous years, it was originally intended to order a complete flotilla comprising eight destroyers—plus a flotilla leader as the ninth unit—in each year. However, only four ships—plus a leader—were ordered under the 1929–1930 Programme as the C class. The other four ships planned for the C class were never ordered as an economy measure and disarmament gesture by the Labour government of Ramsay MacDonald. A complete flotilla—the 'D' class—was ordered under the 1930–1931 Programme. The five ships of the C class were assigned to Home Fleet upon their completion, although they reinforced the Mediterranean Fleet during the Italian invasion of Abyssinia of 1935–1936 and enforced the Non-Intervention Agreement during the Spanish Civil War of 1936–1939. They were transferred to the Royal Canadian Navy (RCN) in 1937–1939 and spent most of their time during World Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities of deities, heroes, and mythological creatures, and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' own cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of myth-making itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan and Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century BC; eventually the myths of the heroes of the Trojan War and its aftermath became part of the oral tradition of Homer's epic poems, the '' Iliad'' and the '' Odyssey''. Two poems by Homer's near contemporary Hesiod, the ''Theogony'' and the '' Works and Days'', contain accounts of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_CT-284.jpg)
