|
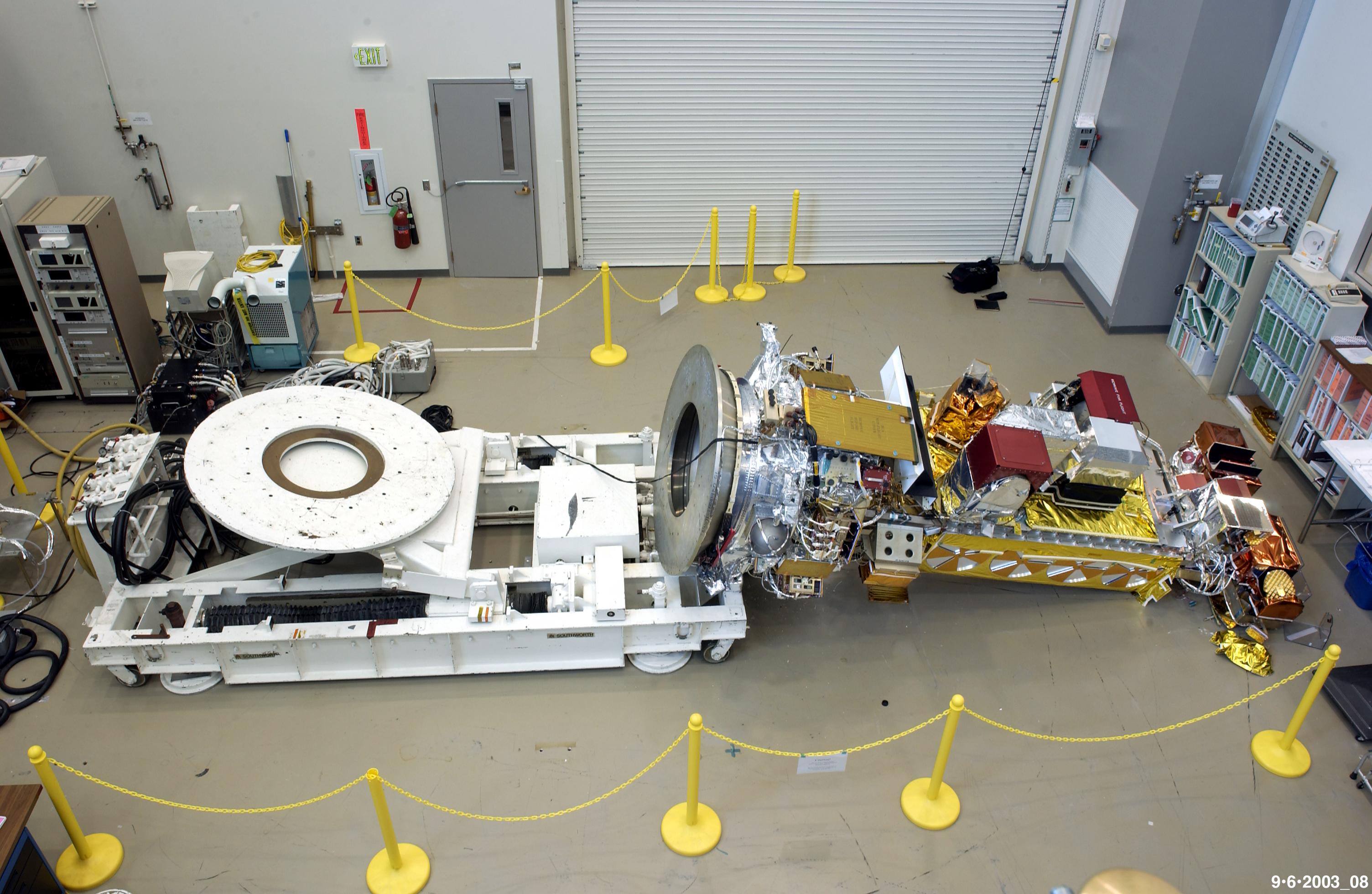
NOAA-18
NOAA-18, also known as NOAA-N before launch, is an operational, polar orbiting, weather satellite series (NOAA K-N) operated by the National Environmental Satellite Service (NESS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-18 also continued the series of Advanced TIROS-N (ATN) spacecraft begun with the launch of NOAA-8 (NOAA-E) in 1983 but with additional new and improved instrumentation over the NOAA A-M series and a new launch vehicle (Titan 23G). NOAA-18 is in an afternoon equator-crossing orbit and replaced NOAA-17 as the prime afternoon spacecraft. Launch NOAA-18 was launched by the Delta II launch vehicle on 20 May 2005 at 10:22:01 UTC from Vandenberg Air Force Base, at Vandenberg Space Launch Complex 4 (SLW-4W), in a Sun-synchronous orbit, at 854 km above the Earth, orbiting every 102.12 minutes. NOAA-18 is in an afternoon equator-crossing orbit and has replaced the NOAA-17 as the prime afternoon spacecraft. Spacecraft The goal of the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Infrared Observation Satellite
TIROS, or Television InfraRed Observation Satellite, is a series of early weather satellites launched by the United States, beginning with TIROS-1 in 1960. TIROS was the first satellite that was capable of remote sensing of the Earth, enabling scientists to view the Earth from a new perspective: space. The program, promoted by Harry Wexler, proved the usefulness of satellite weather observation, at a time when military reconnaissance satellites were secretly in development or use. TIROS demonstrated at that time that "the key to genius is often simplicity". TIROS is an acronym of "Television InfraRed Observation Satellite" and is also the plural of "tiro" which means "a young soldier, a beginner". Participants in the TIROS project included the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), United States Army Signal Research and Development Laboratory, Radio Corporation of America (RCA), the United States Weather Bureau Service, the United States Naval Photographic In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOAA-19
NOAA-19, known as NOAA-N' (NOAA-N Prime) before launch, is the last of the American National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) series of weather satellites. NOAA-19 was launched on 6 February 2009. NOAA-19 is in an afternoon Sun-synchronous orbit and is intended to replace NOAA-18 as the prime afternoon spacecraft. Launch On 4 November 2008, NASA announced that the satellite had arrived at Vandenberg aboard a Lockheed C-5 Galaxy military transport aircraft. Installation of the payload fairing took place 27 January 2009; second stage propellant was loaded on 31 January 2009. Several attempts were made to conduct the launch. The first attempt, 4 February 2009, was scrubbed after a failure was detected in a launch pad gaseous nitrogen pressurization system. The second attempt, 5 February 2009, was scrubbed after the failure of a payload fairing air conditioning compressor, which is also part of the ground support equipment at the launch pad. The satellite was suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Satellite
A weather satellite or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites can be polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asynchronously), or geostationary (hovering over the same spot on the equator). While primarily used to detect the development and movement of storm systems and other cloud patterns, meteorological satellites can also detect other phenomena such as city lights, fires, effects of pollution, auroras, sand and dust storms, snow cover, ice mapping, boundaries of ocean currents, and energy flows. Other types of environmental information are collected using weather satellites. Weather satellite images helped in monitoring the volcanic ash cloud from Mount St. Helens and activity from other volcanoes such as Mount Etna. Smoke from fires in the western United States such as Colorado and Utah have also been monitored. El Niño and its effects on weather are monitored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argos (satellite System)
