|
NQuery Sample Size Software
nQuery is a clinical trial design platform used for the design and monitoring of adaptive, group sequential, and fixed sample size trials. It is most commonly used by biostatisticians to calculate sample size and statistical power for adaptive clinical trial design. nQuery is proprietary software developed and distributed by Statsols. The software includes calculations for over 1,000 sample sizes and power scenarios. History Janet Dixon Elashoff, creator of nQuery, is a retired American statistician and daughter of the mathematician and statistician Wilfrid Joseph Dixon, creator of BMDP. Elashoff is also the retired Director of the Division of Biostatistics, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center. While at UCLA and Cedars-Sinai during the 1990s, she wrote the program nQuery Sample Size Software (then named nQuery Advisor). This software quickly became widely used to estimate the sample size requirements for pharmaceutical trials. She joined the company Statistical Solutions LLC in order t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sample Size Determination
Sample size determination is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences about a population from a sample. In practice, the sample size used in a study is usually determined based on the cost, time, or convenience of collecting the data, and the need for it to offer sufficient statistical power. In complicated studies there may be several different sample sizes: for example, in a stratified survey there would be different sizes for each stratum. In a census, data is sought for an entire population, hence the intended sample size is equal to the population. In experimental design, where a study may be divided into different treatment groups, there may be different sample sizes for each group. Sample sizes may be chosen in several ways: *using experience – small samples, though sometimes unavoidable, can result in wide confiden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
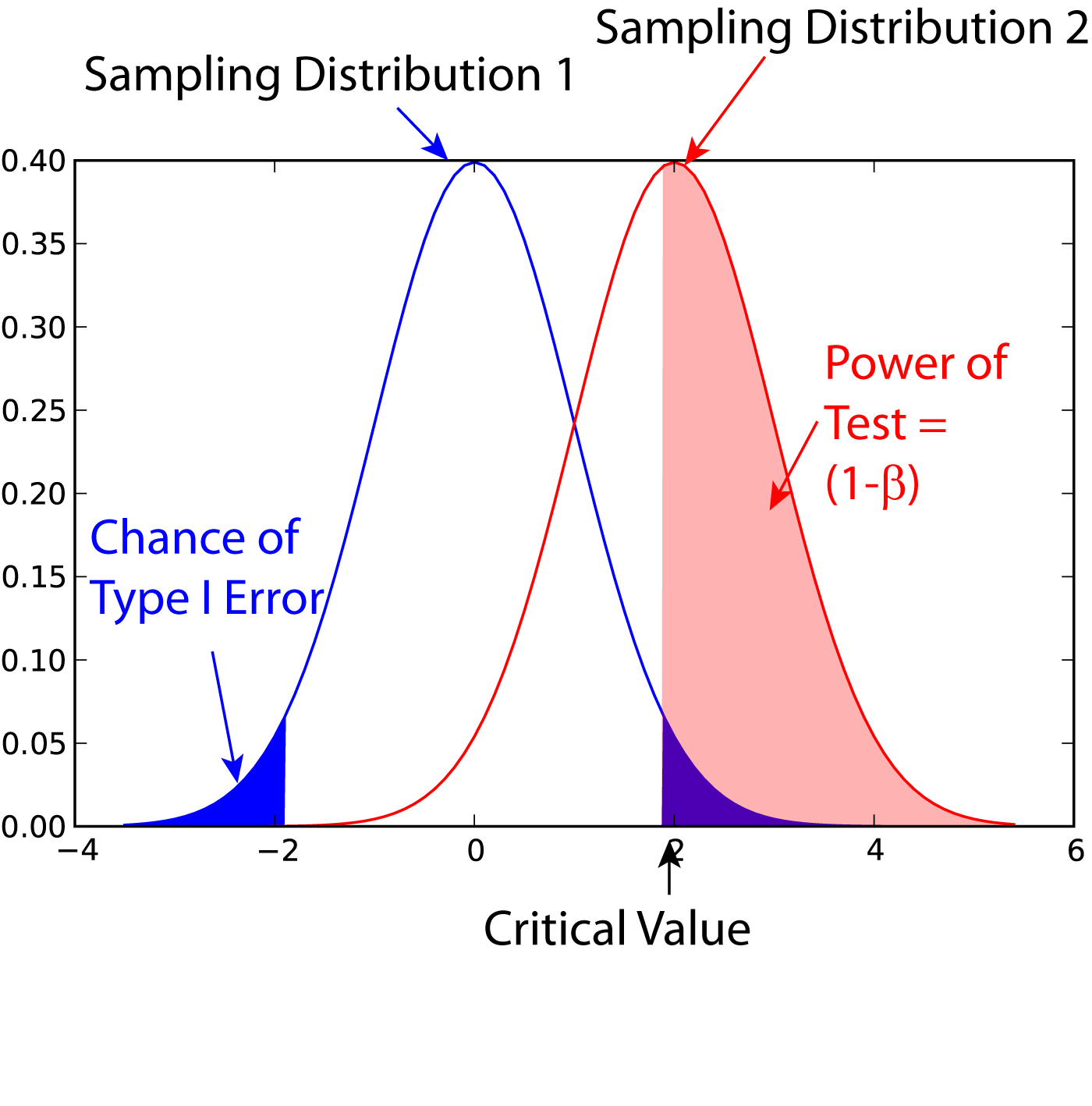
Statistical Power
In statistics, the power of a binary hypothesis test is the probability that the test correctly rejects the null hypothesis (H_0) when a specific alternative hypothesis (H_1) is true. It is commonly denoted by 1-\beta, and represents the chances of a true positive detection conditional on the actual existence of an effect to detect. Statistical power ranges from 0 to 1, and as the power of a test increases, the probability \beta of making a type II error by wrongly failing to reject the null hypothesis decreases. Notation This article uses the following notation: * ''β'' = probability of a Type II error, known as a "false negative" * 1 − ''β'' = probability of a "true positive", i.e., correctly rejecting the null hypothesis. "1 − ''β''" is also known as the power of the test. * ''α'' = probability of a Type I error, known as a "false positive" * 1 − ''α'' = probability of a "true negative", i.e., correctly not rejecting the null hypothesis Description For a ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Hypothesis Testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data at hand sufficiently support a particular hypothesis. Hypothesis testing allows us to make probabilistic statements about population parameters. History Early use While hypothesis testing was popularized early in the 20th century, early forms were used in the 1700s. The first use is credited to John Arbuthnot (1710), followed by Pierre-Simon Laplace (1770s), in analyzing the human sex ratio at birth; see . Modern origins and early controversy Modern significance testing is largely the product of Karl Pearson ( ''p''-value, Pearson's chi-squared test), William Sealy Gosset ( Student's t-distribution), and Ronald Fisher ("null hypothesis", analysis of variance, "significance test"), while hypothesis testing was developed by Jerzy Neyman and Egon Pearson (son of Karl). Ronald Fisher began his life in statistics as a Bayesian (Zabell 1992), but Fisher soon grew disenchanted with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Clinical Trial