Argos is a global satellite-based system that collects, processes, and disseminates environmental data from fixed and mobile platforms around the world. The worldwide tracking and environmental monitoring system results from Franco-American cooperation. Besides satellite data collection, the Argos system's main feature is the ability to geographically locate the data source from any location on Earth using the Doppler effect. History and utilization Argos was established in 1978 and has provided data to environmental research and protection groups that was previously unobtainable. Many remote automatic weather stations report via Argos. Argos is a component of many global research programs including: Tropical Ocean-Global Atmosphere program (TOGA), Tagging of Pacific Pelagics (TOPP), World Ocean Circulation Experiment (WOCE), Argo. There are 22,000 active transmitters (8,000 of which are used in animal tracking) in over 100 countries. Since the late 1980s, Argos transmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Very-high-resolution Radiometer
The Advanced Very-High-Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) instrument is a space-borne sensor that measures the reflectance of the Earth in five spectral bands that are relatively wide by today's standards. AVHRR instruments are or have been carried by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) family of polar orbiting platforms ( POES) and European MetOp satellites. The instrument scans several channels; two are centered on the red (0.6 micrometres) and near-infrared (0.9 micrometres) regions, a third one is located around 3.5 micrometres, and another two the thermal radiation emitted by the planet, around 11 and 12 micrometres. The first AVHRR instrument was a four-channel radiometer. The last version, AVHRR/3, first carried on NOAA-15 launched in May 1998, acquires data in six channels. The AVHRR has been succeeded by the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite, carried on the Joint Polar Satellite System spacecraft. Operation NOAA has at leas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOAA-17
NOAA-17, also known as NOAA-M before launch, was an operational, polar orbiting, weather satellite series (NOAA K-N) operated by the National Environmental Satellite Service (NESS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-17 also continued the series of Advanced TIROS-N (ATN) spacecraft begun with the launch of NOAA-8 (NOAA-E) in 1983 but with additional new and improved instrumentation over the NOAA A-L series and a new launch vehicle (Titan 23G). Launch NOAA-17 was launched by the Titan 23G launch vehicle on 24 June 2002 at 18:23:04 UTC from Vandenberg Air Force Base, at Vandenberg Space Launch Complex 4 (SLW-4W), in a Sun-synchronous orbit, at 823 km above the Earth, orbiting every 101.20 minutes. NOAA-17 was in an afternoon equator-crossing orbit and has replaced the NOAA-15 as the prime afternoon spacecraft. Spacecraft The goal of the NOAA/NESS polar orbiting program is to provide output products used in meteorological prediction and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charts the seas, conducts deep sea exploration, and manages fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the U.S. exclusive economic zone. Purpose and function NOAA's specific roles include: * ''Supplying Environmental Information Products''. NOAA supplies to its customers and partners information pertaining to the state of the oceans and the atmosphere, such as weather warnings and forecasts via the National Weather Service. NOAA's information services extend as well to climate, ecosystems, and commerce. * ''Providing Environmental Stewardship Services''. NOAA is a steward of U.S. coastal and marine environments. In coordination with federal, state, local, tribal and international authorities, NOAA manages the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Operational Environmental Satellites
The Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite (POES) was a constellation of polar orbiting weather satellites funded by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) with the intent of improving the accuracy and detail of weather analysis and forecasting. The spacecraft were provided by NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA), and NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center oversaw the manufacture, integration and test of the NASA-provided TIROS satellites. The first polar-orbiting weather satellite launched as part of the POES constellation was the Television Infrared Observation Satellite-N (TIROS-N), which was launched on 13 October 1978. The final spacecraft, NOAA-19 (NOAA-N Prime), was launched on 6 February 2009. The ESA-provided MetOp satellite operated by EUMETSAT utilize POES-heritage instruments for the purpose of data continuity. The Joint Polar Satellite System (JP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBUV/2
The Solar Backscatter Ultraviolet Radiometer, or SBUV/2, is a series of operational remote sensors on NOAA weather satellites in Sun-synchronous orbits which have been providing global measurements of stratospheric total ozone, as well as ozone profiles, since March 1985. The SBUV/2 instruments were developed from the SBUV experiment flown on the Nimbus-7 spacecraft which improved on the design of the original BUV instrument on Nimbus-4. These are nadir viewing radiometric instruments operating at mid to near UV wavelengths. SBUV/2 data sets overlap with data from SBUV and TOMS instruments on the Nimbus-7 spacecraft. These extensive data sets (January 1979 to the present) measure the density and vertical distribution of ozone in the Earth's atmosphere from six to 30 miles. SBUV/2 looks down at the Earth's atmosphere and the reflected sunlight at wavelengths characteristic of ozone. The SBUV/2 wavelength "channels" range from 252 nanometer (nm) to 340 nm. Ozone is measured a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defense Meteorological Satellite Program
The Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) monitors meteorological, oceanographic, and solar-terrestrial physics for the United States Department of Defense. The program is managed by the United States Space Force with on-orbit operations provided by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The (originally classified) mission of the satellites was revealed in March 1973. They provide cloud cover imagery from polar orbits that are Sun-synchronous at nominal altitude of . History During the 1960s, one of the most important projects that the United States civil space program was involved in dealt with meteorology and weather forecasting. Unbeknownst to many, the U.S. military services were also starting up a weather satellite program. This program, the DMSP, would relay important weather and climate data to the military for more effective operations. From the onset of the DMSP program, knowledge of its existence was limited to "need-to-know" person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)