In an adaptive design of a clinical trial, the parameters and conduct of the trial for a candidate approved drug, drug or vaccine may be changed based on an interim analysis. Adaptive design typically involves advanced statistics to interpret a clinical trial clinical endpoint, endpoint. This is in contrast to traditional single-arm (i.e. non-randomized) clinical trials or randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that are static in their protocol and do not modify any parameters until the trial is completed. The adaptation process takes place at certain points in the trial, prescribed in the trial protocol. Importantly, this trial protocol is set before the trial begins with the adaptation schedule and processes specified. Adaptions may include modifications to: dosage, sample size, drug undergoing trial, patient selection criteria and/or "cocktail" mix. The PANDA (A Practical Adaptive & Novel Designs and Analysis toolkit) provides not only a summary of different adaptive designs, but also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statsols
Statsols (formerly known as Statistical Solutions) is the producer and distributor of the proprietary nQuery sample size software. History In 1984, Statsols (Originally known as Statistical Solutions) was a distributor for the statistical software BMDP. This was statistical package developed in 1965 by Wilfrid Joseph Dixon at the University of California, Los Angeles, which performed different parametric and nonparametric statistical analyses. Through a management buy-out in 1995, President & CEO Mary Byrne who led the all-female buy-out, which was not common at the time, to form the independent company Statistical Solutions Ltd, now known as Statsols. The company now only offers its most successful statistical product, nQuery Sample Size Software. nQuery Sample Size Software Janet Dixon Elashoff is a now-retired American statistician and daughter of the mathematician and statistician Wilfrid Joseph Dixon, creator of BMDP. Janet is the retired Director of the Division of Bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proprietary Software
Proprietary software is software that is deemed within the free and open-source software to be non-free because its creator, publisher, or other rightsholder or rightsholder partner exercises a legal monopoly afforded by modern copyright and intellectual property law to exclude the recipient from freely sharing the software or modifying it, and—in some cases, as is the case with some patent-encumbered and EULA-bound software—from making use of the software on their own, thereby restricting his or her freedoms. It is often contrasted with open-source or free software. For this reason, it is also known as non-free software or closed-source software. Types Origin Until the late 1960s computers—large and expensive mainframe computers, machines in specially air-conditioned computer rooms—were usually leased to customers rather than sold. Service and all software available were usually supplied by manufacturers without separate charge until 1969. Computer vendors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Power
In statistics, the power of a binary hypothesis test is the probability that the test correctly rejects the null hypothesis (H_0) when a specific alternative hypothesis (H_1) is true. It is commonly denoted by 1-\beta, and represents the chances of a true positive detection conditional on the actual existence of an effect to detect. Statistical power ranges from 0 to 1, and as the power of a test increases, the probability \beta of making a type II error by wrongly failing to reject the null hypothesis decreases. Notation This article uses the following notation: * ''β'' = probability of a Type II error, known as a "false negative" * 1 − ''β'' = probability of a "true positive", i.e., correctly rejecting the null hypothesis. "1 − ''β''" is also known as the power of the test. * ''α'' = probability of a Type I error, known as a "false positive" * 1 − ''α'' = probability of a "true negative", i.e., correctly not rejecting the null hypothesis Description For a ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janet D
Janet may refer to: Names * Janet (given name) * Janet (French singer) (1939–2011) Surname * Charles Janet (1849–1932), French engineer, inventor and biologist, known for the Left Step periodic table * Jules Janet (1861–1945), French psychologist and psychotherapist * Maurice Janet (1888–1983), French mathematician * Paul Janet (1823–1899), French philosopher and writer * Pierre Janet (1859–1947), French psychologist, philosopher and psychotherapist * Roberto Janet (born 1986), Cuban hammer thrower Other uses * Janet, Alberta, a Canadian hamlet * Janet (airline), a military transport fleet known for servicing the US Air Force "Area 51" facility * JANET, a high-speed network for the UK research and education community * ''Janet'' (album), by Janet Jackson * ''Janet'' (video), a video compilation by Janet Jackson * Janet, a character in the TV series ''The Good Place'' * Hurricane Janet, 1955 * Janet, a character in the video game ''Brawl Stars ''Brawl Stars'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilfrid Dixon
Wilfrid Joseph Dixon (December 13, 1915 – September 20, 2008) was an American mathematician and statistician. He made notable contributions to nonparametric statistics, statistical education and experimental design. A native of Portland, Oregon, Dixon received a bachelor's degree in mathematics from Oregon State College in 1938. He continued his graduate studies at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, where he earned a master's degree in 1939. Under supervision of Samuel S. Wilks, he then earned a Ph.D. in mathematical statistics from Princeton in 1944. During World War II, he was an operations analyst on Guam. Dixon was on the faculties at Oklahoma (1942–1943), Oregon (1946–1955), and UCLA (1955–1986, then emeritus). While at Oregon, Dixon (together with A.M. Mood) described and provided theory and estimation methods for the adaptive Up-and-Down experimental design, which was new and poorly documented at the time. This article became the cornerstone publication f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center is a nonprofit, tertiary, 886-bed teaching hospital and multi-specialty academic health science center located in Los Angeles, California. Part of the Cedars-Sinai Health System, the hospital employs a staff of over 2,000 physicians and 10,000 employees, supported by a team of 2,000 volunteers and more than 40 community groups. As of 2022-23, '' U.S. News & World Report'' ranked Cedars-Sinai the best hospital in the western United States. It ranked as the best hospital in California and 2nd best hospital in the entire United States; and was placed nationally in 11 adult medical specialties and rated high performing in 21 adult specialties, procedures and conditions. Cedars-Sinai is a teaching hospital affiliate of David Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), which was ranked # 19 on the U.S. News 2023 Best Medical Schools: Research. Cedars-Sinai focuses on biomedical research and technologically advanced medical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, Los Angeles
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the southern branch of the California State Normal School (now San José State University). This school was absorbed with the official founding of UCLA as the Southern Branch of the University of California in 1919, making it the second-oldest of the 10-campus University of California system (after UC Berkeley). UCLA offers 337 undergraduate and graduate degree programs in a wide range of disciplines, enrolling about 31,600 undergraduate and 14,300 graduate and professional students. UCLA received 174,914 undergraduate applications for Fall 2022, including transfers, making the school the most applied-to university in the United States. The university is organized into the College of Letters and Science and 12 professional schools. Six of the schools offer undergraduate degre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequentist Inference
Frequentist inference is a type of statistical inference based in frequentist probability, which treats “probability” in equivalent terms to “frequency” and draws conclusions from sample-data by means of emphasizing the frequency or proportion of findings in the data. Frequentist-inference underlies frequentist statistics, in which the well-established methodologies of statistical hypothesis testing and confidence intervals are founded. History of frequentist statistics The history of frequentist statistics is more recent than its prevailing philosophical rival, Bayesian statistics. Frequentist statistics were largely developed in the early 20th century and have recently developed to become the dominant paradigm in inferential statistics, while Bayesian statistics were invented in the 19th century. Despite this dominance, there is no agreement as to whether frequentism is better than Bayesian statistics, with a vocal minority of professionals studying statistical infer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Clinical_Trial_Design_after_PMID_29490655.png)


